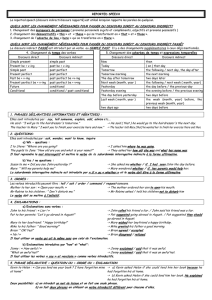
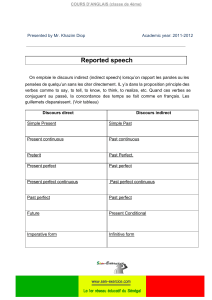
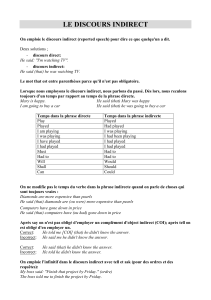
N. GILLES
TD L2
LEADERSHIP
« We all work together as a team. And that means you do everything I say”
Michael Caine, British film actor (in the film The Italian Job)
A)- VOCABULARY:
I)- Which of the adjectives below would you use to describe an ideal leader? Give reasons for your
choice. What adjectives would you add?
Decisive informal accessible motivating charismatic
Passionate thoughtful impulsive cautious adventurous
Flexible opportunistic aggressive energetic persuasive
Open magnetic ruthless
II)- Can you think of adjectives with opposite meanings to the ones above?
Decisive – indecisive
III)- Read what some commentators think about leadership. Do you agree with their ideas?
Leadership is not magnetic personality- that can just as well be a glib tongue. It is not “making friends
and influencing people” – that is flattery. Leadership is lifting a person’s vision to higher things, the
raising of a person’s performance to a higher standard, the building of personality beyond its normal
limitations.
(Peter F. Drucker, author and management theorist)
A leader is best when people barely know he exists, not so good when people obey and acclaim him, worse
when they despise him... But of a good leader who talks little when his work is done, his aim fulfilled, they will
say, “We did it ourselves”.
(Anonymous)
Good leaders make people feel they’re at the heart of things, not at the periphery. Everyone feels he or
she makes a difference to the success of the organisation. When that happens, people feel centred and
that gives their work meaning.
(Warren Bennis, author and professor of business administration.)

If there is a trait that does characterise leaders it is opportunism. Leaders are people who seize
opportunity and take risks. Leadership then seems to be a matter of personality.
(John Viney, former Chairman of Heidrick and Struggles, top recruitment consultants.)
B)- VIDEO:
Watch the video about leadership and answer the questions:
« A leader is one who knows the way, goes the way & …shows the way » - John C Maxwell
1). What definition of leadership do they give?
Democratic bioctratic and autocratic
Refers to the art of motivation people in an organization and communication to advice
common goals
An art of communication ideas effectively to others and encouraging them to take
responsibilities
2). It’s important that leaders must have certain critical thinking skills
3). Leadership styles:
a). democratic leadership:
The leaders make …or break decision democratically, based on their team’s …… opinion
and …………………………………feed back …………. Every opinion………comes is
important even if the leader makes the final décision
b). autocratic ………………………………… leadership: It is the.
…………………………opposite………………… of the first ont. The opinions of employees
are not …considered and leaders expect others to
adhere…………………………………………… to their decisions. On the long run, it is not
sustainable
c). ……laisser faire ………………………………… leadership: It is the least
…………………………………………… style and leaders ensure that the.
…………………………………………… lies with the employees. It can
……………………empower……………………… but it may also limit
……………………development ………………………
d). ………………strategic ………………………… leadership: It acts as a
………………………bridge…………………… between the senior team and the employees.
Bot executive …interest………………………………………… and working
……………………………conditions……………… are
…stable………………………………………… when a decision is made.
e). …………………………transformation ………………… leadership: it aims at
………………………transforming…………………… and improving
……………………functions……………………… and

…………………capabilities…………………………. Leaders ask their employees to push
their ……boundaries……………………………………… constantly.
f). …transaction ………………………………………… leadership: it is based on the
……………………………action ……………… and
…………………………reward………………… concept. Employees get an
………………………………incentive …………… or a bonus if they achieve a
……………………………target……………… set by the company.
g). …………………coach style ………………………… leadership: It focuses on larger
…………………………growth ………………… while encouraging
……………………individual……………………… team members to focus on their
…………………………………………strength… and
……………………………………talent………. The focus is on the individual.
h). …………………bureaucratic ………………………… leadership: Even is leaders listen
to their employees and their opinions, they may negate
…………………………………………… it or
…………………………rejected………………… it if they go against the company’s
……………………………ethos……………… or …policy…………………………………
C)- READING: The Founder of Ikea:
TEXT 1:
I)- The following article is about Ingvar Kamprad, the founder of Ikea, the home furnishings retail
giant. Which of the following do you expect Ingvar to do or to be?
- drive an old car - be careful with money:
- travel first class - dress smartly
- be dyslexic - love detail
- be formal - make short-term decisions
II)- Read the article to check your answers:
III)- What winning formula is behind Ikea’s success?
Make affordable well designed furniture available to the masses
IV)- Read the article again and make notes about Mr Kamprad under these headings:
Wealth: very rich 13.4bn
Personality: charismatic humble private
Lifestyle: extremely modest life style
Leadership style: setting a good example
Overdraft u spend more money than u have
V)- Find words or phrases in the article that match these definitions:

a). An awareness of the price of things cost consciousness
b). The feeling you have when you are part of a group of people who have a close relationship with
each other togetherness.
c). A relaxed and friendly situation without too many rules of correct behavior informal
d). The lack of a system in an organization where a group of people have power or control
e). An extremely strong focus on every small fact or piece of information: .obsessive.
he was good at choosing people who work with him
deceive
e ad good feeling
reluctant to stop working: I don’t won’t to stop working
TEXT

III)- What winning formula is behind Ikea’s success?
IV)- Read the article again and make notes about Mr Kamprad under these headings:
Wealth:
Personality:
Lifestyle:
Leadership style:
V)- Find words or phrases in the article that match these definitions:
a). An awareness of the price of things
.................................................................................................................
b). The feeling you have when you are part of a group of people who have a close relationship with
each other .................................................................................................................
c). A relaxed and friendly situation without too many rules of correct behaviour
.................................................................................................................
d). The lack of a system in an organisation where a group of people have power or control
.................................................................................................................
e). An extremely strong focus on every small fact or piece of information:
.................................................................................................................
VI)- Discuss these questions:
1). What, in your opinion, are the strengths and weaknesses of Ingvar Kamprad?
2). Would you like to work for him?
3). When is the correct time for a leader to leave his or her company?
TEXT 2:
Ingvar Kamprad’s leadership style
Ingvar Kamprad is the perfect example of a charismatic leader. IKEA is the perfect example of a
successful family business. We need to question whether in a family business; the leadership style is
influenced by the company culture, structure, and business model/operational strategy, or the other
way around.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
1
/
9
100%