Moyens d`étude de la réponse immunitaire locale après

RESUME
L’évaluation de la réponse immunitaire après
traitement prophylactique des tumeurs superfi-
cielles de vessie par BCG a plusieurs objectifs:
définir de nouveaux paramètres pronostiques et
mettre au point des outils de rationalisation du
traitement. Après l’étude initiale de la valeur
des infiltrats inflammatoires vésicaux et de la
conversion des tests cutanés, plusieurs auteurs
s’orientent maintenant vers des techniques plus
spécifiques: analyse immunohistochimique et
c y t o f l u o rométrique des sous populations lym-
p h o c y t a i r es activées localement, dosage des
cytokines urinaires.
Cet article fait une revue de ces différentes tech-
niques, discute la signification de leurs résultats
et leurs intérêts potentiels dans la conduite du
traitement et la compréhension des mécanismes
d’action du BCG.
Mots clés : cancer de vessie, immunothérapie, BCG,
cytokines urinaires.
Progrès en Urologie (1993), 3, 745-751
INTRODUCTION
L’évaluation de la réponse immunitaire après trai-
tement endo-vésical par BCG a tout d’abord porté
sur l’étude de la valeur pronostique des infiltrats
inflammatoires vésicaux et de la conversion des
tests cutanés. De nouvelles approches tendent à
développer des méthodes plus fines d’analyse de la
réponse immunitaire locale: immunohistochimie,
dosage des cytokines urinaires, cytométrie de flux.
Le but de ce travail est de passer en revue ces nou-
veaux outils et d’identifier des paramètres immu-
nologiques simplement quantifiables liés à l’action
antitumorale du BCG qui pourraient avoir un inté-
rêt potentiel dans la conduite du traitement (dosi-
métrie et marqueurs pronostiques). Ce travail ten-
tera par ailleurs de situer le rôle de ces paramètres
dans les mécanismes d’action du BCG et dans le
cadre plus général du rejet des tumeurs.
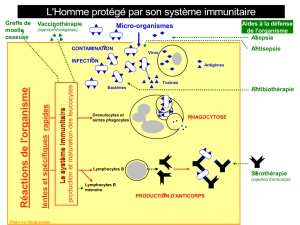
MOYENS D'ETUDE
1. Tests cutanés, histologie (infiltrats vésicaux)
La première évaluation de la réponse immunitaire
au BCG intra-vésical a porté sur la conversion
positive de tests cutanés et l’apparition d’infiltrats
inflammatoires vésicaux témoignant d’une activa-
tion du système immunitaire locale et générale.
Les auteurs ont alors voulu faire de ces tests des
marqueurs pronostiques. Ainsi LA M M en 1982,
notait que 6% des patients qui avaient une conver-
sion de leurs tests cutanés récidivaient comparés à
38% pour ceux dont les tests restaient négatifs
(p=0,022) [20]. KE L L E Y en 1986, notait que 77%
des patients qui avaient une conversion cutanée
étaient sans tumeur contre 34% de ceux dont les
tests restaient négatifs. De même il montrait que
77% des patients qui avaient des infiltrats vésicaux
étaient sans tumeur contre 32% pour ceux qui
n’avaient p a s d'infiltrat inflammatoire [18]. Ces
résultats soulignaient le lien qui existe entre la
réponse immunitaire et la réponse antitumorale
mais ne sont pas apparus suffisamment spécifiques
pour servir de marqueurs pronostiques. TORRENCE
en 1988, montrait qu’avec un recul plus important
la réponse granulomateuse locale perdait sa signifi-
Manuscrit reçu le 10 janvier 1993
Adresse pour correspondance : Dr. J . J . Patard, Service
d'Urologie, Hôpital Henri Mondor, 94010 Créteil.
Progrès en Urologie (1993), 3, 745-751
745
Moyens d'étude de la réponse immunitaire locale
après traitement endovésical par BCG : Revue
Jean-Jacques PATARD, Claude ABBOU, Dominique CHOPIN
Service d'Urologie, Hôpital Henri Mondor, 94010 Créteil
ARTICLE DE REVUE

cation statistique et que la signification statistique
des test cutanés était trop peu nette pour faire de ce
critère un marqueur pronostique [35].
2. Immunohistochimie
Deux études ont été consacrées à la répartition des
lymphocytes dans la vessie normale [13, 15].
