divergence des vecteurs, evolution de

DIVERGENCE DES VECTEURS, EVOLUTION DE MICROPATHOGENES ET
CONSEQUENCES EPIDEMIOLOGIQUES: LE CAS DE LA BACTERIE BORRELIA
BURGDORFERI S.L. CHEZ LES TIQUES D’OISEAUX MARINS
Déposé le : 23 fevrier 2007
Date de début : 1 octobre 2007
Sujet susceptible d'obtenir une : Allocation Recherche
Le financement des travaux de terrain en zone arctique est assuré par le programme n°333 de
l’Institut Polaire Français (IPEV) conduit en collaboration avec Thierry BOULINIER (CEFE,
CNRS UMR 5175, Montpellier). Des financements du Bureau des Ressources Génétiques et
de l’Agence Nationale de Recherche (projet jeunes chercheurses/jeunes chercheurs) ont été
obtenus pour les travaux de biologie moléculaire (Responsable: K. McCOY).
Directeur : Karen MCCOY
04 67 41 62 07 - 04 67 41 62 99 - [email protected]
Si vous êtes intéressé(e), merci de faire parvenir un CV et une lettre de
motivation à Karen McCoy ([email protected]) avant le 29 mai 2007.
CoDirecteur : Francois Renaud
04 67 41 6253 - 04 67 41 62 99 - [email protected]
Encadrement : Le thésard sera basé au sein du laboratoire GEMI, IRD-CNRS UMR 2724 à
Montpellier où les analyses génétiques pourront être réalisés. Comme ces travaux seront faits
en collaboration partielle avec une équipe de l’Institut Pasteur de Paris, des séjours à Paris
pourraient être impliqués.
Thématique : Une approche génétique est essentielle pour la compréhension de la
structuration spatiale, l’adaptation et l’histoire évolutive des micropathogènes,
particulièrement dans des systèmes à vecteur où la spécialisation d’hôte peut jouer un rôle
important. Ce projet portera sur la diversification des borrélies circulant entre les oiseaux
marins et leur tique Ixodes uriae. Plus spécifiquement, il vise à caractériser le rôle de la
spécialisation du vecteur sur l’évolution de cette bactérie et d’évaluer l’importance relative du
vecteur et de l’hôte vertébré dans la différenciation et l’épidemiologie de ce microorganisme
au travers la comparaison de la variabilité de différents gènes (neutres et fonctionels).
Profil recherché: Cette thèse impliquera à la fois une bonne compréhension de la biologie
moléculaire (théorie et pratique), mais aussi du terrain en zone arctique. Le candidat doit donc
être prêt de faire des missions d'un mois ou deux en zone arctique (non-francophone) chaque
été pour la récolte des parasites sur les oiseaux marins. Expérience en biologie moléculaire,
ainsi que avec l'analyse des séquences est désirable.
Domaine : Ecologie évolutive, Interactions hôte-parasite
Objectif : Pour caractériser le rôle de la spécialisation du vecteur sur l’évolution du
micropathogène et d’évaluer l’importance relative du vecteur et de l’hôte vertébré dans la
différenciation et l’épidemiologie de la borrélie, deux axes de recherches complémentaires

seront abordés: (i) la différenciation génétique de B. burgdorferi s.l. entre races d’hôtes du
vecteur (Multi-locus Sequence Analysis) et (ii) les sélections spécifiques du vecteur ou de
l’hôte vertébré sur la bactérie au travers de la diversité des gènes connus pour intervenir
directement dans l’interaction avec les deux types d’hôtes (gènes Osp).
Mots clés : épidémiologie, Ixodes uriae, coévolution, sélection hôte-vecteur, génétique,
maladie à vecteur, spécialisation
Contexte : Il est parfois avancé que seule l’interaction du microparasite avec son hôte
vertébré détermine l’évolution du microparasite (e.g., Ricklefs & Fallon 2001). Néanmoins,
une telle supposition n’est jamais vérifiée et s’avère même particulièrement inadéquate dans
les cas où le vecteur impose des contraintes importantes sur la dynamique du micropathogène
(e.g., Azad & Beard 1998). Le cas des races d’hôte de la tique d’oiseaux marins Ixodes uriae,
du fait de sa bonne caractérisation, offre aujourd’hui la possibilité de démêler les actions
directes et indirectes des différences génétiques des hôtes vertébrés et du vecteur dans
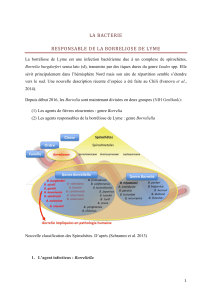
l’évolution d’un microparasite: la bactérie Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. Les différentes
génoespèces de cette bactérie sont responsables de la maladie de Lyme (Baranton et al. 2001,
Rosa et al. 2005). A ce jour, l’épidémiologie de cet agent est principalement étudiée dans des
écosystèmes continentaux impliquant des tiques du complexe Ixodes ricinus (Kurtenbach et
al. 2006) et l’interaction du cycle marin avec le cycle terrestre reste inconnue (Olsen et al.
1993). Cette thèse visera de caractériser le rôle de la spécialisation du vecteur sur l’évolution
du micropathogène et d’évaluer l’importance relative du vecteur et de l’hôte vertébré dans la
différenciation et l’épidémiologie de la borrélie.
Méthode : (1) Distribution de la variation génétique de Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. entre races
d’hôtes de vecteur
La spécificité des races d’I. uriae vis-à-vis d’espèces d’oiseaux marins a été démontré par des
études précédentes (McCoy et al. 2001, 2003, 2005) et pourraient être alors une contrainte
importante pour le patron de transmission du microparasite (McCoy 2003). Si tel est le cas, on
s’attend à une structuration de la variation génétique du microparasite entre espèces d’oiseaux
et entre races de vecteurs. On testera donc l’impact de la spécialisation d’I. uriae sur la
distribution de la diversité des borrélies dans et entre les colonies et les espèces d’oiseaux,
mais aussi d’un hémisphère à l’autre. La caractérisation de la variabilité génétique de la
borrélie portera sur différents gènes de ménage utiliser pour typer ces bactérie (Richter et al.
2006).
(2) Importance relative des vecteurs et des oiseaux dans la différenciation de Borrelia
burgdorferi s.l.: les protéines de surfaces osp:
Les gènes de Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. qui codent pour des protéines de surface sélectionnées
par l'hôte sont différents selon qu’il s’agit de l'hôte vertébré (gène ospC) ou du vecteur (gène
ospA) (Wang et al. 1999, Qiu et al. 2002). Ces deux gènes et leur polymorphisme s’avèrent
donc d’excellents candidats pour préciser les pressions de sélection subies par ce
micropathogène de la part de ses hôtes vertébrés et de ses vecteurs. Nous allons donc analyser
la diversité aux loci ospC et ospA et la mettre en relation avec les résultats concernant la
structuration génétique de tiques en races d’hôtes.
On dispose déjà d’un grand nombre d’échantillons de la tique de l’hémisphère Nord récoltés
ces dernières années, ainsi qu’un échantillonnage complet de colonies de manchot dans
l’hémisphère Sud (Terres Australes Antarctique Française) effectué en collaboration avec
Michel GAUTHIER-CLERC de la Tour-du-Valat et Yvon LEMAHO de l’UPR CNRS 9010 à

