Correction C#3

Lycée Alexandre Dumas – 2009-2010
Didier Aribaud
C
C
o
o
r
r
r
r
e
e
c
c
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
C
C
#
#
3
3
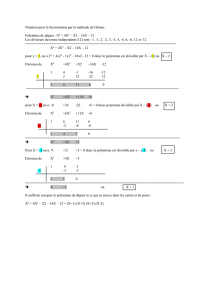
1. Développer, réduire et ordonner :
A = (3x – 4)²
A = 9x² – 2×3x×4 + 16
A = 9x² – 24x +16
B
= (3
x
–
5)
2
+(9
–
x
)(2
x
–
1)
B = (9x² – 2×3x×5 + 25) + (9×2x + 9×(–1) – x×2x – x×(–1))
B = (9x² – 30x + 25) + (18x – 9 – 2x² + x)
B = 9x² – 30x + 25 + 19x – 9 – 2x²
B = 7x² – 11x + 16
C
= (5
x
–
2)(1
–
3
x
)
–
(3
x
–
4)
2
C = 5x×1 – 5x × 3x – 2×1 + (–2)×(–3x) – [(3x)² – 2×3x×4 + 4²]
C = 5x – 15x² – 2 + 6x – 9x² + 24x – 16
C = – 24x² + 35x – 18
2. Factoriser :
D
= 27
x
3
–
12
x
D = 3 × 9 × x² × x – 3 × 4x
D = 3x × (9x² – 4)
D = 3x(3x – 2)(3x + 2)
E
= 16
x
2
–
25
E = (4x – 5)(4x + 5)
F = 5(x + 3) + (x + 3)(x + 2)
F = (x + 3)(5 + x + 2)
F = (x + 3)(x + 7)
G
=
6
x
(2
x
–
3)
–
(
x
–
5)
(2
x
–
3)
G = (2x – 3)[6x – (x – 5)]
G = (2x – 3)(6x – x + 5)
G = (2x – 3)(5x + 5)
G = 5(2x – 3)(x + 1)
H
= (
x
–
5)(7
x
–
4) +
49
x
2
–
56
x
+ 16
H = (x – 5)(7x – 4) + (7x – 4)²
H = (7x – 4)[x – 5) + (7x – 4)]
H = (7x – 4)(x – 5 + 7x – 4)
H = (7x – 4)(8x – 9)
I =
(3
–
2
x
)
2
–
(4
x
–
5)
2
I = [(3 – 2x) – (4x – 5)][(3 – 2x) + (4x – 5)]
I = (3 – 2x – 4x + 5)(3 – 2x + 4x – 5)
I = (8 – 6x)(2x – 2)
I = 2(4 – 3x)×2(x – 1)
I = 4(4 – 3x)(x – 1)
3.
On donne P = (4x – 5)² + (4x – 5)(x + 1)
1.
Développer, réduire et ordonner
P
.
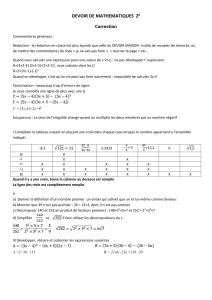
P = (4x – 5)² + (4x – 5)(x + 1)
P = (16x² – 2×4x×5 + 25) + (4x×x + 4x×1 – 5×x –5×1)
P = 16x² – 40x + 25 + 4x² + 4x – 5x – 5
P = 20x² – 41x + 20
2.
Factoriser
P.
P = (4x – 5)² + (4x – 5)(x + 1)
P = (4x – 5)[(4x – 5) + (x + 1)]
P = (4x – 5)(5x – 4)
3. Résoudre l’équation P = 0 en utilisant le résultat de la question 2.
P = 0 ou encore (4x – 5)(5x – 4) = 0
4x – 5 = 0 ou 5x – 4 = 0
4x = 5 ou 5x = 4
x =
5
4
ou
4
5
x
=
4.
Calculer P pour x = 1, puis pour x = 0 et enfin pour
4
5
x
=
.
x = 1 : P = 20x² – 41x + 20 = 20×(1)² – 41×(1) + 20 = 20 – 41 + 20 = – 1
x = 0 : P = 20x² – 41x + 20 = 20×0² – 41×0 + 20 = 20

Lycée Alexandre Dumas – 2009-2010
Didier Aribaud
4
5
x
=
: P = (4x – 5)(5x – 4) =
4 4 4
4 5 5 4 4 5 0 0
5 5 5
× − × − = × − × =
. On aurait pu prévoir ce résultat puisque
4
5
x
=
est une des solutions qui annulent P !
x
+ 1
2 + 4
x
S
4.
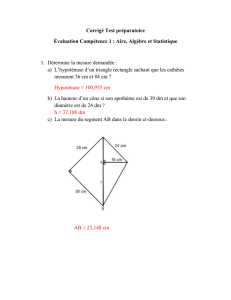
La figure ci-contre est composée de deux carrés.
1. Exprimer la surface de chacun d’eux en fonction de x.
2. Exprimer la surface grisée S en fonction de x. (On donnera
le résultat sous forme factorisée et sous forme
développée).
3. Quelle doit être la valeur de x pour que la surface S soit
égale à 15 cm².
1.
Petit carré : (
x
+ 1)² =
x
² + 2
x
+ 1
Grand carré : (2
x
+ 4)² = 4
x
² + 16
x
+ 16
2.
S = (2
x
+ 4)² – (
x
+ 1)²
S = [(2
x
+ 4) – (
x
+ 1)][(2
x
+ 4) + (
x
+ 1)]
S = (2
x
+ 4 –
x
– 1)(2
x
+ 4 +
x
+ 1)
S = (
x
+ 3)(3
x
+ 5)
S = 3
x
² + 5
x
+ 9
x
+ 15
S = 3
x
² + 14
x
+ 15
ou encore
S = (4
x
² + 16
x
+ 16) – (
x
² + 2
x
+ 1)
S = 4
x
² + 16
x
+ 16 –
x
² – 2
x
– 1
S = 3
x
² + 14
x
+ 15
Mais l’inconvénient de cette méthode est qu’elle ne permet pas d’obtenir la forme factorisée.
3.
Pour que l’aire soit égale à 15, il faut que 3
x
² + 14
x
+ 15 = 15, ou encore
3
x
² + 14
x
= 0
Cette égalité est vraie pour
x
= 0.
Dans le cas où
x
est différent de 0, on peut diviser tous les termes des deu
x
membres par
x
et on obtient :
3
x
+ 14 = 0 ou encore
x
= – 14/3.
1
/
2
100%