Conf Eiffelvet Immuno dec 14

•EIFFELVET
•
1
Immunotherapie et cancer
Une révolution est en cours
Paris 9/12/14
Docteur Olivier Keravel
EIFFELVET EIFFELVET
Petit Retour en Prépa
Immunité innée et adaptative
Innée/non spécifique: Peau et cellules NK
Adaptative/spécifique: Lymphocytes B/T
B: humorale extracellulaire (anticorps)
T: intracellulaire
EIFFELVET
Complexe majeur
d’histocompatibilité
CMH
Classe 1: toutes cellules nucléées
Classe 2: cellules présentant les
antigènes (ex: Langerhans si cutané,
Dendritique si ganglion)
EIFFELVET
Lymphocytes T helper CD4
Lymphocytes T
cytotoxiques CD8
Lymphocytes T régulateurs
1

•EIFFELVET
•
2
EIFFELVET
LTh1 LTh2
EIFFELVET
CPA
LT
EIFFELVET
Immunothérapie et cancer
LT
LT
EIFFELVET

•EIFFELVET
•
3
EIFFELVET
Les ‘coley toxins’ (streptocoques inactivés)
la grande occasion manquée
William B. Coley (1862-1936) EIFFELVET
?
EIFFELVET
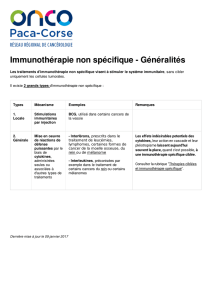
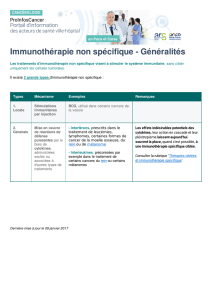
Immunothérapie Non spécifique
BCG (carcinome vésical)
Cytokines (IFN, IL2*)
Cellules NK*
Thérapies ciblées (spécifique passive)
AC monoclonaux simples* ou couplés effecteur*
Inhibiteurs des tyrosines kinases*
Immuno modulation
T reg (AINS, chimio métro)*
« Check point inhibitor »
Vaccinothérapie*
Oncept melanoma*
Vaccin télomérase*
EIFFELVET
«
Natural Killer
Cells
»
Lymphocytes non B non
T capables de lyser une cellule étrangère sans
passer par l’antigène
« Lignée NK92 » (société Conkwest) brevetée
dépourvue de récepteur inhibiteur
Forte activité antitumorale
indépendante du système immunitaire
du receveur
Injection in situ
NK K

•EIFFELVET
•
4
EIFFELVET
Preclinical studies with human NK cells for cellular therapy of canine
lymphoma, Klingemann H, VCS oct 2012
K
NK
EIFFELVET
Immunothérapie Non spécifique
BCG (carcinome vésical)
Cytokines (IFN, IL2*)
Cellules NK*
Thérapies ciblées (spécifique passive)
AC monoclonaux simples* ou couplés effecteur*
Inhibiteurs des tyrosines kinases*
Immuno modulation
T reg (AINS, chimio métro)*
« Check point inhibitor »
Vaccinothérapie*
Oncept melanoma*
Vaccin télomérase*
EIFFELVET EIFFELVET

•EIFFELVET
•
5
EIFFELVET Herceptin 1998
Trastuzumab
K sein
MAB
NIB
Erbitux 2004
Cetuximab
K colon
Avastin 2004
Bevacizumab
K colon
EIFFELVET
AC monoclonal et Lymphome Canin
AC CD20 Lymphome B
AC CD 52 Lymphome T
“Treatment of Canine B-cell Lymphoma with Doxorubicin With or Without an
Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody: An Open-Label Pilot Study,” Dr. Julie
Bulman-Fleming. VCS Saint Louis 10/14
“Treatment of Canine B-Cell Lymphoma with Chemotherapy and a Canine Anti-
CD20 Monoclonal Antibody: A Prospective Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-
Controlled Study,” Dr. Gregory Ogilvie VCS Saint Louis 10/14
EIFFELVET
lymphoma cell
CD45
Anti-CD45 mAb
211Astatine
Radio immunothérapie
Essai clinique en cours
Oregon State University
Pr Stuart Helfand
EIFFELVET
α- versus β-emitters
Normal tissueVessel, marrow
Short path length
High linear energy transfer
(LET)
Short half-life
Favorable properties of α-emitters
α-particle
β-particle
Radio Immunothérapie
Anticorps monoclonal couplé à un émetteur alpha
But: limiter la chimiothérapie
intensive
But: limiter la radiothérapie
Corps entier
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
1
/
9
100%