Ceux-ci se trouvent en plus grand nombre au
contact de la membrane basale versant chorion et
sont essentiellement des lymphocytes de phénoty-
pe CD8. On trouve également quelques macro-
phages et quelques cellules NK mais en petit
nombre. Les cellules urothéliales n’expriment que
des antigènes de classe I du CMH et pas les anti-
gènes de classe II. Plusieurs études se sont atta-
chées à définir la réponse immunitaire après instil-
lations endovésicales. Des biopsies vésicales, avant
et après traitement, avec marquage immunohisto-
chimique afin d’étudier les sous-populations
immunocompétentes, ont été réalisées. Des anti-
corps monoclonaux spécifiques de chacune des
sous populations ont été utilisés: anti MHC de
classe I, anti MHC de classe II, anti CD4, anti CD8
(lymphocytes T), anti CD25 (récepteur à l’IL2),
anti CD22 (lymphocytes B), anti CD 68 (macro-
phages), anti CD 57, anti CD 16 (NK). Il a été
montré une inversion de la répartition de ces cel-
lules avec prédominance de lymphocytes T auxil-
liaires sur les cellules T suppresseurs dans la sous
muqueuse (CD 4 > CD 8), la présence de cellules
B, de macrophages et de cellules NK en plus petit
nombre. Les cellules T exprimaient le récepteur à
l’IL2 qui persiste à distance du traitement. Les cel-
lules immunitaires et urothéliales exprimaient des
antigènes de classe II du complexe majeur d’histo-
compatibilité [3, 14, 22, 28, 29]. Ces données sont
résumées dans le Tableau 1.
B
Ö H L E
récemment a montré que cette activation loca-
le des cellules immunocompétentes pouvait persister
à long terme. Par une technique d’immunohistochi-
mie avec amplification (APAAP) sur du matériel
biopsique il a montré que 4 patients sur 8 traités par
BCG avaient encore une réactivité contre l’ILl, le
T N F, L’IL2 deux ans après le traitement [5].
746
Tableau 1. Etude immunohistochimique de la réponse au BCG. Données de la littérature.
Auteurs El Demiry Prescott Bohle Leong
Patients 7 CIS 9 Ta, T1, CIS 6 Ta, T1 19 Ta, T1, CIS
Urothélium Urothélium Avant traitement Après
TH/TS normal : Ts > TH normal TH/TS = 1/2 traitement
avant traitement TH/TS = 0,68 après traitement TH/TS = 2/1
CD4/CD8 TH > TS après traitement TH/TS = 2/1
après traitement TH/TS = 3,13
TH/TS x 4
Macrophages Infiltrats sous Infiltrats sous Infiltrats sous Infiltrats
Lymphocytes B muqueux Muqueux muqueux muqueux
Urothélium + dans les
normal: (-) infiltrats
avant traitement
IL2 R 9%
après traitement
28,2%
Urothélium Urothélium pic 6-12 S 8/18
normal: (-) normal : (-) persiste
lymphocytes avant traitement à 3 mois
HLDR et cellules (+)
urothéliales après traitement
(++) (++)

3. Cytométrie de flux (CMF)
Certains auteurs utilisant la cytométrie de flux se
sont attachés à étudier dans les urines le profil cel-
lulaire (9) après BCG-thérapie. Ils ont mis en évi-
dence une forte augmentation du nombre des cel-
lules du culot urinaire. Ces cellules étaient: des
granulocytes, des monocytes, des macrophages,
des cellules NK et, en plus petit nombre, des lym-
phocytes. Les lymphocytes ont pu être étudiés
grâce à un panel d’anticorps [10], il s’agissait
essentiellement de lymphocytes T auxillaires pré-
dominant sur les lymphocytes T suppresseurs,
exprimant le récepteur à l’interleukine 2 et les anti-
gènes du CMH de classe II, donc sensibilisés.
Cette répartition des sous-populations lymphocy-
taires après BCG endovésical confirmait les don-
nées des biopsies après traitement.
4. Dosage des cytokines (Bioassay, RIA, ELISA)
La réponse immunitaire met en jeu des cellules qui
interagissent et communiquent entre elles grâce à
des facteurs solubles appelés cytokines.
