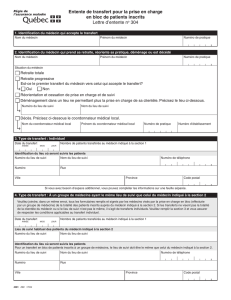
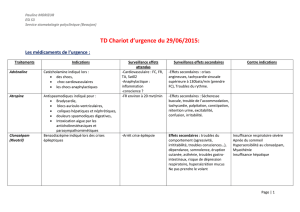
Insuffisance cardiaque ambulatoire

L’insuffisance cardiaque en
ambulatoire
L
L’
’insuffisance cardiaque en
insuffisance cardiaque en
ambulatoire
ambulatoire
P. Jourdain
Unité Thérapeutique d’Insuffisance Cardiaque,
CH R Dubos, 95300 Pontoise.
CNCH 2010
Insuffisance cardiaque : un problème
médical croissant
•970 000 admissions/an aux États-Unis avec diagnostic primaire d'insuffisance cardiaque
1, 2
(130 000
en France d’après les données du PMSI 2005). Entre 500 et 800.000 français atteints
•3 000 000 admissions/an aux États-Unis avec diagnostic primaire ou secondaire d'insuffisance
cardiaque
1
1
Haldeman GA et al. Am Heart J. 1999; 137: 352
2
American Heart Association. Heart and Stroke Statistics. Mise à jour 2004. 2003 : 19
3
ESC Task Force. Eur Heart J. 2001; 22: 1527
Prévalence Incidence Mortalité Sorties
d'hôpital Coût
Europe
3
10 000 000 500 000
50 %
sous
5 ans
1 000 000
États-
Unis 5 000 000 550 000 1 000 000
24,3
milliards
de
dollars

Insuffisance cardiaque et coûts
Billions of $
O’Connell JB, et al. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1994;13:S107-S112..
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Ins.
Cardiaque Cancer Infarctus
L’insuffisance cardiaque n’est pas un problème
de cardiologue mais un problème de société !
Optimal therapy is cheaper than
rehospitalization
American Heart Association, 2000 Heart and Stroke Statistical Update
Hospital/Nursing home
Healthcare
providers
Indirect Costs Home health/Other
medical durables
15.5
2.2 1.5 1.1 2.2
Drugs
ANNUAL COST OF HF ESTIMATED TO BE $22.5 BILLION (USA)
Costs in billions of dollars

ANALYSE PRONOSTIQUE
insuffisance cardiaque chronique, la polythérapie une règle ?
rétention hydrique combinaison
(sous surveillance)
si FA ou si d’une
IC sévère en RS
I II III IV
Classe NYHA
IEC
Diurétiques
Bêtabloquant
Digoxine
Spironolactone
Candesartan
post-IDM
si FA
indiqué
si IEC non toléré
Ou added
combinaison
(sous surveillance)
si IEC non toléré
Ou added si IEC non toléré
ou added
indiqué indiqué indiqué
indiqué
indiqué indiqué
indiquéindiquéindiqué
Ivabradine
indiquéindiqué
Thérap électriques
QRS > 150 ms QRS > 120 ms QRS > 120 ms

En pratique… jusqu’ou…
Traiter l’OAP, c’est bien mais
prévenir c’est mieux…
Nos missions
• Assurer ou faciliter le suivi
• Optimiser les thérapeutiques
• Faire le bilan pronostic
• Faire bénéficier les patients d’une ETP de
qualité.
• Faciliter la réadaptation.

ACEI
Ivabradine
Anti aldostérone
ARB 2
ARB 2
Beta blockers
NYHA 2 NYHA 3 or 4
NYHA 3 or 4NYHA 1 (?)
Pacemaker (resynchronization)
Therapeutic patient education
Réadaptation
ACEI ACEI
Beta blockers Beta blockers
Diuretics
Ivabradine
Heart rate
Heart rate
Renal function
Renal function
QRS wide
QRS wide
Compliance
Compliance
Risk stratificat
Risk stratificat°
°(Echo
(Echo
BNP, Vo2,
BNP, Vo2,…
…)
)
Diuretics
Diuretic increase
Les composantes d’une prise en
charge ambulatoire
• Clinique ( IC / Rythmo / Echo) avec optimisation
thérapeutique
• Système de suivi qualité
• Education thérapeutique
• Réadaptation auto réadaptation
• Télé-cardiologie
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
1
/
17
100%