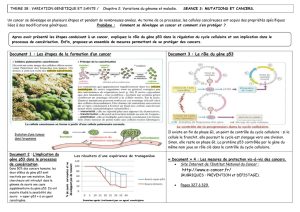
Le syndrome de Li Fraumeni

Le syndrome de Li Fraumeni :
à propos d’un cas familial avec cancers multiples
et présentant une mutation germinale du gène p53
Li Fraumeni syndrome: a case with multiple primary cancers
and presenting a germline p53 mutation
Sondess Landolsi
1
Olfa Gharbi
1
Makram Zrig
2
Moez Gribaa
3
Leila Njim
4
Abdelfattah Zakhama
4
Abderrazek Abid
2
Thierry Frébourg
5
Slim Ben Ahmed
1
1
Service de médecine carcinologique,
CHU Farhat Hached, Sousse, Tunisie
2
Service d’orthopédie, CHU Fattouma
Bourguiba, Monastir, Tunisie
3
Laboratoire de cytogénétique
et de biologie de la reproduction,
CHU Farhat Hached, Sousse, Tunisie
4
Service d’anatomie et de cytologie
pathologique, CHU Fattouma
Bourguiba, Monastir, Tunisie
5
Service de génétique, CHU Hôpitaux
de Rouen, France
Article reçu le 2 décembre 2009,
accepté le 18 janvier 2010
Résumé. Le syndrome de Li Fraumeni (LFS) est une forme rare de cancers
multiples affectant le sujet jeune et constituant une prédisposition héréditaire à
diverses tumeurs. Le LFS se transmet sur le mode autosomique dominant et
une mutation germinale du gène suppresseur TP 53 a été décrite dans 70 %
des cas de familles LFS. Nous rapportons le cas d’un homme ayant comme
antécédents familiaux de premier degré des cancers à des âges jeunes ; il a été
opéré pour un carcinome papillaire superficiel de la vessie à l’âge de 31 ans.
À 36 ans, le patient a développé un sarcome pléomorphe de haut grade de la
cuisse gauche traité par chirurgie suivie de chimiothérapie et de radiothérapie.
Deux ans après, suite à une symptomatologie faite de douleurs abdominales,
les explorations radiologiques ont révélé un troisième cancer localisé au
niveau du pancréas avec des métastases osseuses et ganglionnaires média-
stinales. Un mois après, le patient est décédé suite à une embolie pulmonaire
compliquée. L’analyse génétique par la méthode du séquençage directe a
révélé que ce patient était porteur d’une mutation codon 1009C>T, protéine
Arg337Cys, exon 10 du gène TP53 et cette dernière était confirmée chez son
neveu (décédé à l’âge de 20 ans d’un sarcome osseux).
Mots clés : cancer multiple, maladie héréditaire, génétique, P53, mutation,
syndrome de Li Fraumeni
Abstract. Li Fraumeni Syndrome (LFS) is a rare autosomal disorder charac-
terized by a familial clustering of tumors. Analysis of several series of LFS
families have shown that 70% of such families are attributable to germ-line
mutations in TP53. We report the case of a patient who had a first degree
family antecedent of cancer in young ages. At the age of 31 years, the patient
was operated of bladder papillary superficial carcinoma; five years later, he
was treated for a high grade pleomorphe sarcoma of the left thigh and treated
by surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy. At the age of 38 years,
after abdominal pain, radiologic examination reveled pancreatic tumor with
bone and lymphatic metastases. The patient died one month later from pulmo-
nary embolism. Sequencing revealed a germiline mutation of this patient that
was confirmed in a member of his family in codon 1009C>T, protein
Arg337Cys, exon 10 of TP53 gene this mutation was revealed in his nephew
(died at the age of 20 from bone sarcoma).
