Le carcinome à cellules claires du rein avant 40 ans

ARTICLE ORIGINAL Progrès en Urologie (2002), 12, 575-578
575
Le carcinome à cellules claires du rein avant 40 ans :
facteurs pronostiques
Saïd MOUDOUNI (1), Ilham EN-NIA (2), Nathalie RIOUX-LECLERQ (2), Karim BENSALAH (1),
François GUILLE (1), Bernard LOBEL (1), Jean-Jacques PATARD (1)
(1) Service d’Urologie, (2) Service d’Anatomie et de Cytologie Pathologique, CHU Pontchaillou, Rennes, France
Le carcinome à cellules rénales représente 90% des
tumeurs du rein de l’adulte. Il intéresse préférentielle-
ment l’homme de plus de 60 ans. La définition des fac-
teurs pronostiques reste un enjeu important pour éva-
luer les traitements de façon reproductible et pour
sélectionner les patients qui peuvent en bénéficier.
L’âge est considéré dans la littérature comme un des
éléments pronostiques du carcinome à cellule rénale
(RCC) avec des meilleurs résultats chez les patients de
moins de 60 ans.
L’adénocarcinome du rein est rare chez le sujet jeune.
Il représente 3,4% des tumeurs du rein chez l’homme
de moins de 40 ans.
L’objectif de cette étude a été d’identifier les facteurs
pronostiques influant sur la survie dans ce groupe par-
ticulier de tumeurs rénales. Nous avons étudié, la
valeur pronostique de la taille tumorale, du stade TNM,
du grade nucléaire de Fuhrman, de l’envahissement de
la veine rénale et de l’expression de la molécule d’ad-
hésion CD44 sur une série rétrospective de 19 patients
de moins de 40 ans.
Manuscrit reçu : mars 2002, accepté : juillet 2002.
Adresse pour correspondance : Dr.J . J . Patard, Service d’Urologie, CHU
Pontchaillou, rue Henri Le Guillou, 35033 Rennes.
e-mail : [email protected]
Ref : MOUDOUNI S., EN-NIA I., RIOUX-MECMERQ N., BENSALAH K.,
GUILLE F., LOBEL B., PATARD J.J., Prog. Urol., 2002, 12, 575-578.
RESUME
But : Etudier dans le carcinome à cellules claires du rein (RCC) survenant avant 40
ans, la valeur pronostique de la taille tumorale, du stade TNM, du grade nucléaire de
Führman et de l’expression de la molécule d’adhésion CD44.
Matériel et Méthodes : 19 patients âgés de moins de 40 ans et opérés d’une néphrec-
tomie totale d’un RCC ont été inclus dans cette étude. Il s’agissait de 12 hommes et
de 7 femmes d’âge moyen 30.8 ans. Pour chaque tumeur ont été définis la taille tumo-
rale, le stade TNM 1997, le grade nucléaire de Führman. L’expression de la molécu-
le CD44 dans sa forme standard (CD44H) a été évaluée semi-quantitativement par
immunohistochimie sur chaque tumeur. La valeur pronostique des différentes
variables a été déterminée par les tests de Mann-Whitney et du chi2. L’étude de la
survie a été réalisée par la méthode de Kaplan-Meier.
Résultats : 6 patients (31,5%) sont décédés de leur cancer au cours d’un suivi moyen
de 81,4 mois. La taille tumorale était de 9 ± 4.5 cm. Les tumeurs étaient Führman I/II
dans 4 cas, Führman III / IV dans 15 cas, T1 /T2 dans 14 cas et T3 / T4 dans 5 cas.
L’expression de CD44H était forte (>= 20%) dans 9 cas (47,3%). Les facteurs pro-
nostiques identifiés dans cette étude étaient : la stade (p =0,01), le grade (p =0,04),
l’extension veineuse (p=0,001) et la surexpression de la molécule CD44H (p =0,003).
Conclusion : Les facteurs pronostiques des cancers du rein de moins de 40 ans ne sem-
blent pas différents de la forme du sujet plus âgé. Les facteurs pronostiques identifiés
dans cette étude doivent être validés par des travaux multicentriques permettant
d’analyser des effectifs de plus grande taille.
Mots clés : Carcinome, cellules rénales, prognostic, survie, âge.

