thèse 2008 - Thèses et Mémoires

1
REPUBLIQUE ALGERIENNE DEMOCRATIQUE ET POPULAIRE
MINISTERE DE L’ENSEIGNEMENT SUPERIEUR
ET DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
UNIVERSITE D’ORAN ES SENIA
FACULTE DES SCIENCES
DEPARTEMENT DE BIOLOGIE
LABORATOIRE DE PHYSIOLOGIE VEGETALE
MEMOIRE
Présenté par
Ouis Miryam
Pour obtenir
LE DIPLOME DE MAGISTER
Spécialité: Physiologie Végétale
Option : Ecophysiologie Végétale
Intitulé
Soutenu le 02 - 06 -2008
Devant le jury composé de :
M. BENSOLTANE Ahmed Président
Professeur
Université d'Oran
M.AOUES Abdelkader Examinateur Professeur Université d’Oran
M.MAROUF Abderrezak Examinateur Maître de Conférences Université d’Oran
M. BELKHODJA Moulay Encadreur
Professeur
Université d'Oran
Année 2008
Polymorphisme protéique chez Atriplex halimus L. sous régime salin et de déficit hydrique

2
Avec des sentiments de
profonde humilité je dédie ce
modeste travail à mes chers
parents de m’avoir donné tout
leur amour, soutien et force pour
le réaliser.

3
Remerciements
Je tiens à exprimer ma profonde reconnaissance à Mr BELKHODJA, Professeur à
l’Université d’Oran pour son encadrement scientifique, sa participation active dans mon
travail ainsi pour la confiance qu’il m’a accordée durant ces trois années de préparation.
J'exprime toute ma gratitude à Mr BENSOLTANE, Professeur à l’Université d’Oran
d’avoir accepté de présider le jury de thèse.
Mes plus vifs remerciements à Messieurs AOUES, Professeur à l’Université d’Oran
et MAROUF Maître de Conférences, à l’Université d’Oran, d’avoir accepté d’en être les
examinateurs, pour tout le temps et l’intérêt qu’ils ont consacrés pour l’évaluation de ce
travail.
Pour la réalisation de ce travail, je voudrais remercier Mr AOUES, une deuxième
fois de m’avoir accueilli dans son laboratoire, pour ces conseils et suggestions qui ont
permis la progression de ce travail, Mr MAROUF pour sa contribution à ma formation,
Mme IGHIL HARIZ de sa précieuse aide dès les premiers instants, un grand merci à Melle
BOUCHENTOUF lila d’avoir accepter de me transmettre son savoir, de sa patience et de
sa disponibilité dont j’ai parfois abusé, à Mr AMROUN, pour son soutient pendant ces
quatre années.
Ma plus sincère reconnaissance à toutes les personnes de notre laboratoire de
physiologie végétale ainsi que tous les autres membres des laboratoires de biochimie, de
physiologie de nutrition et de biologie moléculaire, qui m’ont aidé de près ou de loin pour
la mise en oeuvre de mon travail et de peur d’oublier quelqu’un je ne citerai personne. Je
n’oublierai pas tous vos aides, vos consolations et vos joies qui mon permet d’accomplir ce
travail.

