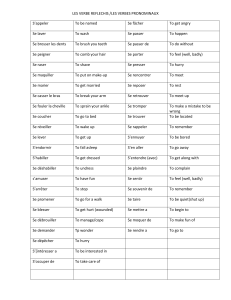
Table des matières - Bookery Education

iii
Remerciements vii
Pour les étudiant-e-s viii
Pour les enseignant-e-s x
Le présent
1 am/is/are (forme affi rmative et négative)
2 am/is/are (forme interrogative)
3 I’m hungry / It’s cold etc.
4 I am doing (present continuous)
5 are you doing? (present continuous, forme interrogative)
6 I do/work/like etc. (present simple, forme affi rmative)
7 I don’t … (present simple, forme négative)
8 Do you … ? (present simple, forme interrogative)
9 I am doing (present continuous) et I do (present simple)
10 I have … et I’ve got …
Le passé
11 was/were
12 worked/got/went etc. (past simple)
13 I didn’t … Did you … ? (past simple,
forme négative et interrogative)
14 I was doing (past continuous)
15 I was doing (past continuous)
et I did (past simple)
Present perfect
16 I have done (present perfect 1)
17 I’ve just … I’ve already … I haven’t … yet (present perfect 2)
18 Have you ever … ? (present perfect 3)
19 How long have you … ? (present perfect 4)
20 for since ago
21 I have done (present perfect)
et I did (past simple)
Le passif
22 is done was done (passif 1)
23 is being done has been done (passif 2)
Les formes du verbe
24 be/have/do (present et past)
25 Verbes réguliers et irréguliers
Le futur
26 What are you doing tomorrow? (présent à valeur future)
27 I’m going to …
28 will/shall 1
29 will/shall 2
Les auxiliaires de mode, l’impératif etc.
30 might
31 can et could
32 must mustn’t don’t need to
33 should
34 I have to …
35 Would you like … ? I’d like …
36 Do this! Don’t do that! Let’s do this!
37 I used to …
Table des matières
SI VOUS NE SAVEZ PAS QUELLES UNITÉS ÉTUDIER, UTILISEZ LE GUIDE D’ÉTUDE À LA PAGE 258
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-71411-2 - Essential Grammar in Use Edition Francaise, Deuxieme Edition
Raymond Murphy
Table of Contents
More information

iv
There
38 there is there are
39 there was/were there has/have been there will be
Les verbes auxiliaires
40 I am, I don’t etc.
41 Have you? Are you? Don’t you? etc.
42 too/either so am I / neither do I etc.
43 isn’t, haven’t, don’t etc. (formes négatives)
La forme interrogative
44 is it … ? have you … ? do they … ? etc. (forme interrogative 1)
45 Who saw you? Who did you see? (
forme interrogative 2)
46 Who is she talking to? What is it like? (
forme interrogative 3)
47 What … ? Which … ? How … ? (
forme interrogative 4)
48 How long does it take … ?
49 Do you know where … ? I don’t know what … etc.
Le discours indirect
50 She said that … He told me that …
-ing et to …
51 work/working go/going do/doing
52 to … (I want to do) et -ing (I enjoy doing)
53 I want you to … I told you to …
54 I went to the shop to …
Go, get, do, make et have
55 go to … go on … go for … go -ing
56 get
57 do et make
58 have
Les pronoms et les possessifs
59 I/me he/him they/them etc.
60 my/his/their etc.
61 Whose is this? It’s mine/yours/hers etc.
62 I/me/my/mine
63 myself/yourself/themselves etc. (pronoms réfl échis)
64 -’s (Kate’s camera / my brother’s car etc.)
A et the
65 a/an …
66 train(s) bus(es) (
singulier et pluriel)
67 a bottle / some water (
noms dénombrables/indénombrables 1)
68 a cake / some cake / some cakes (
noms dénombrables/indénombrables 2)
69 the …
70 go to work go home go to the cinema
71 I like music I hate exams
72 the … (avec les noms de lieu)
SI VOUS NE SAVEZ PAS QUELLES UNITÉS ÉTUDIER, UTILISEZ LE GUIDE D’ÉTUDE À LA PAGE 258
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-71411-2 - Essential Grammar in Use Edition Francaise, Deuxieme Edition
Raymond Murphy
Table of Contents
More information

