Evaluation et gestion du risque hémorragique en rhumatologie

10
Revue Marocaine de Rhumatologie
Disponible en ligne sur
www.smr.ma
Les gestes locaux, notamment les infiltrations, font partie de
l’arsenal thérapeutique du rhumatologue. Ils se font dans
la majorité des cas en ambulatoire à hôpital de jour ou au
cabinet du rhumatologue. L’information du malade de tous
les risques encourus est une nécessité médico-légale.
Parmi ces risques, le risque hémorragique particulièrement
chez les patients sous anticoagulant et anti-agrégant
plaquettaire (AAP) doit être évalué.
La question est donc de savoir si le fait que le patient
soit sous un traitement anti coagulant ou anti-agrégant
plaquettaire constitue un obstacle à la réalisation d’un geste
local, ceci nous incite à des interrogations secondaires :
- Peut-on réaliser un geste sous un traitement anticoagulant
ou un traitement anti-agrégant plaquettaire ?
- Le fait d’arrêter ou de modifier un traitement anticoagulant
ou antiagrégant fait-il courir un risque plus important que
le bénéfice du geste ?
- Y a-t-il des données de la littérature ou des
recommandations professionnelles sur ce sujet ?
Nous allons essayer de répondre à ces questions à travers
cette mise au point en se basant sur les données de la
littérature.
QUELS SONT LES TRAITEMENTS
ANTICOAGULANTS DISPONIBLES AU
MAROC? (TABLEAU 1)
Le risque hémorragique, est-il le même pour toutes ces
molécules ?
Résumé
En cas d’un geste local en rhumatologie
interventionnelle, le risque hémorragique
particulièrement chez les patients sous
anticoagulant et anti-agrégant plaquettaire
(AAP) doit être évalué. La Société française
de rhumatologie a établi un classement des
risques hémorragiques des actes invasifs
en rhumatologie comme suit : haut risque,
risque modéré, risque faible, En accord avec
cette société, il n’est pas jugé nécessaire
d’interrompre le traitement AVK, sous réserve
d’un contrôle de l’INR, dans les situations à
risque faible. Les situations à risque modéré
ou élevé nécessitent un arrêt des AVK, avec ou
sans relais suivant le risque thromboembolique.
Mots clés : Geste local ; Risque hémorragique
; Anticoagulant ; Anti-agrégant plaquettaire.
Abstract
In interventional rheumatology, the
hemorrhagic risk particularly in patients
receiving anticoagulant and antiplatelet
therapy must be evaluated. The French
Society of Rheumatology has established
a classication of hemorrhagic risk in
rheumatology invasive acts as follows: high
risk, moderate risk, low risk, in agreement with
this society, it is not considered necessary
to stop vitamin K antagonists treatment
under subject to a control of INR, in low-risk
situations. Situations at moderate or high
risk necessitate interruption of vitamin K
antagonists, with or without relay according to
thromboembolic risk.
Key words : Local act; Hemorrhagic risk;
Anticoagulant therapy; Antiplatelet therapy.
Evaluation et gestion du risque hémorragique
en rhumatologie interventionnelle.
Evaluation and management of hemorrhagic risk in interventional rheumatology.
Sofia Talbi, Fatima Ezzahra Abourazzak, Taoufik Hazry.
Service de Rhumatologie, CHU Hassan II, Fès - Maroc.
Rev Mar Rhum 2014; 28: 10-3
Correspondance à adresser à : Dr S. Talbi
Email : talbi-sofi[email protected]
FMC

11
Revue Marocaine de Rhumatologie
Le risque hémorragique lié à l’anticoagulation orale est
plus important chez des patients ayant des comorbidités
comme l’hypertension artérielle, le diabète, la maladie
cérèbrovasculaire, la cardiopathie sévère, l’insuffisance
rénale, le cancer, l’anémie et les antécédents d’une
hémorragie majeure [1]. L’association entre l’alcoolisme
chronique ou l’hépatopathie et le risque hémorragique
reste controversée
Anti-agrégants plaquettaires (APP)
Le risque hémorragique est indépendant de la dose avec
l’aspirine, la ticlopidine et le clopidrogel du fait de leur
mode d’action irréversible sur les plaquettes par le biais
d’une inhibition de la cyclo-oxygénase pour l’aspirine et
en inhibant la fixation de l’adénosine diphosphate pour les
thiénopyridines (clopidrogel). L’action de ces molécules se
poursuit jusqu’à la mort de la plaquette (sept à dix jours)
[2, 3].
