Verbes : -‐ayer et

FICHES'DE'REVISION'
CONTRÔLE'1!'
'
Verbes'–ayer'&'9uyer'
Le'présent''
L’impératif'
Infinitifs'présents'et'passes'
Faire'causatif'
'
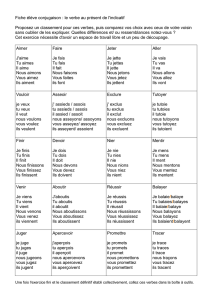
Verbes!:!(ayer!et!(uyer!
'
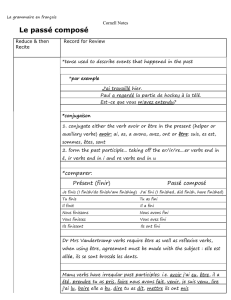
Il'y'a'deux'façons'pour'conjuguer'les'mots'qui'terminent'dans'–uyer'et'–ayer!
'
Nous'et'vous'formes'sont'différents'que'le'reste'des'formes'dans'le'présent,'et'ont'seulement'
façons'pour'la'conjugaison.'
'
Exemple':'Balayer,'«'to'sweep'»'
'
Présent!!
!
Je'balaie'(balaye)'
Nous'balayons'
Tu'balaies'(balayes)'
Vous'balayez'
Il/elle'balaie'(balaye)'
Ils/elles'balaient'(balayent)'
'
Subjonctif!
!
Je'balaie'(balaye)!
Nous'balayions'
Tu'balaies'(balayes)!
Vous'balayiez'
Il/elle'balaie'(balaye)!
Ils/elles'balaient'(balayent)'
'
Future!
!
Je'balaierai'(balayerai)'
Nous'balaierons'(balayerons)'
Tu'balaieras'(balayeras)'
Vous'balaierez'(balayerez)'
Il/elle'balaiera'(balayera)'
Ils/elles'balaieront'(balayeront)'
'
Conditionnel!!
!
Je'balaierais'(balayerais)'
Nous'balaierions'(balayerions)'
Tu'balaierais'(balayerais)'
Vous'balaieriez'(balayeriez)'
Il/elle'balaierait'(balayerait)'
Ils/elles'balaieraient'(balayeraient)'
'
Toutes'temps'du'verbe'pour'les'verbes'avec'–uyer'changement'«'y'»'à'«'i'»'pour'les'formes'je,'
tu,'il/elle,'et'ils/elles'
'
'
Exemple':'Essuyer,'to'swipe'
'

Présent!!
!
J’essuie'
Nous'essuyons'
Tu'essuies'
Vous'essuyez'
Il/elle'essuie'
Ils/elles'essuient'
'
Subjonctif!
!
J’essuie'
Nous'essuyions'
Tu'essuies'
Vous'essuyiez'
Il/elle'essuie'
Ils/elles'essuient'
'
Pour'le'future'et'conditionnel,'vous'conjuguez'avec'un'«'i'»'pour'toutes'ses'formes.''
'
''
'
II.!Présent!Indicatif!''
'
En'anglais….'
The'present'tense'has'multiple'uses,'which'are'listed'below':'
•!To'tell'what'is'happening'at'the'moment'
•!Make'generalizations'
•!Indicate….'
o!What'will'happen'in'the'near'future'(including'using'aller'+'infinitive)'
o!What'just'happened'(using'venir'+'infinitive)'
o!A'continuous'action'that'started'in'the'past'but'is'still'going'on'
'
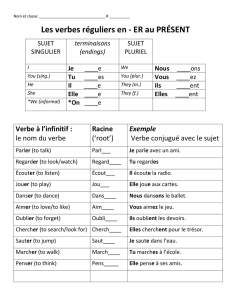
9er'verbs'conjugation'
'
using'the'example'écouter':'take'off'the'«'er'»'ending'and'apply'the'following'endings':'
(e!
(ons!
(es!
9ez'
(e!
9ent'
''
'
Exceptions':'sensitive'verbs'such'as'remplacer'and'manger,'pronunciation'would'change.'To'
prevent'that…..'
'
9GER'verbs':'Nous'form':'add'an'«'e'»'before'«'ons'»''
Ex!:!mangeons!
'
9CER'verbs':'nous'form':'add'a'cédille'«'ç'»'before'«'ons'»'
Ex!:!remplaçons!!
'
Verbs''such'as'APPELER'and'JETER'allow'for'double'consonants'in'the'je,'tu,'il/elle,'and'ils/elles'

'
Ex:!J’appelle!et!je!jette!vs.!nous!appelons!et!nous!jetons!
'
Verbs'like'acheter'change'the'first'«e»'to'«è»'in'the'je,'tu,'il/elle,'and'ils/elles'form.'The'nous'
and'vous'forms'remain'the'same'without'the'accent'grave'
'
Ex:!Tu!achètes!vs.!vous!achetez!
''
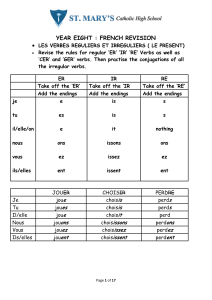
Regular'9IR'Verbs'
Take'off'the'R'and'add'the'following'endings….'
'
9s'
9issons'
9s'
9issez'
9t'
9issent'
'
Ex:'Je'finis,'nous'finissons'
'
Irregular'–IR'Verbs''
Groups'such'as'dormir,'partir,'sentir,'and'sortir'
Singular'forms:'take'off'the'last'THREE'letters'of'the'word'and'add'the'following'endings':'(9s,'9
s,'9t)'
Ex:'Je'pars''
Plural:'take'off'–IR'and'add'the'following'endings':'9ons,'9ez,'9ent''
Ex:'Nous'sortons'
'
III.!Infinatif!
Used'if…'
'A'verb'directly'follows'another'verb'
Ex:'je'vais'faire'du'jogging.'
The'verb'follows'a'preposition'
Ex:'Nous'avons'regardé'un'film'avant'de'le'nettoyer'
'
IV.!Imperatifs!!
Giving'commands:'Three'forms:'tu,'nous,'vous'
Tu:'for'people'you'know'well'[Ex:'Écoute'!]'
*for'–er'verbs,'drop'the'S'unless'followed'by'y'or'en'
Nous:'if'the'speaker'is'including'themselves'in'the'command'[Regardons'le'filme'!]'
Vous:'for'people'you'don’t'know'well'[Ex:'Mangez'bien'!]'
'
V.!Faire!Causatif!
When'the'subject'is'having'something'done,'but'not'doing'the'action'himself'or'herself'
Using'faire'+'infinitive''
[Ex:'Ma'soeur'fait'laver'le'chien]'
1
/
3
100%