REPORTED SPEECH – cf p174 + p206

REPORTED SPEECH
Le reported speech (discours indirect/discours rapporté) est utilisé lorsqu’on rapporte les paroles de quelqu’un.
QUELS SONT LES CHANGEMENT NECESSAIRES POUR PASSER DU DISCOURS DIRECT AU DISCOURS INDIRECT?
1. Verbe introducteur (say, tell, ask, explain, wonder...)
2. Changement des marqueurs de personnes ( pronoms personnels sujets et compléments, adjectifs et pronoms possessifs )
3. Changement des démonstratifs « this » et « these » qui se transforment en « that » et « those ».
4. Changement de l'adverbe de lieu « here » qui se transforme en « there ».
Si le verbe introducteur est au passé (said, told, asked, explained, wondered)
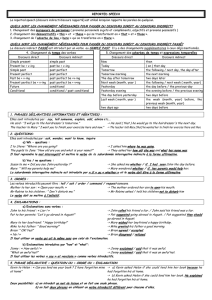
5. Changement du temps des verbes (tous les auxiliaires se mettent au passé, le simple past devient past perfect cf tableau 5)
6. Changement des adverbes de temps et expressions temporelles (cf tableau 6)
5. Changement du temps des verbes de la subordonnée
6. Changement des adverbes de temps et expressions temporelles
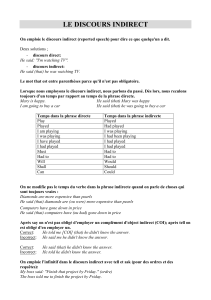
Discours direct
Discours indirect
Discours direct
Discours indirect
simple present (ex : likes)
simple past (liked)
now
then
simple past (ex : liked)
past perfect (ex : had liked)
today
( on ) that day
is/are
was/were
tomorrow
the following / next day, the day after
can
could
tomorrow morning
the next morning
will
would
next week (month, year )
the following / next week ( month, year)
must
had to
yesterday
the day before / the previous-day
may
might
last week ( month, year )
the week (month, year) before
two days ago
two days before
1. PHRASES DECLARATIVES (AFFIRMATIVES ET NEGATIVES) :
Elles sont introduites par : say, tell someone, explain, add, advise etc...
He said : "I will go to the hairdresser's tomorrow."
-> He said ( that ) he would go to the hairdresser's the next
day.
The teacher to Mary " I want you to finish your exercise here and now."
-> The teacher told Mary (that) he wanted her to finish her exercise there and then.
2. QUESTIONS:
Elles sont introduites par : ask, wonder, want to know, inquire
a) Wh - questions :
I to Steve: "Where are you going?
-> I asked him where he was going.
The pupils to Jane: "How old are you and what is your
name?"
-> They asked her how old she was and what her name was.
Il faut reprendre le mot interrogatif et mettre le verbe de la subordonnée interrogative indirecte à la forme affirmative.
b) Yes / no questions :
Susan to me « Did you see John yesterday ?"
-> She asked me whether / if I had seen John the day before.
Mary: " Will my parents help me"
-> Mary wondered whether / if her parents would help her.
La subordonnée interrogative indirecte est introduite par « if » ou « whether » et le verbe doit être à la forme
affirmative.
3. ORDRES :
Les verbes introductifs peuvent être : tell / ask / order / command / request someone
Mother to her son : « Open your mouth. »
-> The mother ordered her son to open his mouth.
Mr Robins to his children : " Don't disturb me."
-> Mr Robins asked / told his children not to disturb him
Le verbe doit se mettre à l'infinitif.
4. PHRASE DECLARATIVE + QUESTION
Kevin to Helen : « Can you lend me your book ? I have
forgotten mine at home"
-> a) Kevin asked Helen if she could tend him her book because he
had forgotten his at home.
-> b) Kevin asked Helen if she could lend him her book. He
explained he had forgotten his at home.
Deux possibilités: a) on introduit un mot de liaison et on fait une seule phrase.
b) on fait deux phrases en utilisant un verbe introductif différent pour chacune d'elles.
1
/
1
100%