L’automesure tensionnelle est-elle utile en transplantation rénale ? »

Le Courrier de la Transplantation - Vol. XI - n° 1 - janvier-février-mars 2011 25
Dossier thématique
Transplantation
rénale
L’automesure tensionnelle est-elle utile
en transplantation rénale ?
Home blood pressure monitoring in renal transplant recipients
Rebecca Sberro-Soussan, Éric Thervet*
L
’hypertension artérielle (HTA), fréquente chez le
patient transplanté – en particulier le transplanté
rénal –, est associée à une détérioration de la
fonction du greffon et de la survie du patient (1). Son
diagnostic repose traditionnellement sur la mesure de
la pression artérielle (PA), en consultation ou à l’hôpital.
Cependant, chez la majorité des individus, il est connu
que la PA est plus élevée lors de la consultation médicale
que lorsqu’ils sont à leur domicile. Ainsi, concernant la
population générale, il est désormais reconnu que la
surveillance de la PA effectuée en dehors de la consul-
tation fournit une meilleure information pronostique
que celle pratiquée par le médecin au moment de la
consultation (2-4). Une revue récente a d’ailleurs souligné
l’intérêt de la surveillance effectuée à domicile chez les
patients atteints d’insuffisance rénale chronique (5).
Les différences de valeurs de PA obtenues par les
méthodes conventionnelles réalisées en consultation
ont donc conduit au développement de méthodes
complémentaires telles que la mesure ambulatoire de
la PA (MAPA) et l’automesure tensionnelle. Réalisée par le
patient lui-même à son domicile avec un appareil homo-
logué, l’automesure tensionnelle consiste à recueillir la PA
pendant 4 jours consécutifs, matin et soir, en 3 mesures
espacées chacune d’un repos de plus de 2 minutes.
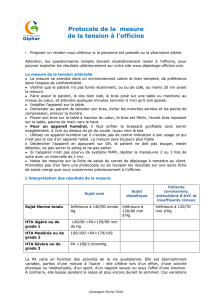
Les limites définissant la PA normale diffèrent donc
selon la méthode : 140/90 mmHg pour la PA en consul-
tation et 135/85 mmHg pour la MAPA et l’automesure
tensionnelle. La comparaison des résultats obtenus par
les différentes méthodes permet de classer les patients
en 4 groupes (6) :
✓
groupe des normotendus (ou “PA contrôlée”) lorsque
la PA est inférieure à la limite définie à la maison et en
consultation ;
✓
groupe des hypertendus (ou “PA non contrôlée”)
lorsque la PA est supérieure ou égale à la limite à la
maison et en consultation ;
✓
groupe “HTA blouse blanche” lorsque la PA est supé-
rieure ou égale à la limite en consultation et inférieure
à la limite à la maison ;
✓groupe “HTA masquée” lorsque la PA est inférieure
à la limite en consultation et supérieure ou égale à la
limite à la maison.
Ces dernières années, l’HTA masquée a particulièrement
retenu l’attention, d’une part en raison de sa prévalence
(7 à 45 %) [7], d’autre part parce qu’elle est associée
Résumé
Summary
»»
L’hypertension artérielle (HTA) est associée a une forte morbi-
mortalité chez le patient transplanté rénal. Son diagnostic est le
plus souvent posé en consultation. Dans la population générale,
l’automesure tensionnelle est supérieure à la pression artérielle
mesurée en consultation pour identifier les vrais hypertendus et les
répondeurs au traitement. Quel est son rôle dans la détermination
et la prise en charge de l’HTA chez le transplanté rénal ? Nous
soulignons ici son accessibilité et son utilité dans la détermination
du profil tensionnel du transplanté, en particulier le dépistage de
l’HTA blouse blanche et de l’HTA masquée.
Mots-clés : Automesure tensionnelle – Transplantation rénale –
HTA – HTA masquée.
Hypertension in renal transplant recipients is a widespread
condition associated with high mortality risk. The diagnostic is
made at office. Home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) was
found to be superior to office blood pressure (BP) in identifying
true hypertensive and responders to treatment. What is the
utility of HBPM, in the assessment and decision-making
processes of post-transplant hypertension and blood pressure
profile? HBPM may help to improve HTA management
and screen white-coat and masked hypertension in renal
transplant recipients.
