Russia (© EUROCLASSICA 2011/Elena Ermolaeva)

Russia/Spain (© Euroclassica 2012/ Elena Ermolaeva – José Navarro)
EUROCLASSICA
ECCL – European Certificate for Classics 2012
www.eccl-online.eu
Ancient Greek Level 1/Vestibulum
Chairwoman: Deborah Davies, Director of National Ancient Greek Exam/
USA
21 years/années www.euroclassica.eu
11 years/annéesEDL 26/09/2012/ Council of Europe
http://edl.ecml.at/tabid/1772/EventID/4912/Default.aspx
Austria
Belgium
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bulgaria
Croatia
Czech Republic
Denmark
France
Germany
Greece
Hungary
Italy
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Netherlands
Poland
Portugal

Russia/Spain (© Euroclassica 2012/ Elena Ermolaeva – José Navarro)
Romania
Russian Federation
Serbia
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Each correct answer gives you one point except multiple response questions (here you must give correct answers to
all questions to reach one point). If you reach 37-40 points, you win a gold medal, 33-36 points is a silver medal,
29-32 points is a bronze medal with the stamp of Euroclassica and the sign of the president of EUROCLASSICA and
the sign of the director of ECCL. (Duration: 40 minutes).
Chaque réponse correcte vaut un point, Si tu obtiens entre 37 et 40 points, tu remportes la médaille d’or, entre 33
et 36 points la médaille d’argent, et entre 29 et 32 points la médaille de bronze, avec le cachet d’Euroclassica et la
signature d’un membre responsable de l’association européenne.(durée 40 minutes)
First read the questions! Lis d’abord les questions!
Text.Texte
Κύκλω
'OdusseÝj τÍ Κυκλώπων γÍ προσπελάζει μετ¦ ˜ταίρων. œστι δὲ τÁς θαλάσσης πλησίον ¥ντρον,
ε„ς Ö 'OdusseÝj œρχεται œχων ¥σκoν ο‡νου. Ãν δὲ Πολυφήμου τÕ ¥ντρον, Öς Ãν Ποσειδîνος καˆ
Θοώσης νύμφης, ¢ν¾ρ ¥γριος ¢νδροφάγος, œχων ›να ÑφθαλμÕν ™πˆ τοà μετώπου.
(Apollodorus, Epitome, VII, 4)
προσπελάζw - come nearer / s’approcher
Ð ˜ta‹roj, -ou -a friend / un compagnon
q£lassa = q£latta
πλησίοj, 3 – near / proche

Russia/Spain (© Euroclassica 2012/ Elena Ermolaeva – José Navarro)
tÕ ¥ντρον, -ou – a cave / une grotte
Ð ¥σκoj, -ou – a sack / une outre
¥γριος, 3 – wild / sauvage
eŒj, m…a, ›n – one / un,une
tÕ mštwpon, -ou – a forehead / le front
Test: (only one correct answer, no multiple response questions)
(une seule réponse est attendue)
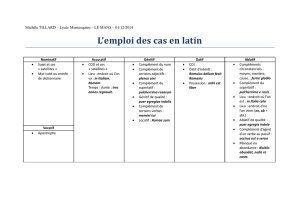
I-MORPHOLOGY MORPHOLOGIE
1. Í which case? Quel est le cas?
a) Dative sg. Datif sg.
b) Nominative sg. Nominatif sg.
c) Genitive sg. Génitif sg.
d) Accusative pl. Accusatif pl
2. ¥ which case? Quel cas?
a) Nominative sg. Nominatif sg.
b) Accusative sg. Accusatif sg.
c) Nominative pl. Nominatif pl.
d) Genitive sg. Génitif sg
3. £ which tense? Quel temps?
a) Present. Présent
b) Aorist. Aoriste
c) Future. Futur
d) Imperfect. Imparfait
4. œ which form of the word? A quelle forme est ce mot?
a) Indicative present . Indicatif présent
b) Participle present. Participe présent
c) Participle aorist. Participe aoriste
d) Noun, genitive pl. Nom au génitif pluriel

Russia/Spain (© Euroclassica 2012/ Elena Ermolaeva – José Navarro)
5. Új is a genitive sing,. Genitive plural is. : Új est un génitif sg. Le génitif pl est :
a) î
b) Új
c) Ú
d) Ú
6. èwhich case? Quel cas ?
a) Dative sg. Datif sg
b) Dative pl. Datif pl
c) Nominative sg. Nominatif sg.
d) Genitive sg. Génitif sg.
7. ¥ nominative plural is; le nominative pl est
a) ¥u
b) ¥j
c) ¥
d) ¥n
8. ο‡νου; dative plural is. Le datif pluriel est:
a) ο‡νJ
b) ο‡νουj
c) ο‡νοij
d) ο‡νwn
9. ε„ς Ó; the same case in plural is; le même cas au pluriel est:
a) ¤
b) ¤j
c) Ó
d) oÛj

Russia/Spain (© Euroclassica 2012/ Elena Ermolaeva – José Navarro)
10. Ã the correspondent plural is; la forme correspondante au pluriel est:
a) Ã
b) Ã
c) Ã
d) Ï
II-SYNTAX SYNTAXE
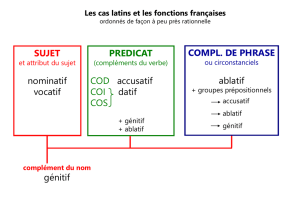
11. τÍ Κυκλώπων γÍ: Κυκλώπων which function? Quelle fonction?
a) genitive partitive ; génitif partitif
b) genitive subjective; génitif objectif
c) genitive possessive; génitif marquant la possession
d) genitive objective ; génitif objectif
12. ›να ÑφθαλμÒν: ›να which function? Quelle fonction?
a) attribute; attribut
b) subject; sujet
c) direct object; complément d’objet
d) indirect object; complément d’objet indirect
13. Ój which function? Quelle fonction?
a) subject; sujet
b) attribute; attribut
c) direct object; complément d’objet direct
d) apposition; apposition
14. ™ˆàè: which function? Quelle fonction?
a) subject; sujet
b) circumstance complement (adverbial phrase) ; complément circonstanciel
c) direct object; complément d’objet direct
d) indirect object; complément d’objet indirect
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
1
/
11
100%