576
MATERIELS ET METHODES
Sélection des patients et analyse des tumeurs
Nous avons revu 506 dossiers de patients opérés d’un
cancer du rein dans le service de 1988 à 1999. Pour
chaque observation était noté : l’âge, le sexe, les cir-
constances de découverte de la tumeur, le stade TNM,
le grade tumoral, l’extension veineuse, lymphatique ou
métastatique. Parmi ces patients, ont été sélectionnés
ceux de moins de 40 ans au moment du diagnostic.
Pour le groupe étudié, une relecture des lames a été
pratiquée et un marquage immuno histochimique par
un anticorps anti CD44 réalisé. La définition du stade
anatomique post-opératoire a utilisé les critères de la
6ème édition 1997 de la classification TNM. Pour
chaque tumeur, le grade nucléaire de Fuhrman [7] a été
défini comme étant le grade tumorale le plus élevé au
sein de la lésion.
Etude immunohistochimique
Pour chaque cas, un bloc tumoral correspondant au
grade nucléaire de Fuhrman le plus élevé a été sélec-
tionné et des coupes de 5µm ont été réalisées.
L’anticorps anti CD44 de type monoclonal (CD44,
RSD systems, Abingdon, Oxon, Grande-Bretagne) a
été utilisé à une dilution au 1/1200e.
L’immunodétection a été réalisée à l’aide d’un kit utili-
sant la technique streptavidine-biotine-peroxydase.
(Dako LSAB, K680, Dakopatts, Dak, Danemark), le
pourcentage de cellules marquées par le CD44 sur
1000 cellules comptées a permis de définir les tumeurs
exprimant fortement le CD44 (positivité) et les tumeurs
exprimant faiblement le CD44 (<20%).
Analyse statistique
L’étude comparative entre les différents paramètres ana-
lysés a été réalisée à l’aide du test non paramétrique de
Mann-Whitney et à l’aide du test chi 2 pour les variables
qualitatives. Les médianes de survie on été comparées par
la méthode de Kaplan-Meier. Les valeurs de p<0.05 ont
été considérées comme significatives.
RESULTATS
Caractéristiques des tumeurs
19 patients étaient âgés de 40 ans ou moins au moment
du diagnostic de la maladie (3,7%). Cette population
comportait 12 hommes et 7 femmes d’âge moyen 30,8
± 10,6 ans. La tumeur avait été révélée par des symp-
tômes dans 9 cas (47%), et était de découverte fortuite
dans 10 cas (53%). La majorité des tumeurs opérées
étaient intra capsulaires (pT1 et pT2) : 14 cas soit
73,6%. Une majorité de tumeurs étaient de grade élevé
(79%). En effet l’évaluation du grade nucléaire retrou-
vait dans 4 cas un Fuhrman I-II, dans 8 cas un Fuhrman
III et dans 7 cas un Fuhrman IV. La taille tumorale
moyenne était de 9 ± 4.5 cm (2 à 20.5). Un thrombus
veineux (VR+) était noté chez 6 patients (31,5%). Un
envahissement ganglionnaire (N+) était noté chez 4
patients (21%). Deux patients étaient d’emblée méta-
statiques sous forme de métastases osseuses et pulmo-
naires (10,5%). Neuf patients (47,3%) exprimaient for-
tement le CD44H (>=20%) avec un marquage à la fois
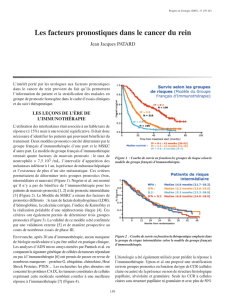
cytoplasmique et membranaire (Figure 1).
Survie
Quatre patients ont eu une progression tumorale métasta-
tique dans le suivi soit 21%. Avec un recul moyen de 81,4
mois, 9 patients sont décédés durant le suivi (47%). Six
patients sont décédés de leur cancer (31,5%) et 3 sont
décédés d’une autre cause. Le diamètre moyen de la
tumeur rénale des patients décédés était de 13 cm alors
qu’il était de 6.8 cm chez les patients vivants (p=0,04). Le
stade pathologique local est apparu comme un facteur
pronostique discriminant puisque 4 des 5 patients avec un
stade local avancé sont décédés de leur cancer ( p=0,01).
Le grade élévé, III-IV vs I-II était également lié à la sur-
vie dans notre étude (p=0,04). Chez les 6 patients ayant un
thrombus veineux, 4 ont développé des métastases et 5
sont décédés de leur cancer. La comparaison des courbes
de survie des patients VR+ et VR- a montré une diff é r e n-
ce significative en faveur des patients VR- (p<0,001)
(Figure 2). Ainsi la médiane de survie était de 117 ± 20
mois en l’absence d’embol et de 19 ± 12 mois en cas
d’embol néoplasique dans la VR.