Key words: multiple cancer, genetic disease, genetics, P53, mutation,
Li Fraumeni syndrome genetic disease
biologie au quotidien
Ann Biol Clin 2010 ; 68 (3) : 346-50
doi: 10.1684/abc.2010.0441
346 Ann Biol Clin, vol. 68, n
o
3, mai-juin 2010
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

Le syndrome de Li Fraumeni (LFS) est une forme de can-
cer multiple rare affectant le sujet jeune et constituant une
prédisposition héréditaire à diverses tumeurs. La définition
historique et classique est basée sur des critères fami-
liaux : elle repose sur l’observation d’un sarcome chez
un sujet atteint à un âge de moins de 45 ans apparenté
au premier degré à une personne ayant eu un cancer de
n’importe quel type avant l’âge de 45 ans ou au deuxième
degré à une personne ayant eu un cancer ou un sarcome à
un âge de moins de 45 ans. Les tumeurs les plus décrites
sont les ostéosarcomes, les sarcomes des tissus mous, les
cancers du sein du sujet jeune, les leucémies, les lympho-
mes, les tumeurs cérébrales et les corticosurrénalomes ;
néanmoins tous les types de tumeurs peuvent se voir.
Le LFS se transmet sur le mode autosomique dominant
et une mutation germinale du gène suppresseur TP 53 a
été décrite dans 70 % des cas de familles LFS [1-3].
Nous rapportons ici un nouveau cas de syndrome de Li
Fraumeni dans une famille, dont un membre a été l’objet
de trois cancers et dont l’analyse génétique a retrouvé une
mutation caractéristique.
L’observation
M.M. est un homme âgé de 31 ans ayant comme antécé-
dents familiaux : un père décédé à l’âge de 72 ans d’une
hémopathie maligne, une sœur décédée à l’âge de 28 ans
d’un cancer bronchopulmonaire, un frère décédé à l’âge
de 32 ans d’un ostéosarcome et un neveu décédé à l’âge
de 20 ans d’un sarcome osseux. M.M. a été opéré à l’âge
de 31 ans pour un cancer papillaire superficiel de la vessie
traité par résection endoscopique. À l’âge de 36 ans, il a
présenté une tuméfaction au niveau de la face antéro-
interne de la cuisse gauche au dépend du muscle grand
adducteur ; l’examen clinique suspectait une lésion néo-
plasique au niveau de la cuisse gauche.
L’imagerie par résonance magnétique (IRM) a révélé une
lésion assez bien limitée de 6 x 5 cm au niveau du muscle
grand adducteur, hypervascularisée sans signe d’extension
locorégionale. Une exérèse tumorale était réalisée et
l’étude histologique a conclu à un sarcome à cellules fusi-
formes pléomorphe de haut grade ; les limites d’exérèse
étaient saines (figure 1). Une chimiothérapie et une radio-
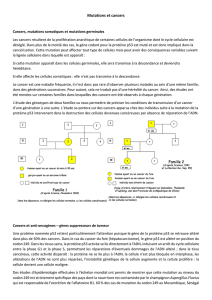
thérapie adjuvantes étaient faites. Il s’agissait d’une
famille comportant 3 membres (VI7, VI9, VI11) apparen-
tés au premier degré, ayant eu des cancers à des âges
jeunes (28, 32, 36 ans) et avec un apparenté au deuxième
degré (neveu) avec un cancer diagnostiqué à l’âge de
20 ans (figure 2). Une analyse génétique par séquençage
direct de l’ADN du neveu a mis en évidence une mutation
du gène TP53 au niveau du chromosome 17. L’analyse
chez notre patient retrouve la même altération génétique
de l’exon 10 qui substitue le codon 1009 d’une cystine en
tyrosine engendrant une protéine tronquée. L’évolution a
été marquée 2 ans après par l’installation de douleurs
abdominales dont les explorations radiologiques ont
conclu à une tumeur de la tête du pancréas (figure 3)
avec des métastases ganglionnaires. Le patient est décédé,
un mois après, dans un tableau d’embolie pulmonaire
compliquée d’une péricardite constrictive. Une étude
génétique complémentaire est en cours chez les autres
membres de la famille.
Discussion
Le syndrome Li Fraumeni (LFS) est une maladie
génétique héréditaire qui accroît fortement les risques de
développer plusieurs types de cancers dès le jeune âge du
patient. La majorité des cas de LFS présentent des muta-
tions héritées du gène suppresseur de tumeurs, le p53 [4].