4
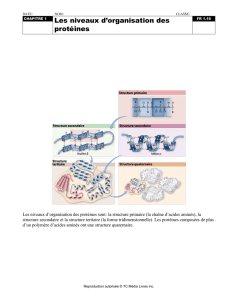
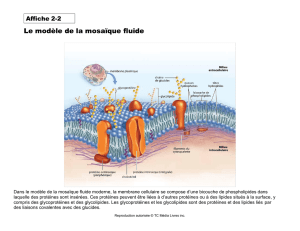
RESUME
Dans cette étude, nous avons analysé la réponse protéique des plantes d’Atriplex
halimus L. âgées de cinq mois, sous un régime salin composée de NaCl et d’un mélange
de NaCl+CaCl
2
à 400meq et 800meq. Dans cette expérimentation, les plantes sont aussi
conduites sous stress hydrique à 30 % et 60% de la capacité de rétention du sol, pendant
neuf jours de traitement. Les protéines solubles extraites à partir des feuilles, des tiges et
des racines sont analysées par la méthode de BRADFORD et par électrophorèse SDS-
PAGE.
Les analyses concluent qu’au cours de l’application du stress, les teneurs en
protéines solubles des plantes d’Atriplex halimus L. varient selon l’organe et la nature du
traitement appliqué. Quant à la séparation électrophorétique des protéines solubles, une
variation est observée dans chaque profil avec l’augmentation ou la diminution du nombre
ainsi que l’intensité des bandes protéiques déterminée par leur présence ou leur absence
selon le régime salin ou hydrique appliqué.
Les analyses des protéines solubles par la méthode de BRADFORD montrent que, sous
les différents traitements aussi bien salin que hydrique, l’accumulation des protéines
solubles se produit principalement au niveau des feuilles. Par contre les racines présentent
toujours les teneurs en protéines solubles nettement basses par rapport à celles des parties
aériennes.
Les analyses des protéines solubles par électrophorèse montrent que pour les plantes
nourries à la solution nutritive, le taux de polymorphisme atteint 50% chez les feuilles
contrairement aux tiges et aux racines où il est nul. Le traitement salin au NaCl à 400 meq,
présente les pourcentages de similarités les plus faibles soit un taux de 10% pour les
feuilles alors qu’il s’annule pour les tiges et les racines comparativement aux mêmes
organes des plantes témoins. Les taux de polymorphisme les plus importants sont obtenus
pour les feuilles des plantes recevant le traitement salin à 800 meq de NaCl (60%) et à 400
meq (33.33%).
Le traitement salin au NaCl + CaCl
2
à 800 meq montre le plus de similarité avec les
plantes témoins où il atteint 50% dans les feuilles, les tiges et les racines. Quant au
polymorphisme protéique il s’exprime seulement aux niveaux des feuilles des plantes
traitées à 400 meq (20%) et à 800 meq (50%) de NaCl + CaCl
2.
Le traitement hydrique à 30% de la capacité de rétention du sol, présente les profils
protéiques à des taux de similarité les plus proches à ceux des plantes témoins, soit 50%
pour les feuilles, les tiges et les racines. Le polymorphisme des bandes protéiques est
exprimer au niveau des feuilles seulement ; ce taux passe de 33.33% pour les plantes
stressées à 60% de la CR jusqu’à 66.66% pour les plantes traitées avec 30% de la CR.
Mots clés : Atriplex halimus L. protéines solubles, stress hydrique, stress salin, techniques
de BRADFORD, électrophorèse SDS- PAGE.

5
SUMMARY
In this study, we analyzed the proteinic response of the plants Atriplex halimus L.
five months old, under a saline mode made up of NaCl and of a mixture of NaCl+CaCl
2,
withe 400meq and 800meq. In this experimentation, the plants are also led under hydrous
stress with 30 % et 60% holding capacity of the ground, during nine days of treatment.
Soluble proteins extracted starting from the sheets, stems and roots are analyzed by the
method of BRADFORD and by electrophoresis SDS-PAGE.
The analyses conclude that during the application of the stress, contents of soluble
proteins of the plants of Atriplex halimus L. vary according to the body and the nature of
the treatment applied. As for the electrophoretic separation of proteins soluble, a variation
is observed in each profile with the increase or the reduction in the number as well as the
intensity of the proteinic bands determined by their presence or their absence according to
the saline or hydrous mode applied.
Analyses of soluble proteins by the method of BRADFORD show that, under the
various treatments as well saline as hydrous, the accumulation of soluble proteins occurs
mainly on the level of the sheets. On the other hand the roots always present the contents
of definitely low soluble proteins compared to those of the air parts.
The analyses of soluble proteins by electrophoresis show that for the plants
nourished with the nutritive solution, the rate of polymorphism reached 50% at the sheets
contrary to the stems and the roots where it is null. Saline treatment NaCl with 400 meq,
present the smallest percentages of the similarities is a rate of 10% for the sheets whereas it
is cancelled for the stems and the roots compared to the same bodies of the pilot plants.
The most important rates of polymorphism are obtained for the sheets of the plants
receiving the saline treatment with 800 meq of NaCl (60%) and with 400 meq (33.33%).
Saline treatment with NaCl + CaCl
2
with 800 meq show the most similarity with
the pilot plants where it reaches 50% in the sheets, stems and roots. As for proteinic
polymorphism it is expressed only on the levels of the sheets of the treated plants with 400
meq (20%) and with 800 meq (50%) of NaCl + CaCl
2.
Hydrous 30% treatment of the holding capacity of the ground, present the proteinic
profiles torates of similarity closest to those to the pilot plants, is 50% for the sheets, stems
and roots. The polymorphism of the proteinic bands is to only express on the level of the
sheets; this rate passes of 33.33% for the stressed plants with 60% % of capacity of the
retention of the ground 66.66% for the treated plants with 30% of capacity of the retention
of the ground.
Key words: Atriplex halimus L., soluble proteins, hydrous stress, saline stress, techniques
of BRADFORD, Electrophoresis SDS- PAGE.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
1
/
93
100%