Lesson Thirteen: Auxiliary Verbs

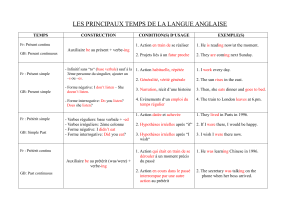
Auxiliary Verbs
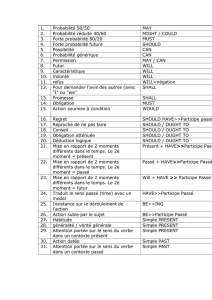
A. Quelques auxiliaires sont suivis d'un
infinitif :
can (capacité) - pouvoir au présent
could (possibilité) - pouvoir au conditionnel
will (futur)
would (conditionnel)
should (conseil) - devoir au imparfait
must (obligation) - devoir au présent
may (permission) - pouvoir au présent
might (probabilité)
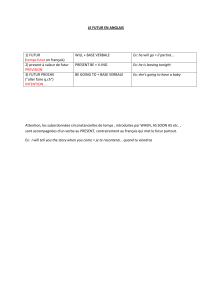
B. D'autres auxiliaires sont suivis de TO + un
infinitif :
be able to = can
be going to = will
ought to = should
have to = must
be allowed to = may
need to (avoir besoin de)
want to (vouloir)
like to (aimer)
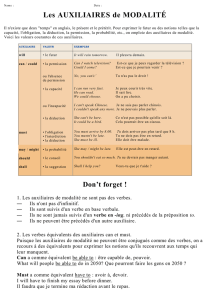
1. Present Tense
La plupart des auxiliaires ne changent pas au présent. Tous les sujets ont la même conjugaison - il
n'y a pas de -s à la troisième personne du singulier - pour ces auxiliaires : can, could, will,
would, should, must, may, might, ought to.
Exemple: I can - you can - he/she/it can - we can - you can - they can
2. Negative
→ Ajoutez NOT après l'auxiliaire (comme BE et HAVE GOT) pour ces auxiliaires : can, could,
will, would, should, must, may, might, be able to, be going to, ought to, be allowed to. Parfois,
il y a des formes contractées avec NOT.
He cannot read. / He can't read.
They must not leave. / They mustn't leave.
I will not do it. / I won't do it.
You may not sit down.
She is not able to sleep. / She isn't able to sleep.
We are not allowed to smoke. / We aren't allowed to smoke.
→ Contractions
cannot = can't could not = couldn't will not = won't
would not = wouldn't should not = shouldn't must not = mustn't
→ Ajoutez DO NOT / DON'T ou DOES NOT / DOESN'T avant ces auxiliaires : have to, need to,
want to, like to (et tous les autres verbes en anglais !)
You do not have to help me. / You don't have to help me.
He does not need to see it. / He doesn't need to see it.
I do not want to be here. / I don't want to be here.
She does not like to read. / She doesn't like to read.

2
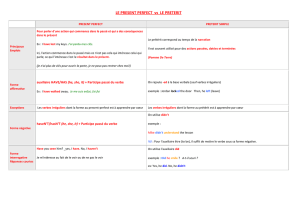
3. Questions
→ Inversion : auxiliaire + sujet (comme BE et HAVE GOT) : can, could, will, would, should,
must, may, might, be able to, be going to, be allowed to. (Il est rare que l'on forme des questions
avec ought to).
Can you be quiet?
Will we eat dinner soon?
May I borrow this book?
Are they going to arrive?
→ DO ou DOES + sujet + verbe : have to, need to, want to, like to (et tous les autres verbes en
anglais !)
Do I have to go?
Do you need to eat now?
Does he want to play soccer?
Does she like to watch TV?
Exercice
1. Present: We are going to leave in 10 minutes.
Negative:
Question:
2. Present: Sarah needs to learn how to drive.
Negative:
Question:
3. Present: They are allowed to smoke here.
Negative:
Question:
4. Present: I can speak three languages.
Negative:
Question:
5. Present: He has to finish his homework.
Negative:
Question:
1
/
2
100%