En 1969, Li et Fraumeni ont rapporté 4 cas de familles
dévoilant une maladie cancéreuse à prédisposition autoso-
mique dominante chez des enfants et des jeunes adultes
présentant des sarcomes de tissus mous et des cancers du
sein [5]. En 1988, et pour mieux déterminer les caracté-
ristiques cliniques et phénotypiques de cette maladie, la
même étude était étendue sur 24 cas de familles présentant
des sarcomes de tissus mous, des ostéosarcomes, des
cancers du sein, des carcinomes adrénocorticaux chez
l’enfant, des tumeurs cérébrales et des leucémies.
Ce groupe de cancers était accepté comme un critère
pour définir cliniquement le LFS [6]. En 1990, Maklin
et al. [7] décrivent que la majorité des familles présentant
le LFS classique ont une mutation du gène TP53, ce qui a
été confirmé par d’autres études [8-10]. En 1994, Brich
et al. [3] ont proposé une définition de LFS like qui ne
présente pas les critères du SLF mais ayant une mutation
au niveau du TP53. Bougeard et al. [11] ont rapporté une
étude clinique et génétique à propos de 474 familles fran-
çaises présentant un LFS et ont confirmé qu’une mutation
du gène p53 peut être responsable de la survenue du can-
cer avant l’âge de 9 ans. Kelly et al. [12] ont décrit une
série de 525 cas présentant un LFS, le premier cancer était
dans la majorité des cas un cancer du sein, la mutation du
gène p53 était retrouvée dans 17 % des cas. Les cas sont
caractérisés par la survenue d’un premier ou d’un
deuxième cancer à un âge plus tardif. Le Frou et al. [13]
ont décrit un cas de LFS avec une néomutation faux sens
au niveau de TP53 ; l’âge de survenue du premier cancer
était de 20 mois et le type du premier cancer était un
sarcome fibroblastique des parties molles suivi d’une
succession de tumeurs, corticosurrénalome, ostéosarcome,
adénocarcinome canalaire bilatéral des seins et un adéno-
carcinome pancréatique. Agir et al. [14] ont décrit un cas
Syndrome de Li Fraumeni
Ann Biol Clin, vol. 68, n
o
3, mai-juin 2010 347
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

de LFS présentant 4 sarcomes, la survenue du 1
er
étant à
l’âge de 16 ans et l’étude génétique révélait une mutation
de p53 au niveau de l’exon 6. Dans le cas que nous décri-
vons, l’âge de survenue du premier cancer était de 31 ans
et le siège vésical du premier cancer n’est pas une locali-
sation classique dans les cas de cancers rattachés au LFS.
En effet, ce type de cancer représente 5 à 8 % de tous les
cancers et atteint surtout l’homme âgé tabagique chronique
[15-17]. Il est très rare chez les sujets jeunes [18, 19]. Dans
un deuxième temps, notre patient a développé un sarcome
de haut grade des parties molles. Le diagnostic d’un 3
e
cancer, du pancréas, métastatique a été porté par la suite.
Ces deux types de cancers sont décrits dans la littérature
dans le cadre d’un LFS.
Les sujets atteints du LFS ont une prédisposition hérédi-
taire à divers types de cancers commençant précocement
dans la vie. Les survivants à un cancer ont un risque
nettement élevé de développer d’autres tumeurs primai-
res ; le cas que nous avons rapporté a développé un
deuxième cancer 5 ans après avoir survécu du premier
cancer puis un troisième, 2 ans après avoir survécu de
son deuxième cancer. La radiothérapie a été incriminée
dans plusieurs études comme accélérateur du processus
de cancérogenèse en cas de prédisposition héréditaire
(mutation p53), une dose reçue de plus de 10 Gy pourrait
être responsable de ce phénomène [20]. Ceci pourrait être
le cas de notre patient qui avait reçu une radiothérapie
dans le cadre du traitement de son deuxième cancer.
Environ 250 mutations germinales du gène p53 ont été
rapportées [21]. Le gène p53 code pour un facteur tran-
scriptionnel capable de réguler le cycle cellulaire, l’apop-
tose et la réparation de l’ADN [22]. Les exons 5 à 8
(codons 102 à 292) codent pour le domaine central de la
protéine p53, qui est responsable de la liaison à l’ADN.