Des cytokines ont été mises en évidence dans les
urines dans certaines circonstances normales et
pathologiques. Un inhibiteur du récepteur à l’inter-
leukine 1 est détectable dans les urines normales
[19], de même que des récepteurs solubles de
l’interleukine 2 [23], de l’interleukine 6, de l’inter-
féron gamma, et du TNF [24, 25]. Dans l’infection
urinaire à E. Coli, le taux d’IL6 urinaire a pu être
corrélé au nombre de bactéries [17]. Dans les
néphropathies à IgA, le taux d’IL6 urinaire évolue
parallèlement aux poussées de la maladie et
s’annule sous traitement [12]. De même, dans les
greffes rénales, le taux de cytokines urinaires IL2,
IL6 a une valeur pronostique puisqu’il s’élève
après l’intervention pour se normaliser en deux à
trois semaines, le rejet étant précédé d’une réas-
cension de ces taux [8, 32, 38].
Dans les tumeurs superficielles de vessie la ciné-
tique des cytokines urinaires après instillations de
BCG endovésical a été bien étudiée. Les cytokines
mises en évidence ont été ILl, IL2,TNF, IFNγ, IL6,
IL8 [4, 11, 30, 31].
Le Tableau 2 résume ces études. Les méthodes de
dosage ont été le plus souvent des tests biolo-
giques, des techniques RIA ou ELISA. Les ciné-
tiques retrouvées ont été comparables: I’ILl et
l’IL6 avaient une élévation précoce dès les pre-
mières instillations, I’IL2, I’IFNγet le TNF
n’étaient retrouvées qu’à partir de la troisième ins-
tillation. Le pic était en général observé à la 6ème
heure. L’IL8 a été mise en évidence dans les urines
des patients traités par résection seule ou par BCG
avec néanmoins des taux significativement plus
élevés dans le groupe BCG [34].
747
Tableau 2. Cytokines après BCG : données de la littérature.
Auteurs Ratliff Böhle Prescott Dejong Thalman
Cytokine IL2 IL1, IL2, TNF IF gamma IL2 IL8
Ta, T1, CIS Ta, T1, CIS CIS Ta, T1 Ta, T1, CIS
Patients 18 patients 10 patients 6 BCG 11 patients
laser YAG 7 MMC
HT2 (IL2 Culture de RIA CTLL 16 ELISA
Dosage dépendante) fibroblastes
ELISA
- Négatif avant IL1 : pic 4-8h - Après 3ème - Après 3ème Pic dans les 24h
traitement IL2 : pic 2-8h semaine semaine après BCG et
- apparaît TNF : pic 2-4h - Pic 2-6h - Pic 2-6h RTU avec
Cinétique 3ème semaine 6/13 MMC: - jamais après différence
- Pic 4-8h taux faible 24 h significative entre
- rarement les deux groupes
après 24 h

DISCUSSION
La présence de récepteurs solubles aux cytokines
dans les urines semble correspondre à un
phénomène général de régulation immunitaire dans
les fluides. On a attribué à ces récepteurs des rôles
d’inhibiteurs, de transporteurs ou encore de ligants
[25]. Leur présence n’a pas été explorée durant le
traitement endovésical par BCG.
Les cytokines peuvent maintenant être dosées dans
les urines par des techniques simples et reproduc-
tibles. En effet les techniques ELISA (immunoen-
zymatiques) sont plus simples à mettre en oeuvre
que les tests biologiques initialement utilisés (cul-
tures cellulaires cytokines dépendantes) ou encore
RIA (radioimmunologiques) plus contraignantes
car nécessitant l’utilisation de produits radioactifs.
D i fférents kits ELISA commercialisés permettent
donc une approche quantitative simple des diff é -
rentes cytokines libérées dans les urines par les cel-
lules immunitaires activées. Les techniques immu-
nohistochimiques pratiquées sur du matériel biop-
sique après traitement fournissent une analyse
semi-quantitative des différents évènements immu-
nitaires importants à considérer (CD4 / CD8, CMH
CLII). L’analyse en cytométrie de flux de ces tissus
ou encore du culot urinaire pourrait permettre
d’évaluer ces critères sur le plan de la dosimétrie et
de la réponse au traitement.
Parmi les différentes cytokines qui ont été mises en
évidence dans les urines après BCG, toutes ne sem-
blent pas avoir la même signification. L’ILl, le
T N Fα, I’IL6, I’IL8, sont libérés par les macro-
phages dans un certain nombre de circonstances
non spécifiques: maladies inflammatoires, infec-
tion urinaire, intervention chirurgicale. La présence
d’IL2, de TNFβ, d’IFNγen revanche traduit l’acti-
vation lymphocytaire. Ces cytokines pourraient être
au centre de l’activité antitumorale du BCG par
leur cytotoxicité directe mais aussi par leur capacité
à stimuler certaines populations cytotoxiques.