Keywords: Home blood pressure monitoring – Kidney trans-
plantation – HTA – Masked HTA.
*Service de transplanta-
tion rénale, hôpital Necker ;
service de néphrologie,
hôpital européen Georges-
Pompidou ; université
Paris-Descartes.

Le Courrier de la Transplantation - Vol. XI - n° 1 - janvier-février-mars 2011
28
Dossier thématique
Transplantation
rénale
à un mauvais pronostic cardio-vasculaire (8-10). Sa
prévalence et son pronostic font de l’HTA masquée
un problème de santé publique. Il est donc important
de la reconnaître et de la traiter comme une HTA non
contrôlée. L’automesure est un excellent moyen dia-
gnostique pour la dépister : elle permet une mesure de
qualité tout en étant moins onéreuse et mieux acceptée
par les patients que la MAPA.
Par ailleurs, la surveillance en ambulatoire reposant sur
plusieurs mesures, elle permet de mettre en évidence
la variabilité de la PA. Des études récentes montrent
qu’une HTA épisodique ainsi que des valeurs de PA
variables d’une consultation à une autre constituent
des facteurs de mauvais pronostic cardio-vasculaire,
même si la PA moyenne est normale. D’ailleurs, les
bénéfices des traitements antihypertenseurs étaient
en partie dus à la réduction de la variabilité de la
PA (11, 12). C’est pourquoi il est actuellement recom-
mandé de réaliser une automesure ou une MAPA chez
les patients dont la PA varie en consultation (13). En
utilisant cette méthode, une étude incluant 68 patients
transplantés rénaux montre que le contrôle de la PA
n’est pas optimal chez un tiers des patients et que les
mesures de PA en consultation sous-estiment la qualité
et l’efficacité des traitements antihypertenseurs (14).
Parmi les différentes méthodes de mesure de la PA
(automesure, MAPA, par une infirmière ou un médecin),
l’automesure est l’option la plus plébiscitée par les
patients ; la mesure ambulatoire (MAPA) est perçue
comme étant inconfortable et perturbant l’activité et
le sommeil (15, 16). Cependant, à côté des nombreuses
études concernant la MAPA chez les patients transplantés
rénaux, peu de données sont disponibles sur l’autome-
sure tensionnelle dans cette population spécifique (17).
Nous avons conduit une étude portant sur l’automesure
tensionnelle, son accessibilité, sa capacité à diagnosti-
quer l’hypertension artérielle, l’effet “blouse blanche”
et l’HTA masquée. Cette étude prospective observa-
tionnelle a inclus 87 patients transplantés rénaux en
situation stable, c’est-à-dire transplantés depuis plus
d’un an, avec une fonction rénale stable sur les 6 der-
niers mois (définie par une variabilité de la créatinine de
moins de 20 %), et un traitement immunosuppresseur
non modifié depuis les 6 derniers mois (en particulier,
non-modification de la dose quotidienne d’anticalci-
neurines et des taux sanguins). Par ailleurs, le traitement
antihypertenseur ne devait pas avoir été modifié durant
les 6 derniers mois si le patient était traité avant l’étude.
Les patients n’étaient pas inclus si leur PA systolique
était inferieure à 100 mmHg ou supérieure à 190 mmHg.
La PA était recueillie par le même appareil en consulta-
tion et à la maison ; elle était mesurée initialement par
le médecin, puis par l’infirmière de consultation, qui
expliquait au patient le fonctionnement de l’appareil. À
la fin de la consultation, l’appareil était prêté au patient,
selon les indications détaillées précédemment. Après
cette période de 4 jours, le patient rapportait l’appareil
avec les mesures de PA collectées par écrit. La PA en
automesure était définie par la moyenne des mesures
obtenues pour un individu donné (4 le matin et 4 le soir).
Parmi les 87 patients inclus, 81 ont pu être analysés
(3 patients n’ont pas remis l’appareil et 3 autres ont mal
réalisé la mesure). Aucun ne s’est plaint de la difficulté
de la méthode. Le délai moyen après transplantation
était de 3,08 années, s’étalant de 1 à 31 ans. À l’inclu-
sion, la créatinine plasmatique moyenne était de 137 ±
39 µmol/l. Le traitement immunosuppresseur était
variable, avec 88 % de patients recevant des anticalci-
neurines. Le nombre moyen de classes de traitements
antihypertenseurs était de 1,5 ± 1. Parmi les patients
recevant un traitement antihypertenseur, 16 ne rece-
vaient aucun traitement, 24 étaient en monothérapie,
28 en bithérapie, 11 en trithérapie et 2 en quadrithé-
rapie antihypertensive ; 62,8 % des patients recevaient
des bêta-bloquants, 53 % des bloqueurs du système
rénine-angiotensine, et 28,2 % des inhibiteurs calciques.