La plupart des mutations germinales du gène p53 ont été
trouvées dans celles-ci [23]. Les mutations du domaine
central du gène p53 entraînent généralement plus de
biologie au quotidien
4
4
I
II
III
IV
V
6
4
4
3
Leucémie myéloïde chronique
Carcinome papillaire de la vessie, Rhadbomyosarcome,
Tumeur au niveau de la tête du pancréas
Cancer broncho-pulmonaire
Ostéosarcome
Sarcome
72 ans
44
32
28 ans 32 ans 36 ans
20 ans
Figure 2. Arbre généalogique de la famille présentant un syndrome de Li Fraumeni.
Figure 1. Prolifération indifférenciée des cellules fusiformes
et pléomorphes manifestement atypiques évoquant un sarcome
pléomorphe de haut grade.
348 Ann Biol Clin, vol. 68, n
o
3, mai-juin 2010
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

cancers survenant à un plus jeune âge [24], que le cas que
nous rapportons. Environ 70 % des mutations du gène
p53 sont des mutations faux sens [21] et jusqu’à90%
des mutations faux sens sont localisées dans les exons
5 à 8 [25]. La mutation du gène P53 n’est pas systémati-
quement retrouvée, probablement du fait de l’existence de
mutations non détectées (dans les introns ou les régions
promotrices), de l’inactivation de la protéine p53 à travers
l’interaction avec d’autres protéines cellulaires ou des
virus et de l’implication d’autres gènes [21]. Ainsi, des
mutations du gène CHK2, codant pour une kinase régu-
lant le cycle cellulaire via p53, ont été mises en évidence
dans des familles atteintes [26]. La pénétrance des cancers
est incomplète mais très élevée (25 % de risque de déve-
lopper une tumeur dans les dix premières années de vie,
50 % passé 35 ans et 90 % passé 60 ans) et est supérieure
chez les femmes (liée au cancer du sein) [27].
La prise en charge du LFS illustre bien les difficultés ren-
contrées lors des consultations d’oncogénétique par les
médecins traitants. Ces mutations constitutionnelles de
l’antioncogène p53 provoquent un risque de cancer très
élevé, en particulier chez l’enfant et l’adulte jeune.
Le risque de tumeurs multiples est important et vient
aggraver le pronostic de ces cancers. La localisation extrê-
mement variée des cancers rend le dépistage particulière-
ment difficile à organiser [28]. La diversité des tumeurs et
la rareté des familles ont contribué à la difficulté à conce-
voir des recommandations efficaces de dépistage pour des
membres des parents atteints de LFS [29]. Un groupe
de travail pluridisciplinaire sur le LFS a proposé des
recommandations sur la prise en charge [28] : le diagnos-
tic positif (recherche d’une mutation de TP53 chez un
sujet atteint d’une tumeur) peut être proposé aux enfants
comme aux adultes, dans le cadre de consultations
de génétique associées à un accompagnement psycholo-
gique, avec confirmation du diagnostic sur des bases
moléculaires. Cela permet de proposer aux patients une
surveillance clinique régulière pour éviter un éventuel
retard de diagnostic d’une autre tumeur. Le diagnostic
génétique pré-symptomatique doit être impérativement
réservé à l’adulte. Comme dans les autres maladies géné-
tiques pour lesquelles son bénéfice n’est pas évident,
le diagnostic pré-symptomatique doit être impérativement
restreint à l’adulte et ne doit pas être proposé aux enfants
à risque. Bien entendu, dans ces familles, la tentation du
praticien est souvent grande de vouloir rassurer les parents
en démontrant l’absence de la mutation constitutionnelle
chez les enfants à risque. Mais cet argument est contreba-
lancé par le risque d’identifier une mutation chez un
enfant asymptomatique, résultat d’intérêt limité sur le
plan médical et souvent dévastateur sur le plan psycholo-
gique. L’âge jeune de survenue des tumeurs, le pronostic
réservé de certaines tumeurs, l’impossibilité d’en assurer
le dépistage précoce et le risque pour les porteurs de
mutations de développer plusieurs tumeurs primitives
justifient que puisse être envisagé, dans les familles attein-
tes, un diagnostic prénatal [28]. Des données préliminaires
fournissent la première preuve d’une stratégie potentielle
de surveillance des cancers qui peut être digne d’une
investigation postérieure chez les patients atteints de
LFS par une imagerie par F18-fluorodéoxyglucose PET
Scan (FDG-PET/CT) [30]. Les effets indésirables de
l’exposition à l’irradiation et les autres problèmes inhé-
rents au dépistage des patients à haut risque doivent
être mieux pris en compte [29]. Le traitement des tumeurs
Li Fraumeni avec p53 constitue une thérapie visant les
défauts moléculaires à l’origine de l’apparition et de la
progression de ces cancers [31]. La monothérapie
(Advexin
®
) a été évaluée sur divers types de cancer
et en combinaison avec plusieurs traitements anticancé-
reux classiques, notamment la radio- et la chimiothérapie.