L’interféron gamma à cet égard est un bon exemple
puisque cette cytokine a des capacités d’immuno-
modulation et des propriétés cytotoxiques. En effet
l ’ I F Nγentraîne une surexpression des antigènes
associés aux tumeurs dans certains modèles tumo-
raux [26, 36] et module l’expression des antigènes
de classe II [2, 16]. Cette expression des antigènes
de classe II du CMH signifie pour les cellules uro-
théliales la capacité acquise par immunostimulation
de présenter un antigène aux cellules eff e c t r i c e s .
L’ I F Nγa, de plus, des capacités cytotoxiques
directes comme cela a été montré sur des lignées
tumorales vésicales [16] et indirectes par activation
s y n e rgique avec d’autres cytokines de populations
cytotoxiques (macrophages, LAK, NK, CTL) [37].
La prédominance des cellules de phénotype CD4
(lymphocytes T auxiliaires) au sein des infiltrats
inflammatoires vésicaux coïncide avec des travaux
expérimentaux récents [21] qui ont montré que la
cellule urothéliale tumorale était capable de présen-
ter par l’intermédiaire des antigènes de classe II du
CMH les antigènes du BCG à des lymphocytes de
phénotype CD4. Ces lymphocytes auxilliaires en
réponse libéraient un certain nombre de cytokines
dont l’IL2 et l’IFNγ, activant d’autres populations
cytotoxiques et pourraient en eux même avoir des
propriétés cytotoxiques.
Ces différents éléments s’intègrent bien dans les
connaissances actuelles des phénomènes de présen-
tation antigénique et de rejet des tumeurs. En effet,
on sait que le récepteur T reconnait un complexe
constitué par un petit fragment peptidique antigé-
nique et une structure codée par le complexe
majeur d’histocompatibilité (CMH) [39]. Le CMH
code pour deux types de molécules membranaires:
les molécules de classe I qui sont exprimées sur
toutes les cellules de l’organisme et les molécules
de classe II qui ne sont exprimées que sur les cel-
lules classiquement présentatrices d’antigènes
(APC). Les antigènes des peptides exogènes sont
habituellement présentés aux cellules T par les
macrophages et les autres cellules présentatrices
(macrophages, lymphocytes B, lymphocytes T acti-
vés) en association avec les molécules de classe II.
La présentation de ces peptides nécessite une endo-
cytose de la protéine et une dégradation endosoma-
le en courts peptides [l]. Ces peptides se lient aux
molécules de classe II et le complexe est présenté à
la surface cellulaire [7]. Ces complexes CMH-pep-
tide sont reconnus par les lymphocytes CD4 [33].
Les peptides endogènes sont habituellement pré-
sentés en association avec les molécules de classe I
du CMH. Les lymphocytes T qui reconnaissent
l’association peptide endogène molécules de classe
I sont de phénotype CD8 [27].
L’immunothérapie par BCG se présente donc
comme un modèle d’immunothérapie non spéci-
fique: un antigène bactérien après dégradation est
748

présenté par des cellules spécialisées ou encore par
les cellules urothéliales par l’intermédiaire des
molécules du complexe majeur d’histocompatibili-
té de classe II aux lymphocytes T auxiliaires
(CD4). Ces lymphocytes CD4 activent les autres
populations cytotoxiques notamment par la libéra-
tion de cytokines. En revanche certains des pep-
tides présentés par les molécules de CMH ont été
identifiés comme antigènes de rejet des tumeurs
(TRA). L’identification de ces antigènes de rejet
des tumeurs a été réalisée en particulier dans le
mélanome humain (antigène Mage) et permet
d’envisager une immunothérapie cette fois spéci-
fique: vaccination, génération de clones de lym-
phocytes T cytolytiques spécifiques par immunosé-
lection [6].
CONCLUSIONS, PERSPECTIVES
On peut donc maintenant disposer d’outils quanti-
tatifs permettant d’évaluer la réponse immunitaire
locale après BCG endovésical. La cytométrie de
flux sur des urines ou encore sur des prélèvements
tissulaires vésicaux pourrait quantifier les diff é-
rentes populations immunitaires mises en jeu: le
rapport CD4/ CD8, l’expression des antigènes de
classe II du CMH, notamment au vu de la littératu-
re semblent intéressants à mesurer. Le dosage des
cytokines spécifiques dont le rôle semble impor-
tant dans l’activité antitumorale du BCG: IL2,
TNF, IFNγ, peut être réalisé par technique ELISA.
