Le modèle de référence : (pronom interrogatif) + auxiliaire conjugué

POSER UNE QUESTION
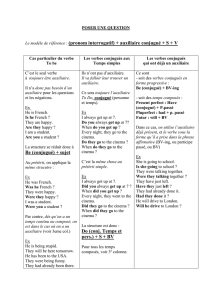
Le modèle de référence :(pronom interrogatif) + auxiliaire conjugué + S + V
Cas particulier du verbe
To be
Les verbes conjugués aux
Temps simples
Les verbes conjugués
qui ont déjà un auxiliaire
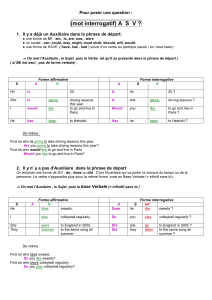
C’est le seul verbe
àtoujours être auxiliaire.
Il n’a donc pas besoin d’un
auxiliaire pour les questions
et les négations.
Ex
He is French.
Is he French ?
They are happy.
Are they happy ?
I am a student.
Are you a student ?
La structure se réduit donc à
Be (conjugué) + sujet
Au prétérit, on applique la
même strucutre :
Ex
He was French.
Was he French ?
They were happy.
Were they happy ?
I was a student.
Were you a student ?
Par contre, dès qu’on a un
temps continu ou composé, on
est dans le cas où on a un
auxiliaire (voir 3eme col.)
Ex
He is being stupid.
They will be here tomorrow.
He has been to the USA.
They were being funny.
They had already been there.
Ils n’ont pas d’auxiliaire.
Il va falloir leur trouver un
auxiliaire.
Ce sera toujours l’auxiliaire
To Do, conjugué (personne
et temps).
Ex
I always get up at 7.
Do you always get up at 7?
When do you get up ?
Every night, they go to the
cinema.
Do they go to the cinema ?
When do they go to the
cinema ?
C’est la même chose au
prétérit simple.
Ex
I always got up at 7.
Did you always get up at 7 ?
When did you get up ?
Every night, they went to the
cinema.
Did they go to the cinema ?
When did they go to the
cinema ?
La structure est donc :
Do (conj. Temps et
pers.) + S + BV
Pour tous les temps
composés, voir 3ecolonne.
Ce sont
- soit des verbes conjugués en
forme progressive :
Be (conjugué) + BV-ing
- soit des temps composés :
Present perfect : Have
(conjugué) + P.passé
Pluperfect : had + p. passé
Futur : will + BV
Dans ce cas, on utilise l’auxiliaire
déjà présent, et le verbe sous la
forme qu’il a prise dans la phrase
affirmative (BV-ing, ou participe
passé, ou BV)
Ex
She is going to school.
Is she going to school ?
They were talking together.
Were they talking together ?
They have just left.
Have they just left ?
They had already done it.
Had they done it ?
He will drive to London.
Will he drive to London ?
1
/
1
100%