Doc

Chapitre 4 : Circuits résonnants
Notions de filtrage
On a vu que des réseaux comportant bobines et/ou condensateurs ont des
impédances qui sont dépendante de la fréquence
Z = U / I
Donc à U fixé, I = f(w)
à I fixé, U = f(w)
On s'intéresse à présent à la réponse en fréquence de U ou de I
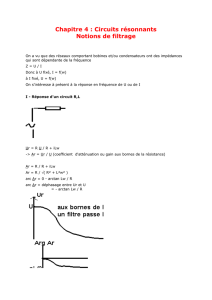
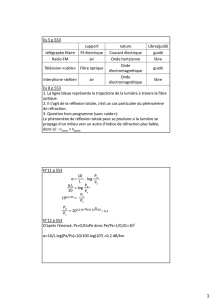
I - Réponse d'un circuit R,L
Ur = R U / R + iLw
-> Ar = Ur / U (coefficient d'atténuation ou gain aux bornes de la résistance)
Ar = R / R + iLw
Ar = R / ( R² + L²w² )
arc Ar = 0 - arctan Lw / R
arc Ar = déphasage entre Ur et U
= - arctan Lw / R

Ul = iLw U / R + iLw
Al = iLw / R + iLw
-> Al = Lw / sqr(R² + L²w²)
arg Al = + /2 - arctg Lw / R
Pour tout w
Ur + Ul = U
<=> Ar + Al = 1
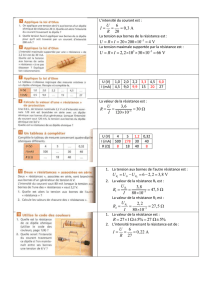
II - Réponse en fréquence d'un circuit RLC série à U fixé
1) Comportement de l'impédance (Z)
Z = R + iLw -i / cw
Z = ( R² + (L w - 1/cw)² )
arg Z = = I>, U>
= arctan ( (Lw - 1/cw ) / R)

Quand :
w -> 0, Z->
et arg Z -> - / 2
w -> , Z ->
et arg Z -> + / 2
Z est minimale pour Lw - 1/cw = 0
<=> w = w0 = 1/Lc pulsation propre
I = U / Z
I = U / Z à U fixé, I passe par un maximum (U/R) pour w=w0
Il y a résonance d'intensité
Remarque : à I fixé, U passe par un minimum pour w=w0. C'est l'anti-résonance

2) Réponse aux bornes de R
Ur = RU / Z
-> Ur = RU / Z
= RU / (R² + (Lw-1/cw)²)
= R I
P = RI² = Ur² / R
P est maximale pour w=w0. Alors Pmax = U² / R
Inversemment, on a atténuation pour P < Pmax / 2
On définit 10 log P exprimé en décibels (dB).
On cherche le domaine de fréquence pour lequel la puissance aux bornes de la
résistance supérieur à Pmax / 2
10 log P >= 10 log Pmax - 10 log 2
= 0.3
On cherche donc l'atténuation à - 3 dB
10 log Ur² / R >= 10 log U²/R - 3
<=> 20 log Ur - 10 log R >= 20 log U - 10 log R - 3
<=> 20 log Ur >= 20 log U - 3
P >= Pmax / 2 <=> Ur² / R >= U² / 2R
<=> Ur >= U / 2
<=> RU / sqr( R² + (Lw - 1/cw)²) >= U / 2
<=> 1 / sqr( 1 + (Lw / R - 1 / Rcw)² ) >= 1 / 2
<=> 1 + (Lw / R - 1 / Rcw)² <= 2
<=> (Lw / R - 1 / Rcw ) <= 1

w = w2 - w1
= bande passante
et w1 et w1 sont les pulsations de coupure à -3 dB
On pose x = w / w0 (on cherche donc x1 = w1 / w0 et x2 = w2 / w0 )
On définit Q = Lw0 / R
= 1 / RCw0
= facteur de qualité (ou de surtension)
On calcule w1 et w2 par les valeurs positives tirées de
(Lw / R - 1 / Rcw)² = 1
( Qx - Q / x)² = 1 <=> (x - 1/x)² = 1/Q²
=> x - 1/x = ± 1/ Q
= / Q (avec = ± 1)
x² + x / Q - 1 = 0
= ² / Q² + 4
= 1 / Q² + 4
x1,2 = - / Q ± (/ 2 )
* = + 1 x1 = - 1 / 2Q + ( (1 / 4Q²) + 1) = w1 / w0
* = - 1 x2 = 1 / 2Q + ( (1/ 4 Q²) + 1) = w2 / w0
w = w1 – w2 = w0 / Q
Plus Q est élevé, plus le circuit est sélectif
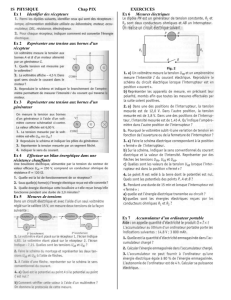
Aux bornes de R on a donc un filtre passe bande
3) Réponse aux bornes de C
Uc = ( Zc U )/ Z
= U / ( icw [ R + i (Lw - 1/cw) ] )
= U / ( iRcw + 1 - Lcw² )
Uc = U / sqr( (1 - Lcw² )² + R²L²w² )
w->0 Uc ->U
w = w0 Uc -> Q U
w -> + Uc -> 0
On étudie Uc = f(w)
 6
6
 7
7
1
/
7
100%