Les valeurs de PA reportées et celles retrouvées dans la
mémoire de l’appareil étaient identiques. Les PA systo-
lique et diastolique moyennes prises par le médecin en
consultation étaient respectivement de 139 ± 14 mmHg
et 83 ± 10 mmHg. Celles prises par l’infirmière étaient
respectivement de 134 ± 15 mmHg et 82 ± 9 mmHg. Les
2 mesures étaient concordantes chez 73 % des patients
(avec 29 % d’hypertendus et 44 % de patients normo-
tendus). Il faut noter que 19 % des patients étaient
hypertendus chez le médecin alors qu’ils n’étaient plus
que 8 % lorsque la PA était mesurée par l’infirmière.
Concernant les relevés obtenus en automesure, les PA
systolique et diastolique moyennes étaient de 133 ± 79
et 79 ± 8 mmHg respectivement. La PA en consultation
et celle en automesure étaient corrélées entre elles
(r
2
= 0,61 ; p < 0,01). Cependant, seuls 58 % des patients
étaient classés dans le même groupe par les 2 méthodes
(28 % de PA contrôlée et 30 % de PA non contrôlée).
Ainsi, 43,2 % des patients contrôlés en consultation
présentaient une HTA masquée. Les facteurs de risque
associés aux différents profils d’HTA étaient, pour l’HTA
non contrôlée, un âge élevé, une HbA1c élevée, un
nombre élevé d’antidiabétiques oraux et le nombre
d’antihypertenseurs. Concernant l’HTA blouse blanche,
seul le nombre d’antihypertenseurs était associé à un
surrisque. Aucune association n’a été mise en évidence
entre le profil d’HTA et la fonction rénale. Cependant,
les patients présentant une HTA persistante avaient

Le Courrier de la Transplantation - Vol. XI - n° 1 - janvier-février-mars 2011 29
une protéinurie plus élevée que les autres populations.
Les événements cardio-vasculaires sont la première cause
de décès chez les patients transplantés rénaux. Parmi les
différents facteurs de risque, le mauvais contrôle de la
PA est associé aux risques de dysfonction du greffon et
de décès du patient (1, 18-20). Bien que la prévalence
de l’HTA soit élevée, les données sur la vraie prévalence
exacte, obtenues par la PA à domicile – qui est l’étalon
pour le diagnostic et le suivi – restent succinctes (21).
Nous avons montré que, même si la PA moyenne est
bien contrôlée, il existe une discordance entre la PA en
automesure et la PA en consultation (chez environ 42 %
des patients). Cela met en évidence les phénomènes
d’HTA masquée et d’HTA blouse blanche. Aucun autre
marqueur ne peut discriminer les patients avec des
PA concordantes selon les 2 méthodes des 2 derniers
profils. Il est donc utile de pratiquer les 2 méthodes
de mesure. Par ailleurs, l’étude souligne l’intérêt des
mesures de PA par l’infirmière de consultation, lesquelles
améliorent la précision du diagnostic en diminuant
l’effet blouse blanche.
La question principale était de démontrer l’intérêt de
l’automesure chez les patients transplantés rénaux.
Nous avons montré que cette méthode est très acces-
sible, permettant une compliance excellente. Stenehjem
avait déjà démontré que l’automesure tensionnelle était
supérieure à la mesure de la PA prise en consultation
dans l’estimation du contrôle de la PA chez les patients
transplantés rénaux avec détérioration de la fonction
rénale (17). En effet, elle permet un contrôle par un
plus grand nombre de mesures (21), mais aussi par la
diminution de l’effet blouse blanche, qui est un facteur
de mauvais pronostic. Un autre intérêt serait d’estimer
la variabilité de la PA, nouveau facteur à prendre en
compte dans ce type d’étude (11, 12).
