cours-43 ( PDF

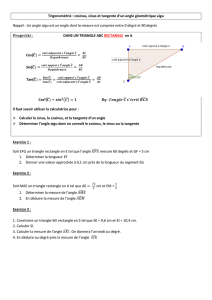
Chapitre LCALCULER UNE LONGUEUR AVEC LA TRIGONOMETRIE 3ème
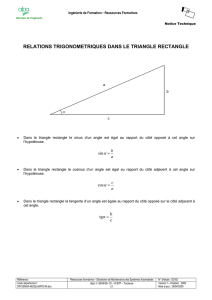
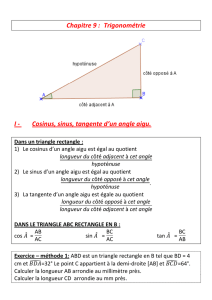
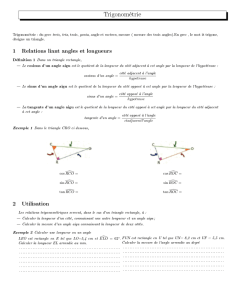
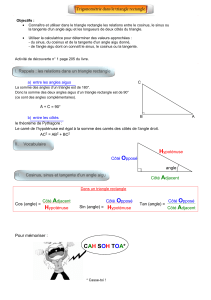
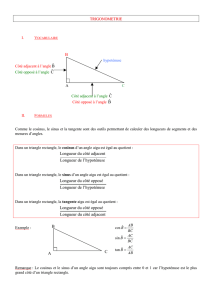
I. Cosinus d'un angle aigu:
Définition: Dans un triangle rectangle, le cosinus d'un angle aigu est égal au quotient du
côté adjacent à l’angle par l’hypoténuse.
Ex:
Dans le triangle BUT rectangle en U :
cos UBT = UB
BT
Rq : Dans ce même triangle rectangle, on a : cos UTB = UT
BT
Propriété:Le cosinus d'un angle aigu est toujours
compris entre 0 et 1
.
II. Sinus d'un angle aigu:
Définition : Dans un triangle rectangle, le sinus d'un angle aigu est égal au quotient du
côté opposé à l’angle par l’hypoténuse.
Ex:
Dans le triangle MAP rectangle en A:
sin MPA = MA
MP
Rq : Dans ce même triangle rectangle, on a sin AMP = AP
MP
Propriété : Le sinus d’un angle aigu est toujours
compris entre 0 et 1
.
III. Tangente d'un angle aigu:
Définition : Dans un triangle rectangle, la tangente d'un angle aigu est égale au quotient du
côté opposé à l’angle par le côté adjacent à l’angle.
Ex:.
Côté opposé Dans le triangle PLI rectangle en L :
à l'angle PIL tan PIL = LP
LI
Côté adjacent à l'angle PIL.
Rq : Dans ce même triangle rectangle, on a : tan LPI = LI
LP
Propriété : La tangente d’un angle aigu est toujours
strictement positive
.
A
M
P
T
U B
L
P
I
Hypoténuse
Côté opposé
à l'angle MPA.
Hypoté
nuse
Côté adjacent à l’angle UBT

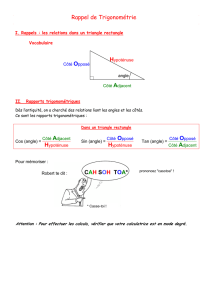
IV. Utiliser les rapports trigonométriques :
Moyen mémo technique pour mémoriser les 3 formules : SOH CAH TOA
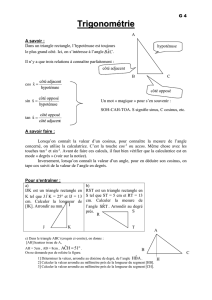
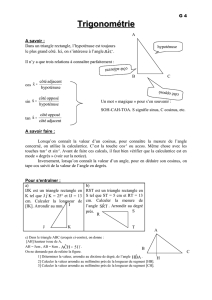
1DOS est un triangle rectangle en D tel que : SO = 4 cm et DOS = 40°. Déterminer la valeur exacte puis
arrondie au millimètre près de DO.
On connait la mesure de DOS et l’hypoténuse.
On cherche le côté adjacent à DOS.
→ On va utiliser le cosinus de DOS
Dans le triangle DOS rectangle en D: cos DOS = DO
OS
cos 40° = DO
4
4 × cos 40° = DO
3,1 cm ≈ DO
2ILE est un triangle rectangle en I tel que : IE = 3 cm et ILE = 58°. Déterminer la valeur arrondie au
millimètre près de la longueur LE.
On connait la mesure de ILE et son côté opposé.
On cherche l’hypoténuse.
→ On va utiliser le sinus de ILE.
Dans le triangle ILE rectangle en I: sin ILE = IE
EL
sin 58° = 3
EL
3
sin 58° = EL
3,5 cm ≈ EL
3ABC est un triangle rectangle en B tel que : AB = 15 m et BAC= 8°. Calculer la longueur BC
(arrondir le résultat au centimètre près).
On connait la mesure de BAC et son côté adjacent.
On cherche le côté opposé à BAC.
→ On va utiliser la tangente de BAC
Dans le triangle ABC rectangle en B : tan BAC = BC
BA
tan 8° = BC
15
BC = 15 × tan 8°
BC ≈ 2,11 m.
1
/
2
100%