Parmi les 9 tumeurs exprimant fortement le CD44H, 6
patients sont décédés de leur cancer (p=0,003).
L’extension ganglionnaire et métastatique dans cette
étude n’atteignaient pas la significativité statistique,
probablement en raison de la taille de l’eff e c t i f .
L‘ensemble de ces résultats est résumé par le
Tableau I.
S. Moudouni et coll;., Progrès en Urologie (2002), 12, 575-578
Figure 1. Carcinome à cellules rénales avec une forte expres -
sion du CD44.

DISCUSSION
Le carcinome à cellules rénales (RCC) représente 3% de
l’ensemble des tumeurs malignes de l’adulte et se trou-
ve au 3éme rang des cancers urologiques. Il intéresse
préférentiellement l’homme de plus de 55 ans avec une
augmentation régulière de l’incidence avec l’âge [13].
Cependant le RCC est rare avant l’âge de 40 ans avec
une incidence de 3,4 % [2]. Ceci correspond à l’inci-
dence (3,7%) retrouvée dans notre étude. Par ailleurs
R
ICHES
EW [16] rapporte une incidence de 0,3% dans
une étude rétrospective de 1735 dossiers de patients
porteurs de tumeur rénale, âgés de moins de 30 ans.
La survie globale de 53% observée dans notre étude est
comparable à celle de la série de BOYKIN [2] qui rap-
porte des survies à 5 et 10 ans, de 70% et 50% respec-
tivement. Les facteurs pronostiques qui peuvent
influencer cette survie ont été largement discutés chez
le sujet de plus de 40 ans [7, 11, 16] et comprennent
essentiellement le stade, le grade nucléaire, l’envahis-
sement métastatique et l’envahissement ganglionnaire.
L’intérêt pronostique du stade tumoral local a été décrit
par de nombreux auteurs [1, 12, 15]. Notre étude
confirme ces constatations pour les sujets de moins de
40 ans. En effet à la fois la taille tumorale et le stade T
sont liés dans notre étude à la mortalité par cancer. Il
est en effet bien établi que, plus les tumeurs sont volu-
mineuses, plus le risque d’envahissement veineux est
important et plus le risque de métastases asynchrones
est élevé [9]. Le mode de révélation a été aussi souli-
gné par certain auteurs comme facteur pronostique [3,
20]. Notre étude soutient indirectement cette hypothè-
se en montrant que les tumeurs de plus petite taille ont
un pronostic plus favorable.
Notre série confirme les données de la littérature sur la
valeur pronostique du grade de Führman [4, 7]. En sub-
divisant les malades en groupes de grades I-II, III et IV
il a été possible de confirmer que les patients jeunes
avec des tumeurs de haut grade décédaient d’avantage
de leur tumeur (p=0,04). Un tel clivage pronostique a
été retrouvé pour LIEBER [12] sur une série de 89
patients âgés de 20 à 40 ans.
La fréquence de l’atteinte ganglionnaire a été appréciée
de manière variable dans la littérature (8,5% à 17,5%)
[10, 11]. Dans notre étude l’atteinte ganglionnaire et
métastatique ne ressortent pas comme des facteurs pro-
nostiques probablement en raison de la faiblesse de
l’effectif.
A côté de ces facteurs classiques, il ressort de notre
étude qu’un facteur pronostique important est la pré-
sence ou l’absence d’un thrombus de la veine rénale au
moment du diagnostic. La médiane de survie est de 117
± 20 mois en l’absence de thrombus veineux contre
19±12 en présence de thrombus.
Les tumeurs rénales épithéliales possèdent une biologie
particulière et plusieurs études ont tenté d’évaluer la
valeur pronostique de nouveaux marqueurs dans le car-
cinome à cellules rénales, comme les marqueurs de
prolifération cellulaire, les mutations de la protéine p
53, l’expression des facteurs de croissance et la densi-
té vasculaire intra tumorale [8]. Mais les résultats de
ces différentes études apparaissent discordants et à ce
jour, aucun de ces paramètres n’a fait la preuve de son
intérêt pronostique.