Chez nos patients, la PA non contrôlée était associée
à un mauvais contrôle glycémique dû à une mauvaise
compliance pour les 2 types de médication antidiabé-
tique et antihypertensive.
Un autre avantage de l’automesure est la détection de
l’HTA blouse blanche et de l’HTA masquée. En raison de
sa difficulté à être dépistée, cette dernière semble être
un facteur de risque d’insuffisance rénale chronique
et d’événements cardio-vasculaires (22). Les variables
associées à l’HTA masquée dans la population non
transplantée sont : une PA en consultation supérieure
à 130 mmHg, le sexe masculin, l’âge, un traitement
comprenant plus de 2 antihypertenseurs et un indice
de masse corporelle (IMC) supérieur à 25 (23). La taille
de notre population nous a permis de mettre en évi-
dence que les 2 facteurs de risque étaient l’âge et le
nombre d’antihypertenseurs ; aucune relation avec
l’âge de la transplantation n’a été montrée. Bien que
l’automesure soit facile à utiliser et peu onéreuse,
certains médecins y sont encore réticents. De plus, il
serait coûteux de recommander l’automesure pour
tous les patients. De ce fait, on pourrait la conseiller
aux patients à risque d’HTA masquée dans notre popu-
lation, c’est-à-dire aux patients âgés et à ceux traités
par un nombre élevé d’antihypertenseurs.
Enfin, notre étude montre que la protéinurie est plus
élevée chez les patients avec une PA non contrôlée et
une HTA masquée, confirmant ainsi les données de
Paoletti, qui montre que la réalisation d’une MAPA chez
le patient transplanté rénal permet de dépister des
hypertensions associées à des protéinuries (20).
Conclusion
Chez les transplantés rénaux, l’automesure tension-
nelle est bien accueillie et acceptée, permettant une
meilleure adhérence au traitement. Avec 42 % de dis-
cordance entre les 2 méthodes de mesure, elle permet
de mieux déterminer le profil tensionnel en détectant
l’HTA blouse blanche et l’HTA masquée. Un suivi mené
sur une plus grande population mettrait en évidence
les effets négatifs, à la fois rénaux et cardio-vasculaires,
de chaque profil d’HTA. Il reste enfin à démontrer que
l’adaptation du traitement aux résultats de l’automesure
permet une meilleure prévention cardio-vasculaire
qu’une adaptation du traitement aux résultats de la
PA en consultation.
◾
L’automesure tensionnelle est-elle utile en transplantation rénale ?

Le Courrier de la Transplantation - Vol. XI - n° 1 - janvier-février-mars 2011
30
Dossier thématique
Transplantation
rénale
1.
Opelz G, Wujciak T, Ritz E. Association of
chronic kidney graft failure with recipient
blood pressure. Collaborative Transplant
Study. Kidney Int 1998;53:217-22.
2.
Pickering T. Recommendations for the
use of home (self) and ambulatory blood
pressure monitoring. American Society of
Hypertension ad hoc panel. Am J Hypertens
1996;9:1-11.
3. Sakuma M, Imai Y, Nagai K et al.
Reproducibility of home blood pressure
measurements over a 1-year period. Am
J Hypertens 1997;10:798-803.
4. Lenfant C, Chobanian AV, Jones DW,
Roccella EJ. Seventh report of the Joint
National Committee on the Prevention,
Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment
of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7): resetting
the hypertension sails. Hypertension
2003;41:1178-9.
5. Andersen MJ, Khawandi W, Agarwal R.
Home blood pressure monitoring in CKD.
Am J Kidney Dis 2005;45:994-1001.
6. Mallion JM, Genes N, Vaur L et al.
Detection of masked hypertension by
home blood pressure measurement: is the
number of measurements an important
issue? Blood Press Monit 2004;9:301-5.
7. Bombelli M, Sega R, Facchetti R et al.
Prevalence and clinical significance of a
greater ambulatory versus office blood
pressure (“reversed white coat” condi-
tion) in a general population. J Hypertens
2005;23:513-20.
8. Bjorklund K, Lind L, Zethelius B, Andren B,
Lithell H. Isolated ambulatory hypertension
predicts cardiovascular morbidity in elderly
men. Circulation 2003;107:1297-302.