Héparines de bas poids moléculaire (HBPM)
Quelques cas d’hémorragies sévères parfois mortelles
sous héparines de bas poids moléculaire (HBPM) et sans
surdosage ont été décrits. Ce risque peut être expliqué
par l’existence de plusieurs facteurs de risque importants
chez ces patients : obésité, insuffisance rénale chronique,
insuffisance cardiaque et pathologie néoplasique [4].
Antivitamine K (AVK)
Thumboo et O’Duffy n’ont observé aucune complication
hémorragique dans les 4 semaines suivant la procédure
au cours de 32 infiltrations articulaires ou des parties
molles réalisées chez 25 patients sous AVK avec un
INR (international normalized ratio) inférieur à 4,5 [5].
Cependant pour diminuer Le risque hémorragique l’INR
doit être compris entre 1,5 et 2 [6].
RISQUE HÉMORRAGIQUE EN FONCTION
DU GESTE
La Société française de rhumatologie (SFR 2008) a établi
un classement des risques hémorragiques des actes
invasifs en rhumatologie comme suit : haut risque, risque
modéré, risque faible.(Tableau 2)
DANS QUELLES SITUATIONS PEUT-ON
POURSUIVE LE TRAITEMENT AAP ET AVK ?
Anti-agrégants plaquettaires (APP)
Aucune précaution particulière n’est recommandée pour
les injections intra-articulaires. Donc un traitement par anti-
agrégant plaquettaire peut être poursuivi en tenant compte
du bilan de coagulation, de la balance bénéfices/risques,
et de la nature de l’articulation (risque plus importants si
articulation profonde) [7].
Tableau 1 : Traitements anticoagulants disponibles au Maroc
Anti-agrégants
plaquettaires Héparines AVK
- KARDEGIC
- ASPEGIC CARDIO
- LISASPIN
- PLAVIX
- THROMBOPAT
- IBUSTRIN
- CATALGINE
- DISGREN
- TICLID
- LOVENOX
- INNOHEP
- NOVEX
- FRAXIPARINE
- CALCIPARINE
- FRAXODI
- ARIXTRA
- FRAGMIN
- HEPARINE ROCHE
- LIQUEMINE
- COUMADINE
- SINTROM
Faible risque Risque modéré Risque élevé
• Inltration
périarticulaire
• Ponction/inltration
simple d’articulation
périphérique hors coxo-
fémorales
• Inltration canalaire
supercielle
• Biopsie des glandes
salivaires accessoires
• Ponction/Inltration
simple des articulations
coxo-fémorales
• Inltration canalaire
• Ténotomie percutanée
• Ponction/inltration
rachidienne des
articulaires postérieures
• Ponction/inltration
rachidienne dorsale
costovertébrale
• Ponction/inltration
rachidienne lombaire,
foraminale
• Lavage articulaire
d’une articulation
périphérique
• Ponction trituration de
l’épaule
• Inltration sacro-iliaque
• Ponction kyste poplité
• Capsulodistension
• Biopsie synoviale
• Biopsie osseuse
• Ponction/inltration
sternoclaviculaire
• Ponction/inltration par
le hiatus sacrococcygien
• Ponction/inltration
rachidienne cervicale ou
lombaire, épidurale ou
intradurale
• Ponction/inltration
rachidienne cervicale,
foraminale
• Ponction-biopsie discale
• Cimentoplastie
Tableau 2 : Risque hémorragique des actes invasifs en rhumatologie selon la
Société française de rhumatologie
Evaluation et gestion du risque hémorragique en rhumatologie interventionnelle.

12
Revue Marocaine de Rhumatologie
Héparines de bas poids moléculaire (HBPM)
Mejjad et Favre recommandent 10 à 14 heures de délai entre
la dernière injection d’HBPM et la ponction et/ou infiltration
[7]. D’autres préfèrent la réalisation de la ponction et/ou
infiltration juste avant l’injection suivante d’HBPM, heure
d’activité la plus faible de l’HBPM (pic d’activité à trois
heures, demi-vie de trois à quatre heures) [8].
Au niveau du rachis : Lorsque l’infiltration est nécessaire il
est prudent de ne pas ajouter un traitement AINS à demi
vie longue. L’infiltration est réalisée juste avant l’injection
d’HBPM. [8].
Antivitamine K (AVK)
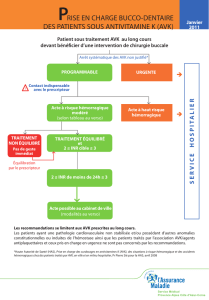
En accord avec cette La Société française de rhumatologie
2008, il n’est pas jugé nécessaire d’interrompre le
traitement AVK, sous réserve d’un contrôle de l’INR, dans
les situations à risque faible.