Le groupe CD44 est représenté par plusieurs isoformes
de glycoprotéines transmembranaires exprimés dans
divers tissus [6]. Elles dérivent toutes d’un même gène,
situé sur le chromosome 11. L’une de leurs principales
fonctions est de permettre l’interaction entre la cellule et
la matrice extracellulaire. Plusieurs études ont montré que
l’expression du CD44H était liée, dans de nombreuses
577
Tableau I. Caractéristiques des tumeurs rénales de moins de
40 ans et impact pronostique des différentes variables.
Caractéristiques Fréquence Valeur pronostique
de la tumeur pour la survie
T1-T2/T3-T4 14 (73,6% contre p : 0,01
5 (16,3%)
G1-II/GIII/GIV 15 (79%) contre p : 0,04
4 (21%)
Taille tumorale 9p : 0,04
moyenne
Envahissement de la 6 (31,5%) p : 0,001
veine rénale
Envahissement 4 (21%) NS
lymphonodal
Métastases à distance 2 (10,5%) NS
Surexpression de CD44 9 (47,3%) p : 0,003
Figure 2. Cancer du rein patients ayant moins de 40 ans.
Survie en fonction de l’atteinte de la veine rénale.
VR (-)
VR (+)
S. Moudouni et coll;., Progrès en Urologie (2002), 12, 575-578

tumeurs, dont le carcinome à cellule rénales, à la progres-
sion tumorale et l’apparition de métastases [19].
Dans notre étude l’expression de la molécule d’adhésion
CD44 est plus forte chez les patients ayant un mauvais
pronostique et sa sur expression est associée à une mor-
talité accrue. Cependant l’effectif est trop faible pour étu-
dier la valeur pronostique indépendante de ce marqueur
comme cela a été montré par P
A R A D I S
[14] et par notre
groupe dans la population générale des RCC [18].
CONCLUSION
Cette étude a permis de mettre en évidence certains fac-
teurs pronostiques péjoratifs du cancer du rein des sujets
de moins de 40 ans. Ceux ci ne semblent pas fonda-
mentalement différents des critères connus chez le sujet
plus âgé. Ce sont : le stade et le grade tumoral, l’enva-
hissement veineux et la surexpression de la molécule
CD44. Néanmoins l’effectif faible en raison de la rareté
de ces tumeurs rend nécessaire la réalisation d’études
multicentriques qui permettront de tester le caractère
indépendant de ces variables pour prédire la survie.
REFERENCES
1. ARONSON DC., MEDARY I., FINALAY J.L., HERR H.W.: Renal
cell carcinoma in childhood and Adolescence: A retrospective sur-
vey for prognostic factors in 22 cases. J. Ped. Sur., 1996,31,183-186.
2. BOYKIN W.H., BRIGHT K.E., ZEIDMAN E.J., THOMPSON
I.M..: Renal tumors in young adults. Urology, 1992, 40, 503 -505
.
3. BRETHEAU D., LECHEVALIER E., EGHAZARIAN C., GRISO-
NI V., COULANGE C.: Prognostic significance of incidental renal
cell carcinoma. Eur Urol., 1995, 43, 17-26.
4. BRETHEAU D., LECHEVALIER E., DE FROMONT M., SAULT
M.C., RAMPAL M., COULANGE C.: Prognostic value of nuclear
grade of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer, 1995, 76, 2543-2549.
5. COULANGE C., RAMBEAUD J.J. Cancer du rein de l’adulte.Prog.
Urol., 1997, 7, 723-909.
6. FLANAGAN B.F., DALCHAU R., ALLEN A.K., DAR A.S.,
FABRE J.W.: Chemical composition and tissue distribution of the
human CDw44 glycoprotein. Immunology, 1989, 67, 167-175.
7. FURHMAN S.A., LASKY L.C., LIMA C.: Prognostic significance of
morphologic parametrs in renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol.,
1982, 6, 655-663.
8. GELB A.B., SUDILOVSKY D., WU C.D., WEISS L.M., MEDEI-
ROS L.J.: Appraisal of intratumoral microvessel density, MIB-1
score, DNA content, and p53 protein expression as prognostic indi-
cators in patients with locally confined renal cell carcinoma. Cancer,
1997, 80, 1768-1775.
9. GIULIANI L., GIBERTI C., MARTORANA G., RODIVA S.:
Radical extensive surgery for renal cell carcinoma: Long term results
and prognostic factors. J. Urol., 1990,143, 468-474.
