MTH 2301 Méthodes statistiques en ingénierie

1
Chapitre 5 distributions discrètes
distribution Bernoulli / binomiale
processus / distribution de Poisson
distribution géométrique
distribution hypergéométrique
Bernard CLÉMENT, PhD
APPLICATIONS
2 méthodes contrôle statistique de la qualité
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
cartes : np -carte p -carte c -carte u
« Acceptance Sampling »
plans d’échantillonnage pour
accepter ou rejeter des produits regroupés en lots
pas au
programme
MTH2302 Probabilités et méthodes statistiques
mais …
concepts
importants
pour un
ingénieur
1-23
23-43

2
distribution constante : c’est une distribution sans variabilité!
Bernard CLÉMENT, PhD MTH2302 Probabilités et méthodes statistiques
distribution Bernoulli
X = c avec probabilité = 1
E(X) = c Var(X) = 0
cX
prob
1
prob
X
0
1
phénomène à 2 résultats
résultat «Succès» «Echec»
noté S E
X 0 1
prob 1 -p p
0 ≤ p ≤ 1
p
1 - p
autre notation
θau lieu de p
E(X) = 0*(1-p) + 1*p = p
Var(X) = p *( 1 –p) ≤ 1/4
base pour distribution binomiale

3
Définition
X= nombre de succès dans une suite de n essais (échantillonnage)
de Bernoulli indépendants avec une probabilité commune de
succès θ
X ila v.a de Bernoulli associée au i ème essai i = 1, 2, …, n
X i= 1 avec probabilité θ ou X i = 0 avec probabilité 1 -θ
X1, X2,…, X nsont indépendantes,
X = ∑X iest appelée une variable aléatoire binomiale
notation :X~ b(n, θ) :Xsuit distribution binomiale paramètres (n, θ)
fonction de masse Statistica : BINOM(x ; θ ; n)
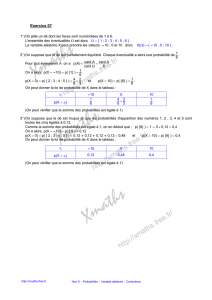
p(x) = P(X = x) = Cnxθx(1- θ) n – x x= 0 , 1 , …., n
fonction de répartition Statistica : IBINOM(x ; θ ;n)
x
F(x) = P(X ≤ x) = ∑Cnkθ k( 1-θ ) n - k besoin table
k = 0
moyenne = E(X) variance = Var(X) écart type = ET(X)
E[X] = n θVar[X] = n θ( 1 -θ) ET[X] = [n θ( 1 -θ )] 0,5
distribution BINOMIALE : distribution résultant de l’échantillonnage
(l’observation) d’une distribution Bernoulli
Bernard CLÉMENT, PhD MTH2302 Probabilités et méthodes statistiques

4
Distribution
Binomiale
Table
Fonction
Répartition
FX(x)
Bernard CLÉMENT, PhD

5
n: taille de l’échantillon = nombre d’observations
paramètre contrôlable connu ou à déterminer
θ : paramètre généralement inconnu
comment estimer θ ? choix de n ?
réponse : l’estimation de θ est θ = X / n c’est un moyenne
où X = nombre succès en n essais de Bernoulli
remarque :le symbole au dessus d’un paramètre indique une estimation
propriétés
a) erreur systématique = écart entre θ et E ( θ)
^
= E ( θ) -θ = E ( X / n ) –θ = ( E(X) / n ) -θ = ( n θ / n) -θ = 0
b) erreur aléatoire = Var ( θ)
= Var( θ) = θ ( 1 –θ ) / n ≤ 0,25 / n pour tout θ
remarque : l’estimation statistique vue au chapitre 10
Bernard CLÉMENT, PhD
distribution B I N O M I A L E
MTH2302 Probabilités et méthodes statistiques
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
1
/
44
100%