Grammaire Anglaise : Temps et Conjugaison

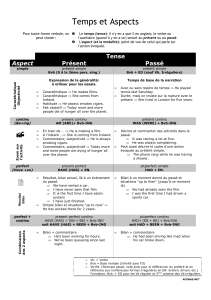
LES PRINCIPAUX TEMPS DE LA LANGUE ANGLAISE
TEMPS
CONSTRUCTION
CONDITION(S) D‘USAGE
EXEMPLE(S)
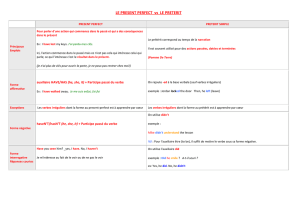
Fr: Présent continu
GB: Present continuous
Auxiliaire be au présent + verbe-ing
1. Action en train de se réaliser
2. Projets liés à un futur proche
1. He is reading now/at the moment.
2. They are coming next Sunday.
Fr : Présent simple
GB: Present simple
- Infinitif sans “to“ (base verbale) sauf à la
3ème personne du singulier, ajouter un
–s ou –es.
- Forme négative: I don’t listen – She
doesn’t listen.
- Forme interrogative: Do you listen?
Does she listen?
1. Action habituelle, répétée
2. Généralité, vérité générale
3. Narration, récit d’une histoire
4. Evènements d‘un emploi du
temps régulier
1. I work every day.
2. The sun rises in the east.
3. Then, she eats dinner and goes to bed.
4. The train to London leaves at 6.pm.
Fr : Prétérit simple
GB: Simple Past
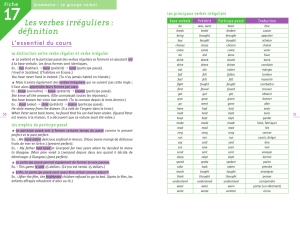
- Verbes réguliers: base verbale + -ed
- Verbes irréguliers: 2ème colonne
- Forme négative: I didn’t eat
- Forme interrogative: Did you eat?
1. Action datée et achevée
2. Hypothèses irréelles après “if“
3. Hypothèses irréelles après “I
wish“
1. They lived in Paris in 1996.
2. If I were there, I would be happy.
3. I wish I were there now.
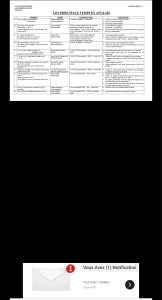
Fr : Prétérit continu
GB: Past continuous
Auxiliaire be au prétérit (was/were) +
verbe-ing
1. Action qui était en train de se
dérouler à un moment précis
du passé
2. Action en cours dans le passé
interrompue par une autre
action au prétérit
1. He was learning Chinese in 1996.
2. The secretary was talking on the
phone when her boss arrived.

Fr : Present perfect
simple (le parfait)
GB: Present perfect
simple
Auxiliaire have au présent + verbe au
participe passé (= -ed pour les verbes
réguliers; 3ème colonne des verbes
irréguliers)
1. Action passée non datée ou
au résultat visible
2. Action passée ayant valeur de
bilan
1. I’m tired. I have worked a lot.
2. I have already been to America.
Fr : Present perfect
progressif (le parfait
progressif)
GB: Present perfect
continuous
Auxiliaire have au présent + been +
verbe -ing
1. Action passée non datée ou
au résultat visible mais
susceptible de se poursuivre
(l’accent est mis sur la durée
de l’action plutôt que le
résultat)
1. I have a lot of work. I have been
studying for three hours now.
1bis. I have a lot of work. I have been
studying since 3pm.
Fr : Plus que parfait
GB: Past perfect simple
Auxiliaire have au prétérit (had) +
verbe au participe passé (= -ed pour
les verbes réguliers; 3ème colonne des
verbes irréguliers)
1. Action antérieure au récit
2. Action antérieure à une autre
action au prétérit
1. They had worked all day because she
wanted to rest at the weekend.
2. She had slept before she left home.
Fr : Plus que parfait
progressif
GB: Past perfect
continuous
Auxiliaire have au prétérit (had) +
been + verbe -ing
1. Action antérieure à une autre
action au prétérit mais cette
première action était
susceptible de se prolonger.
(l’accent est mis sur la durée)
1. They had been driving all night long
when the car suddenly broke down.

Fr : Futur simple
GB: Future simple
- Auxiliaire will + base verbale
1. Prédiction sur l’avenir
2. Généralité, vérité générale
sans valeur de futur en anglais
scientifique
3. Le présent simple a une valeur
de futur après les conjonctions
de temps (when, as soon as,
once, etc.)
1. French people will speak better
English in the next decades.
2. The sun will rise in the east.
3. I will stop working when/as soon as/
once bob returns home.
Fr : Futur progressif
GB: Future continuous
- Auxiliaire will + be + verbe -ing
1. Action qui sera en train de se
dérouler à un moment donné
du futur
1. Tomorrow evening, I will be
watching the game at 8.
Fr : Futur antérieur
GB: Future perfect
- Auxiliaire will + have + participe passé
1. Action future antérieure à un
moment du futur.
1. Next week, she will have finished
her project.
Fr : Conditionnel présent
GB: Simple conditional
- would + base verbale
1. Situation iréelle du présent
(après “if“, utilisation du
prétérit modal = action
irréaliste)
1. If I had a car, I would drive there.
1
/
3
100%