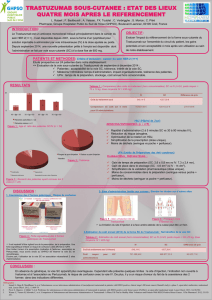
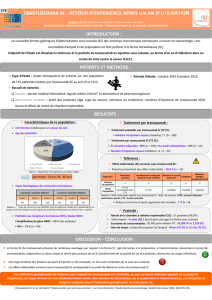
Stratégie dans le cancer du sein métastatique

Stratégie dans le cancer du sein
métastatique
Nouveaux référentiels de prise en charge
•Dr Cristian Villanueva
•Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Hôpital Jean Minjoz, Besançon, France

CONSIDÉRATIONS
GÉNÉRALES

OUI
BIOPSIE de la récidive métastatique
IB
98 %

Longues survivantes OUI
ABC durablement stable, une imagerie mammaire devrait continuer
à être réalisé de manière régulière.
Avis
d’experts 53%
L’ablation de la tumeur primitive chez les patientes ayant un cancer
du sein stade IV de novo n’a pas montré un prolongement de la
survie, à l’exception des patientes ayant des métastases osseuses
exclusives
1B 70%
Une partie non négligeable des patientes ayant un ABC, comme par
exemple celles ayant une maladie oligo-métastatique ou une masse
tumorale faible très sensibles aux traitements systémiques, peut être
mise en rémission complète et avoir une survie longue.
Une approche pluridisciplinaire, comprenant des traitements
locorégionaux à visée curative, devraient être envisagés pour ces
patientes.
Avis
d’experts 91%
Les patientes ayant un ABC et une maladie stable traitées dans le
cadre d’une ‘maladie chronique”, devraient pouvoir bénéficier d’une
reconstruction mammaire.
Avis
d’experts 82%

MALADIE OLIGOMETASTATIQUE OUI
La maladie oligométastatique est définie comme une maladie
avec un faible volume et un nombre limité de
lésions métastatiques (jusqu’à 5 et pas nécessairement dans
le même organe), potentiellement éligible pour un traitement
local destiné à obtenir une rémission complète.
Avis
d’experts 78 %
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
1
/
32
100%