v
Les déterminants et les pronoms
73 this/that/these/those
74 one/ones
75 some et any
76 not + any no none
77 not + anybody/anyone/anything nobody/no-one/nothing
78 somebody/anything/nowhere etc.
79 every et all
80 all most some any no/none
81 both either neither
82 a lot much many
83 (a) little (a) few
Les adjectifs et les adverbes
84 old/nice/interesting etc. (adjectifs)
85 quickly/badly/suddenly etc. (adverbes)
86 old/older expensive / more expensive
87 older than … more expensive than …
88 not as … as
89 the oldest the most expensive
90 enough
91 too
L’ordre des mots
92 He speaks English very well. (ordre des mots 1)
93 always/usually/often etc. (ordre des mots 2)
94 still yet already
95 Give me that book! Give it to me!
Les conjonctions et les relatives
96 and but or so because
97 When … If …
98 If I had … If we went … etc.
99 a person who … a thing that/which … (
propositions relatives 1)
100 the people we met the hotel you stayed at (
propositions relatives 2)
Les prépositions
101 at 8 o’clock on Monday in April
102 from … to until since for
103 before after during while
104 in at on (prépositions de lieu 1)
105 in at on (prépositions de lieu 2)
106 to in at (prépositions de lieu 3)
107 under, behind, opposite etc.
108 up, over, through etc. (prépositions de mouvement)
109 on at by with about
110 afraid of … , good at … etc. of/at/for etc. (prépositions) + -ing
111 listen to … , look at … etc. (verbe + préposition)
Phrasal verbs
112 go in, fall off, run away etc. (phrasal verbs 1)
113 put on your shoes put your shoes on (phrasal verbs 2)
SI VOUS NE SAVEZ PAS QUELLES UNITÉS ÉTUDIER, UTILISEZ LE GUIDE D’ÉTUDE À LA PAGE 258
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-71411-2 - Essential Grammar in Use Edition Francaise, Deuxieme Edition
Raymond Murphy
Table of Contents
More information

vi
Annexes
Annexe 1 L’actif et le passif 229
Annexe 2 Liste des verbes irréguliers 230
Annexe 3 Verbes irréguliers par groupes 231
Annexe 4 Formes contractées (he’s / I’d / don’t etc.) 232
Annexe 5 Spelling (Orthographe) 234
Annexe 6 Phrasal verbs (take off / give up etc.) 236
Annexe 7 Phrasal verbs + objet (put out a fi re / give up your job etc.) 237
Annexe 8 Quantifi cateurs (very/much/many etc.) 238
Exercices supplémentaires 239
Guide d’étude 258
Corrigés des exercices 269
Corrigés des exercices supplémentaires 290
Corrigés du guide d’étude 293
Index 295
SI VOUS NE SAVEZ PAS QUELLES UNITÉS ÉTUDIER, UTILISEZ LE GUIDE D’ÉTUDE À LA PAGE 258
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-71411-2 - Essential Grammar in Use Edition Francaise, Deuxieme Edition
Raymond Murphy
Table of Contents
More information

A
62
Unité
31 can et could
CAu passé (yesterday / last week etc.) on emploie could/couldn’t:
When I was young, I could run very fast. … je courais très vite.
Before Maria came to Britain, she couldn’t understand much English. Now she can
understand everything.
… elle ne comprenait pas … Maintenant elle comprend tout.
I was tired last night, but I couldn’t sleep. … mais je ne pouvais pas dormir.
I had a party last week, but Paul and Rachel couldn’t come. … n’ont pas pu venir.
BI can do something = ‘je sais faire … ’ ou ‘je peux faire … ’ ou ‘je suis capable de faire’ quelque chose.
I can play the piano. My brother can play the piano too.
Sarah can speak Italian, but she can’t speak Spanish.
‘Can you swim?’ ‘Yes, but I’m not a very good swimmer.’ ‘Sais-tu nager?’ …
A: Can you change twenty pounds? Pouvez-vous changer … ?
B: I’m sorry. I can’t. Désolé, je ne peux pas.
I’m having a party next week, but Paul and Rachel can’t come. … ne peuvent pas venir.
En anglais, on emploie can avec les verbes de perception ( I can see / we can hear etc.). En français, on dit
simplement ‘je vois’, ‘nous entendons’, etc.
Can you hear me? Vous m’entendez?
I can see a light. Je vois une lumière. (= je distingue une lumière)
He can play the piano. Il sait jouer du piano. Pouvez-vous ouvrir la porte, s’il vous plaıˆt?
I can play
the piano.
Could you open
the door, please?
Can est suivi de l’infi nitif (can do / can play / can come etc.):
do
I/we/you/they can play
he/she/it can’t (cannot) see
come etc.
do?
can I/we/you/they play?
he/she/it see?
come? etc.
Observez que la forme négative s’écrit en un seul mot: cannot (et non pas can not).
DCan you … ? Could you … ? Can I … ? Could I … ?
On emploie Can you … ? ou Could you … ? pour demander quelque chose à quelqu’un:
Can you open the door, please? ou Could you open the door, please?
Can you wait a moment, please? ou Could you wait … ?
On emploie Can I have … ? ou Could I have … ? pour demander quelque chose:
(dans un magasin) Can I have these postcards, please? ou Could I have … ?
Can I … ? ou Could I … ? = Puis-je … ?:
Tom, can I borrow your umbrella? ou Tom, could I borrow your umbrella?
(au téléphone) Hello, can I speak to Gary, please? ou … could I speak … ?
May I ... ? → Unité 30
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-71411-2 - Essential Grammar in Use Edition Francaise, Deuxieme Edition
Raymond Murphy
Excerpt
More information
 6
6
1
/
6
100%