9. Bobrie G, Chatellier G, Genes N et al.
Cardiovascular prognosis of “masked
hypertension” detected by blood pressure
self-measurement in elderly treated hyper-
tensive patients. Jama 2004;291:1342-9.
10. Pierdomenico SD, Lapenna D, Bucci A
et al. Cardiovascular outcome in treated
hypertensive patients with responder, mas-
ked, false resistant, and true resistant hyper-
tension. Am J Hypertens 2005;18:1422-8.
11.
Rothwell PM. Limitations of the usual
blood-pressure hypothesis and importance
of variability, instability, and episodic
hypertension. Lancet 2010;375:938-48.
12.
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E et
al. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit
variability, maximum systolic blood pres-
sure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet
2010;375:895-905.
13. O’Brien E, Asmar R, Beilin L et al.
Practice guidelines of the European Society
of Hypertension for clinic, ambulatory
and self blood pressure measurement.
J Hypertens 2005;23:697-701.
14. Covic A, Goldsmith DJ, Gusbeth-
Tatomir P et al. What added value does
ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
brings to the management of post renal
transplantation hypertension? Rev Med
Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2003;107:89-97.
15. Little P, Barnett J, Barnsley L, Marjoram
J, Fitzgerald-Barron A, Mant D. Comparison
of acceptability of and preferences for diffe-
rent methods of measuring blood pressure
in primary care. BMJ 2002;325:258-9.
16. Little P, Barnett J, Barnsley L, Marjoram
J, Fitzgerald-Barron A, Mant D. Comparison
of agreement between different measures
of blood pressure in primary care and
daytime ambulatory blood pressure. BMJ
2002;325:254.
17. Stenehjem AE, Gudmundsdottir H, Os I.
Office blood pressure measurements over-
estimate blood pressure control in renal
transplant patients. Blood Press Monit
2006;11:125-33.
18.
Mange KC, Cizman B, Joffe M, Feldman
HI. Arterial hypertension and renal allograft
survival. Jama 2000;283:633-8.
19. Fernandez-Fresnedo G, Palomar R
et al. Hypertension and long-term renal
allograft survival: effect of early glomeru-
lar filtration rate. Nephrol Dial Transplant
2001;16:105-9.
20. Paoletti E, Gherzi M, Amidone M,
Massarino F, Cannella G. Association
of arterial hypertension with renal
target organ damage in kidney trans-
plant recipients: the predictive role of
ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Transplantation 2009;87:1864-9.
21.
Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I et al. Home
blood pressure measurement has a
stronger predictive power for mortality
than does screening blood pressure mea-
surement: a population-based obser-
vation in Ohasama, Japan. J Hypertens
1998;16:971-5.
22.
Bobrie G, Clerson P, Menard J, Postel-
Vinay N, Chatellier G, Plouin PF. Masked
hypertension: a systematic review.
J Hypertens 2008;26:1715-25.
23. Obara T, Ohkubo T, Funahashi J et
al. Isolated uncontrolled hypertension
at home and in the office among treated
hypertensive patients from the J-HOME
study. J Hypertens 2005;23:1653-60.
Références
bibliographiques
Résumé
Ce compte-rendu a été réalisé sous la seule responsabilité
du coordonnateur, des auteurs et du directeur de la publication
qui sont garants de l’objectivité de cette publication.
SITE RÉSERVÉ AUX PROFESSIONNELS DE LA SANTÉ
Philadelphie,
30 avril-4 mai 2011
American Transplant Congress
Coordonnateur:
Pr Éric Rondeau, Paris
Recevez en direct de l’ATC
les temps forts du congrès
sur simple demande à :
clariviere@edimark.fr
Accédez au compte-rendu
présenté sous forme de brèves
et d’interviews d’experts,
en vous connectant sur
www.edimark.fr/ejournaux/ATC/2011/
“Attention, ceci est un compte-rendu de congrès et/ou résumés des communications
de congrès dont l’objectif est de fournir des informations sur l’état actuel de la recherche ;
ainsi, les données présentées sont susceptibles de ne pas être validées par la Commission
d’AMM et ne doivent donc pas être mises en pratique.”
1
/
4
100%






![EXII Exploitation d’une installation industrielle Installations haute tension [nouvelle version]](http://s1.studylibfr.com/store/data/008500893_1-ce1bcbfa853c7dcb5fe9f0d1673b72f8-300x300.png)