Des données provenant de plusieurs essais précliniques et
thérapeutiques, dont les résultats ont été publiés, ont
démontré l’activité de p53 en tant que monothérapie.
Son innocuité en tant que promoteur des effets anticancé-
reux de l’irradiation et de la chimiothérapie a été aussi
prouvée [31].
Conflit d’intérêts : aucun.
Références
1. Tena Sanabria ME, Herrera Sánchez D, Hernández López J, Huico-
chea Montiel JC, Rodríguez A. Li Fraumeni syndrome familial cancer
case report and literature review. Acta Orthoped Mexic 2007 ; 21 :
99-104.
Syndrome de Li Fraumeni
Figure 3. Tumeur au niveau de la tête du pancréas.
Ann Biol Clin, vol. 68, n
o
3, mai-juin 2010 349
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

2. Li FP, Fraumeni Jr JF, Mulvihill JJ, Blattner WA, Dreyfus MG, Tuc-
ker MA, et al. A cancer family syndrome in twenty-four kindreds. Can-
cer Res 1988 ; 48 : 5358-62.
3. Birch JM, Hartley AL, Tricker KJ, Prosser J, Condie A, Kelsey AM,
et al. Prevalence and diversity of constitutional mutations in the p53
gene among 21 Li-Fraumeni families. Cancer Res 1994 ; 54 :
1298-304.
4. Chompret A, Abel A, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Brugières SL, Pagès S,
Feunteun J, et al. Sensitivity and predictive value of criteria for p53
germline mutation screening. J Med Genet 2001 ; 38 : 43-7.
5. Li FP, Fraumeni JF. Soft tissue sarcomas, breast cancer, and other
neoplasms : a familial syndrome ? Ann Intern Med 1969 ; 71 : 747-52.
6. Li FP, Fraumeni JF, Mulvihill JJ, Blattner WA, Dreyfus MG, Tucker
MA, et al. A cancer family syndrome in 24 kindreds. Cancer Res 1988 ;
48 : 5358-62.
7. Malkin D, Li FP, Strong LC, Fraumeni JF, Nelson CE, Kim DH,
et al. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer,
sarcomas and other neoplasms. Science 1990 ; 250 : 1233-8.
8. Varley JM, McGown G, Thorncroft M, Santibanez-Koref MF, Kelsey
AM, Tricker KJ, et al. Germ-line mutations of TP53 in Li-Fraumeni
families : an extended study of 39 families. Cancer Res 1997 ; 57 :
3245-52.
9. Birch JM, Alston RD, McNally RJ, Evans DG, Kelsey AM, Harris
M, et al. Relative frequency and morphology of cancers in carriers of
germline TP53 mutations. Oncogene 2001 ; 20 : 4621-8.
10. Bougeard G, Limacher JM, Martin C, Charbonnier F, Killian A,
Delattre O, et al. Detection of 11 germline inactivating TP53 mutations
and absence of TP63 and HCHK2 mutations in 17 French families with
Li-Fraumeni or Li-Fraumeni-like syndrome. J Med Genet 2001 ; 38 :
253-6.
11. Bougeard G, Sesboue R, Baert-Desurmont, Vasseur S, Martin C,
Tinat J, et al. Molecular basis on the Li-Fraumeni syndrome : an update
from the French LFS families. J Med Genet 2008; 45 : 535-8.