Ce dosage pourrait fournir un moyen simple de
suivi et de rationalisation du traitement : adaptation
des doses et de la durée du traitement en fonction
du profil de réponse de chaque malade. Ces cri-
tères enfin devraient être évalués comme mar-
queurs pronostiques.
L’utilisation du BCG comme agent antitumoral sur
un modèle de tumeurs immunogéniques telles que les
tumeurs de vessie est une bonne approche des phéno-
mènes d’immunité antitumorale. L’ i d e n t i f i c a t i o n
d’antigènes de rejet des tumeurs dans les tumeurs
urothéliales devrait permettre de développer des
méthodologies d’immunothérapie spécifique.
REFERENCES
1. ALLEN P.M., STRYDOM D., UNANUE F.R. Processing of
lysozyme by macrophages. Identification of the determinant
recognized by two T-cell hybridomas. Proc. Natl.Acad. Sci.
USA, 1984, 81, 2489-2493.
2. BASHAM T. Y., MERIGAN T. C . Recombinant interferon
gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J .
Immunol., 1983, 130, 1492-1495.
3. BOHLE A., GERDES A., ULMER A.J., HOFSTETTER
A.G., FLAD H.D. Effects of local Bacillus Calmette Guérin
therapy in patients with bladder carcinoma on immunocom-
petent cells of the bladder wall. J. Urol., 1990, 144, 53-58.
4. BOHLE A., NOWC C.H., ULMER A.J., MUSEHOL J.,
GERDES J., HOFSTETTER A.G., FLAD H.D. Elevations
of cytokines interleukin-1, interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis
factor in the urine of patients after intravesical bacillus
Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. J. Urol., 1990, 144, 59-63.
5. BOHLE A., BUSEMAN E., GERDES A., FLAD H.D.,
JOCHAM D. Immuno-histological assessment of long trm
cytokine production after intra-vesical bacillus Calmette-
Guérin therapy. EAU, 1992, Abstract 166, p. 284.
6. BOON T. Toward a genetic analysis of tumor rejection anti-
gens.Advances in Cancer Research, 1992, 58, 177-210.
7. BUUS S., SETTE A., COLON S., MILES C., GREY H.M.
The relation between major histocompatibility complex
(MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind to immuno-
genic peptides. Science, 1987, 235,1353-1358.
8. CORNABY A., SIMPSON M., VANN RICE R., DEMPSEY
R., JENKINS R., MONACO A. Interleukin 2 levels and
urine cytology distinguish between cyclosporine toxicity
and rejection in renal and liver a llograft recipients.
Transplant. Proc., 1988, 20, 827-830.
9. DE BOER E.C., DE JONG W.H, VAN DER MEIJDEN
A . P.M., STEERENBERG P.A., WITJES F., VEGT P. D . J . ,
DEBRUYNE F.M.J., RUITENBERG EJ. Leucocytes in urine
after intravesical treatment for superficial bladder cancer. A
flow cytofluorometric analysis. Urol. Res., 1991, 19, 45-50.
10. DE BOER E.C., DE JONG W.H., VAN DER MEIJDEN
A . P.M., STEERENBERG P.A., WITJES F., VEGT P. D . J . ,
DEBRUYNE F.M.J., RUITENBERG E.J. Lymphocytes in
the urine of patients with superficial bladder cancer after
intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guérin.
Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 1991, 33, 411-416.
11. DE JONG W.H., DE BOER E.C., VAN DER MEIJDEN
A . P.M., VEGT P., STEERENGERG P.A., DEBRUYNE
FMJ, RUITENBERG EJ. Presence of interleukin-2 in
patients after intravesical treatment with bacillus Calmette-
Guérin. Cancer Immunol. Immunother., 1990, 31, 182-186.
12. DOHI K., IWANO M., MURAGUCHI A., HORII Y. ,
H I R AYAMA T., OGAWA S., SHIIKI H., HIRANO T. ,
KISHIMOTO T., ISHIKAWA H. The prognostic significan-
ce of urinary interleukin 6 in IgA nephropathy. Clin.
Nephrol., 1991, 35, 1-5.
13. EL DEMIRY M.I.M., HARGREAVE T.B., BUSUTTIL A.,
JAMES K., CHISHOLM G.D. Immunohistochemical iden-
tification of lymphocyte subsets and macrophages in nor-
mal human urothelium using monoclonal antibodies. Br. J.
Urol., 1986, 58, 436- 442.
749
 6
6
 7
7
1
/
7
100%