Le traitement par AVK peut alors être poursuivi après avoir
vérifié l’absence de surdosage. Toutefois, la prise d’autres
médicaments interférant avec l’hémostase ou l’existence
d’une comorbidité augmente le risque hémorragique.
DANS QUELLES SITUATIONS DOIT-ON
ARRÊTER LE TRAITEMENT AVK ET AAP ET
QUELLES SONT LES MODALITÉS D’ARRÊT
ET DE REMPLACEMENT THÉRAPEUTIQUE
POUR CHAQUE MOLÉCULE ?
Anti-agrégants plaquettaires (APP)
Au niveau du rachis, la répétition des infiltrations à 48
heures d’intervalle augmente le risque d’hématome.
IL est considéré comme plus prudent, même si le risque
semble très faible, d’obtenir l’arrêt de l’antiagrégant sept
à dix jours avant l’hospitalisation programmée pour la
réalisation d’infiltrations péridurales.
Par ailleurs, on ne peut se permettre d’interrompre un
traitement anti-agrégant chez un patient ayant comme
antécédent récent (inférieur à trois à cinq mois) un accident
vasculaire cérébral ischémique, un infarctus du myocarde ou
un angor. Il est donc préférable de remplacer l’anti-agrégant
par un AINS dont le fort pouvoir anti-agrégant a été démontré
en pathologie cardiovasculaire et dont le principal intérêt est
d’avoir un effet réversible en quelques heures. Il s’agit du
flurbiprofène (Cebutid) à la dose de 100 mg par jour en une
prise mais cette modalité n’est pas consensuelle (indication
hors AMM). L’infiltration péridurale sera réalisée dix jours
après l’arrêt de l’antiagrégant plaquettaire et vingt-quatre
heures après la dernière prise de flurbiprofène [9-11].
Antivitamine K (AVK)
Ce sont les situations à risque hémorragiques modéré
ou élevé.
En relais des AVK il faut utiliser une HBPM à dose curative
chez les patients porteurs d’une valve cardiaque mécanique
ou ayant fait un épisode thrombotique récent de moins
d’un mois. Il a en effet été démontré que l’utilisation d’une
HBPM était possible au même titre que l’héparine, chez
des patients venant d’avoir un remplacement valvulaire,
en respectant une activité anti Xa entre 0,5 et 1 UAntiXa/
mL et sur une période de 14 jours [12]. Chez des patients
porteurs d’une valve cardiaque mécanique, les HBPM ont
aussi été utilisées chez les femmes enceintes [13]. Il faut
néanmoins souligner que les HBPM n’ont pas l’AMM dans
cette indication et que le traitement des patients porteurs
de valves cardiaques mécaniques reste difficile.
Il est recommandé de mesurer l’INR 7 à 10 jours avant
le geste : si l’INR est en zone thérapeutique, il est
recommandé d’arrêter l’AVK 4 à 5 jours avant le geste
et de commencer l’héparine à dose curative 48 heures
après la dernière prise de fluindione (Previscan) ou de
warfarine (Coumadine) ou 24 heures après la dernière
prise d’acénocoumarol (Sintrom). Il est suggéré que les
patients ayant un INR supérieur à 1,5 la veille bénéficient
de l’administration de 5 mg de vitamine K per os. Dans ce
cas, un INR de contrôle est réalisé le matin.
Il est souhaitable que les gestes aient lieu le matin et
l’arrêt des héparines est recommandé comme suit :
- HNF intraveineuse à la seringue électrique: arrêt 4 à 6
heures avant le geste
- HNF sous-cutanée : arrêt 8 à 12 heures avant le geste
- HBPM : dernière dose 24 heures avant le geste
Les héparines doivent être administrées à dose curative
dans les 6 à 48 heures
Apres le geste selon le risque hémorragique et le risque
thrombo-embolique. Il est recommandé de ne pas
reprendre les héparines à dose curative avant la 6e heure.
En l’absence de risque hémorragique majeur et persistant,
il est recommandé de reprendre les AVK dans les
24 premières heures. Sinon, dès que possible après
l’intervention.
Il est recommandé de reprendre les AVK aux posologies
habituellement reçues par le patient sans dose de charge.
Le traitement par héparine est interrompu après 2 INR
successifs en zone thérapeutique à 24 heures d’intervalle
FMC S. Talbi et al.

13
Revue Marocaine de Rhumatologie
Evaluation et gestion du risque hémorragique en rhumatologie interventionnelle.