12. Gonzalez KD, Noltner KA, Buzin CH, Gu D, Wen-Fong CY,
Nguyen VQ, et al. Beyond Li Fraumeni Syndrome : clinical characteris-
tics of families with p53 germline mutations. JCO 2009 ; 27 : 1250-6.
13. Lefrou L, Godart B, De Muret A, Scotto B, Dorval E. Néomutation
germinale du gène p53 chez un malade présentant un syndrome de Li-
Fraumeni et un adénocarcinome du pancreas. Gastro Enter Clin Biol
2006 ; 30 : 484.
14. Agir H, Mackinnom C, Tan S. Li-Fraumeni syndrome : a case with
4 separate primary sarcomas and 5 sequential free flaps in the maxillo-
facial region. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008 ; 66 : 1714-9.
15. Johanson SL, Cohen SM. Epidemiology and etiology of bladder
cancer. Semin Surg Oncol 1997 ; 13 : 291-8.
16. Dimenza L, Bourou JC, Vieillefond A, Chondot D, Boccon Gibod
L, Zummer K. Facteurs de risques des tumeurs de vessie; étude épidé-
miologie chez 701 sujets en Île-de-France. Press Med 1991 ; 20 :
1436-9.
17. Haleblian E, Skinner C, Dickinson G, Lieskovsky G, Skinner G.
Hydronephrosis as a pronostic indicator in bladder cancer patients.
JUrol1998 ; 160 : 2011-4.
18. Melicow MM. Tumors of the bladder : a multifaceted problem.
JUrol1974 ; 112 : 467-78.
19. Aboutaieb R, Dakir M, Sarf I, Meziane F, Benjelloun S. Les
tumeurs de vessie chez le jeune. Prog Urol 1998 ; 8 : 43-6.
20. Ghnassia JP, Wagner M, Velten M. Les tumeurs stromales du tube
digestif : evaluation prognostique d’une série de 36 cas. Ann Pathol
1996 ; 16 : 27-32.
21. Olivier M, Goldgar DE, Sodha N, Ohgaki H, Kleihues P, Hainaut P,
et al. Li-Fraumeni and related syndromes : correlation between tumor
type, family structure, and TP53 genotype. Cancer Res 2003 ; 63 :
6643-50.
22. Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP. Crystal structure of a
p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex : understanding tumorigenic muta-
tions. Science 1994 ; 265 : 346-55.
23. Birch JM, Blair V, Kelsey AM, Evans DG, Harris M, Tricker KJ,
et al. Cancer phenotype correlates with constitutional TP53 genotype
in families with the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Oncogene 1998 ; 17 :
1061-8.
24. Chompret A. The Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Biochimie 2002 ; 84 :
75-82.
25. Vahteristo P, Tamminen A, Karvinen P, Eerola H, Eklund C, Aalto-
nen LA, et al. p53, CHK2, and CHK1 genes in Finnish families with Li-
Fraumeni syndrome : further evidence of CHK2 in inherited cancer pre-
disposition. Cancer Res 2001 ; 61 : 5718-22.
26. Evans SC, Lozano G. The Li-Fraumeni syndrome : an inherited sus-
ceptibility to cancer. Mol Med Today 1997 ; 3 : 390-5.
27. Expertise collective Inserm. Risques héréditaires de cancers du sein
et de l’ovaire. Quelle prise en charge ? Paris : Inserm, 1998.
28. Frebourg T, Abel A, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Brugières L, Berthet P,
Bressac-de Paillerets B, et al. Le syndrome de Li-Fraumeni : mise au
point, données nouvelles et recommandations pour la prise en charge.
Bull Cancer 2001 ; 88 : 581-7.
29. Varley JM. Germline TP53 mutations and Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Hum Mutat 2003 ; 21 : 313-20.
30. Asciari S, Van den Abbeele AD, Diller LR, Rastarhuyeva I, Yap J,
Schneider K, et al. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/
computed tomography screening in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. JAMA
2008 ; 299 : 1315-9.
31. Senzer N, Nemunaitis J, Nemunaitis M, Lamont J, Gore M, Gabra
H, et al. P53 therapy in a patient with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Mol Can-
cer Ther 2007 ; 6 : 1478-82.
biologie au quotidien
350 Ann Biol Clin, vol. 68, n
o
3, mai-juin 2010
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.
1
/
5
100%