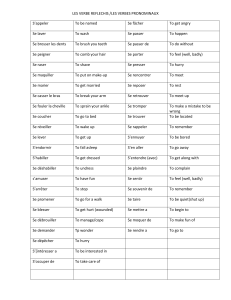
Reported speech - Sen
publicité

COURS D’ANGLAIS (classe de 4ème) Presented by Mr. Khazim Diop Academic year: 2011­2012 Reported speech On emploie le discours indirect (indirect speech) lorsqu’on rapport les paroles ou les pensées de quelqu’un sans les citer directement. IL y’a dans la proposition principle des verbes comme to say, to tell, to know, to think, to realize, etc. Quand ces verbes se conjuguent au passé, la concordance des temps se fait comme en français. Les guillemets disparaissent. (Voir tableau) Discours direct Discours indirect Simple Present “I work hard to succeed”, he said Simple Past He said that he worked hard to succeed Present continuous “We are watching Sanex”, the children said. Preterit “We won the match”, the players said. Present perfect “How long have you been her? “, he asked. Present perfect continuous “I have been reading “, Nabou said. Past continuous The children said that they were watching Sanex. Past Perfect. The players said that they had won the match Past perfect He wanted to know how long I had been there. Past perfect “The cat had killed the rat” jack said. Past perfect Jack said that the cat had killed the rat. Past perfect continuous Nabou said that she had been reading. Future Present Conditional “I won’t come again «The guest declared. The guest declared that he would not come again. Imperative form “Stay awhile” she said. Infinitive form She pleased me to stay awhile. COURS D’ANGLAIS (classe de 4ème) ● Les adverbes et les locutions changent: Today That day Now Then Here There Yesterday The day before/the previous day Last week (month, year…) The previous week (month, year…) Tomorrow The day after/ the net day Next year (week month…) The following year (week, month…) ● Lorsqu’on rapporte des questions avec les “Wh­questions, l’inversion disparait. Exemple: « where do you live? », he asked me­He wanted to know where I lived. S’il s’agit d’une yes/no question on fait appel à if ou whether. Attention à l’ordre des mots et à la forme du verbe dans les questions indirectes. Le sujet précède toujours le verbe. IL n’y a pas do/did. Exemples: “Is he Modou’s brother?”, she asked ­She asked if he was the brother of Modou “Will you come with us?”, she asked me­She asked me if I would come with them.