Lorsque les AVK sont prescrits dans une autre indication
(en de heure des patients en ACFA, porteurs d’une
valve cardiaque mécanique ou ayant fait un épisode
thrombotique récent de moins d’un mois), nous utilisons
une HBPM à dose préventive [14]. Il est recommandé
d’utiliser l’enoxaparine administrée à raison d’une
injection sous-cutanée à 40 mg/j à midi, l’infiltration
étant pratiquée dans la matinée [14-17].
CONCLUSION
En cas d’un geste locale en rhumatologie interventionnelle
chez les patients sous anticoagulant la gestion du traitement
anticoagulant doit prendre en compte le classement
des risques hémorragiques des actes invasifs, du risque
thromboembolique et hémorragique de chaque situation,
Il est clair qu’une analyse des cas particuliers doit toujours
être effectuée, en gardant à l’esprit que la décision choisie
doit procurer les meilleurs bienfaits au patient.
DÉCLARATION D’INTÉRÊT
Les auteurs déclarent n’avoir aucun conflit d’intérêt.
RÉFÉRENCES
1. Levine MN, Raskob G, Beyth RJ, Kearon C, Schulman S.
Hemorrhagic complications of anticoagulant treatment : The
Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic
Therapy. Chest 2004; 126:287S-310S.
2. Patrono C, Coller B, Dalen JE, Fuster V, Gent M, Marker LA, et al.
Platelet-active drugs : the relationships among dose, effectiveness
and side effects. Chest 1998 ; 114: 470-88.
3. Samama M, Lecompte T. Est-il possible de réaliser une anesthésie
locorégionale rachidienne chez un patient traité avec un ou
plusieurs antithrombotiques ? STV 1999 ; 9 : 661-70.
4. Grateau G, Chauvenet L, Oudard S, Bachmeyer C, Capron L,
Horellou MH, et al. Complications hémorragiques sévères sous
héparine de bas poids moléculaire. À propos de 2 cas. Rev Med
Interne 1997 ; 5 : 411-5.
5. Thumboo J, O’Duffy JD. A prospective study of the safety of joint
and soft tissue aspirations and injections in patients taking warfarin
sodium. Arthritis Rheum 1998 ; 41 : 736-9.
6. Derlon A, Fiessinger JN. Utilisation des antivitamines K en pratique
médicale courante. STV 1993 ; 8 : 15-21.
7. Mejjad O, Favre S. Anticoagulants et antiagrégants plaquettaires:
l’infiltration est-elle possible, et comment ? La lettre du
Rhumatologue 1997 ; 237 : 12-3
8. Lemaire V, Charbonnier B, Gruel Y, et al. Joint injections in patients
on antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy: risk minimization. Joint
Bone Spine 2002;69:8–11.
9. Lemaire V, Charbonnier B, Gruel Y, et al. Joint injections in patients
on antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy: risk minimization. Joint
Bone Spine 2002;69:8–11.
10. Pincus KT, Spruill WJ, Parish RC. Effect of flurbiprofen and aspirin
on platelet aggregation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1991;10:935–8.
11. Brochier ML, for the Flurbiprofen French Trial. Evaluation of
flurbiprofen for prevention of reinfarction and reocclusion after
successful thrombolysis or angioplasty in acute myocardial
infarction. Eur Heart J 1993;14:951–7.
12. Montalescot G, Polle V, Collet JP, Leprince P, Bellanger A,
Gandjbakhch I, et al. Low molecular weight heparin after
mechanical heart valve replacement. Circulation 2000 ; 14 :
1083-6.
13. Arnaout MS, Kazma H, Khalil A, Shasha N, Nasrallah A, Karam
K, et al. Is there a safe anticoagulation protocol for pregnant
women with prosthetic valves ? Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 1998 ;
25 : 101-4.
14. Ansell J, Hirsh J, Dalen JE, Bussey H, Anderson DR, Poller L, et
al. Managing oral anticoagulant therapy. Sixth ACCP Consensus
Conference on Antithrombotic Therapy. Chest 2001 ; 119: 22-38.
15. Samama M, Cohen AT, Darmon JY, Desjardins L, Eldor A,
Janbon C, et al. A comparison of enoxaparin with placebo for
the prevention of venous thromboembolism in acutely ill medical
patients. N Engl J Med. 1999 ; 331 : 793-800.
16. Anne Godier, Gilles Pernod, Pierre Sié, pour le groupe de travail
des recommandations Chirurgies ou actes invasifs Chapitre IV
Sang Thrombose Vaisseaux 2008 ; 20: 84-102
17. Haute Autorité de Santé. Prise en charge des surdosages, des
situations à risque hémorragique et des accidents hémorragiques
chez les patients traités par antivitamines K en ville et en milieu
hospitalier. Avril 2008.
1
/
4
100%