Strasbourg. L’étudiant aura la possibilité de compléter ces échantillons dans des colonies
d’oiseaux marins de l’Océan Pacifique, et de participer aux travaux effectués dans notre site
principal d’étude dans le nord de la Norvège. La mise en place des méthodes et des analyses
préliminaires de la première partie du projet a été faites dans le cadre d’un stage de Master II
en 2006.
Résultat attendu : Les résultats attendus permettront de mettre en évidence les conséquences
épidémiologiques des processus évolutifs étudiés et d’identifier les liens entre cycle terrestre
et cycle marin de la bactérie.
Référence biblio : Azad, A.F. & Beard, C.B. 1998 Rickettsial pathogens and their arthropod
vectors. Emerging Infectious Diseases 4, 179-186.
Baranton, G., Seinost, G. Theodore, G., Postic, D. & Dykhusizen, D. 2001 Distinct levels of
genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi are associated with different aspects of pathogenicity.
Research in Microbiology 152, 149-156.
Kurtenbach K, Hanincova K, Tsao JI, Margos G, Fish D, Ogden NH. 2006. Fundamental
processes in the evolutionary ecology of Lyme borreliosis. Nature Rev Microbiol. 4:660-9.
McCoy, K.D. 2003 Sympatric speciation in parasites: what is sympatry? Trends in
Parasitology 19: 400-404.
McCoy, K.D., T. Boulinier, C. Tirard & Y. Michalakis. 2001. Host specificity of a generalist
parasite: genetic evidence of sympatric host races in the seabird tick Ixodes uriae. Journal of
Evolutionary Biology 14: 395-405.
McCoy, K.D., T. Boulinier, C. Tirard & Y. Michalakis. 2003. Host-dependent genetic
structure of parasite populations: differential dispersal of seabird tick host races. Evolution 57:
288-296.
McCoy, K.D., E. Chapuis, C. Tirard, T. Boulinier, Y. Michalakis, C. LeBohec, Y. LeMaho &
M. Gauthier-Clerc. 2005. Recurrent evolution of host-specialized races in a globally-
distributed ectoparasite. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B. 272 (1579): 2389-
2395.
Olsen, B., Jaenson, T. G. T., Noppa, L., Bunikis, J. & Bergstrom, S. 1993 A Lyme borreliosis
cycle in seabirds and Ixodes uriae ticks. Nature 362, 340-342.
Qiu, W.G., Dykhuizen, D.E., Acosta, M.S. & Luft, B.J. 2002. Geographic uniformity of the
Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi) and its shared history with tick vector (Ixodes
scapularis) in the Northeastern United States. Genetics 160, 833-849.
Ricklefs, R. & Fallon, S. 2002 Diversification and host switching in avian malaria parasites.
Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 269, 885-892.
Richter D, Postic D, Sertour N, Livey I, Matuschka FR, Baranton G. 2006. Delineation of
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species by multilocus sequence analysis and confirmation of
the delineation of Borrelia spielmanii sp nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 56:873-81.
Rosa, P.A, Tilly, K. & Stewart, P.E. 2005 The burgeoning molecular genetics of the Lyme
disease spirochaete. Nature Reviews Microbiology 3, 129-143.
Wang, I., Dykhuizen, D.E., Qui, W., Dunn, J.J., Bosler, E.M. et Luft, B.J. 1999. Genetic
diversity of ospC in a local population of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto. Genetics 151, 15-
30.
1
/
3
100%