1
0. HERLLINGER A., SCHROTT K.M., SCHOT G., SIGEL A.: What are
the benefits of extended dissection of the regionalrenal lymph nodes in
the therapy of renal cell carcinoma?. J. Urol., 1991, 146, 1224-1227.
11. JACQMIN D., BLOUM J.H., VAN POPPEL H. : Valeur de la lymphadé-
nectomie dans le cancer du rein non metastatique. Résultats préliminaires
d'une étude phase III de l'EORTC. Prog. Urol. 1992, 2 (Supp.), A3.
12. LIEBER M.M., TOMERA F.M., WILLIAM F.T., FARROW G.:
Renal adenocarcinoma in young adults: Survival and variables
affecting prognosis. J. Urol., 1981, 125,164-168.
13. NOBLES J.G., PARIKH A.M., CHAPPLE C.R., WORT H
P.H.L.: Renal adeno-carcinoma in young adults. Urol. Int.,
1994,53, 40-43.
14. PARADIS V., FERLICOT S., GHANNAM E., ZEIMOURA L.,
BLANCHET P., ESCHWEGE P., JARDIN A., BENOIT G.: CD44
is independent prognostic factor in conventional renal cell carcino-
ma. J.Urol., 1999, 161, 1984-1987.
15. RAINWATER L.M., FARROW G.M., ZINCKE H., GONCHO-
ROFF N.J.: Renal cell carcinoma in young and old patients.
Urology, 1991, 38, 1-5.
15. RICHARD F., SCHAETZ A., CHATELAIN C.: Facteurs pronos-
tiques du cancer du rein. Séminaires d'Uro-néphrologie. Pitié-
Salpétrière, 1988, 14: 157-175.
17. RICHES E.W., GRIFFITHS I.H., THACKRAY AC.: New growth of
the kidney and ureters. B.J.U., 1951, 23, 297-356.
18. RIOUX-LECLERCQ N., PATARD J.J., EPSTEIN J.I., ALVA A.,
BENSALAH K., BANSARD J.Y., LOBEL B.: Impact of CD44H
expression of the prognosis of locally confined renal cell carcinoma.
J. Urol. Pathol., 2001, 13, 85-93.
19. THOMAS L., ETOH T., STAMENKOVIC I., MIHM M.,
BYERS H.R.: Migration of human melanoma cells on hyaluro-
nate is related to CD44 expression. J. Invest. Dermatol., 1993,
100, 11 5 - 1 2 0 .
20. VALLANCIEN G., TORRES L.O., GURFINKEL E., VEILLON B.,
BRISSET J.M.: Incidental detection of renal tumor by abdominal
ultrasonography. Eur. Urol., 1990, 18, 94-96.
____________________
SUMMARY
Prognostic factors of renal cell carcinoma before the age of 40.
O b j e c t i v e: To study the prognostic value of tumour diameter, TNM
stage, Führman’s nuclear grade and CD44 adhesion molecule
e x p r ession in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) before the age of 40 years.
Material and Methods: Nineteen patients under the age of 40
(12 males and 7 females; mean age 30.8 years), undergoing
total nephrectomy for RCC were included in this study. Tumour
diameter, TNM 1997 stage, and Führman’s nuclear grade were
defined for each tumour. Standard CD44 adhesion molecule
(CD44H) expression was evaluated semiquantitatively by immu -
nohistochemistry on each tumour. The prognostic value of the
various variables was determined by Mann-Whitney and Chi-
square tests and survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-
Meier method.
Results: Six patients (31.5%) died from their cancer with a
mean follow-up of 81.4 months. Mean tumour diameter was 9 ±
4.5 cm. Tumours were Führman I/II in 4 cases, Führman III/IV
in 15 cases, T1/T2 in 14 cases and T3/T4 in 5 cases. CD44H
expression was high (≥ 20%) in 9 cases (47.3%). The prognos -
tic factors identified in this study were: tumour stage (p=0.01),
grade (p=0.04), venous extension (p=0.001) and CD44H ove -
rexpression (p=0.003).
Conclusion: Prognostic factors of renal cancer in patients under
the age of 40 years do not appear to be different from those of
older patients. The prognostic factors identified in this study must
be validated by multicentre studies based on larger populations.
Key-words: carcinoma, renal cell; prognosis; survival, age.
578
____________________
S. Moudouni et coll;., Progrès en Urologie (2002), 12, 575-578
1
/
4
100%