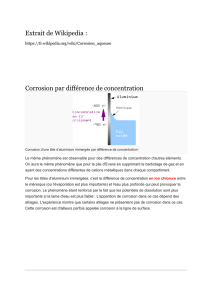
Influence de la température et de l`agitation du liquide de

République Algérienne Démocratique Et Populaire
Ministère de l’enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique
Université du 20 Août 1955-Skikda
Faculté de Technologique
Département de Génie Mécanique
MEMOIRE DU MAGISTER
Option : Mécanique des matériaux et des surfaces
Présenté Par: HAROUAKA Saad
Soutenu le : 27 / 12 / 2013
Devant le jury
Président Mr. LEGOUERA Messaoud Professeur U.Skikda
Rapporteur Mr. BELIARDOUH Nasser Eddine Maitre de conférences U.Annaba
Examinateurs
Mme.
ABDERRAHMANE Sihem Professeur U.Annaba
Mr. ASSALA Omar Maitre de conférences U.Annaba
Mr. METATLA Abderrezak Maitre de conférences U.Skikda
Année 2012/2013
Université 20 Août 1955
SKIKDA
Influence de la température et de l'agitation du liquide de
refroidissement sur la tenue à la corrosion des alliages
d'aluminium utilisé
s
dans l'industrie automobile

Remerciements
Je tiens tout d’abord à remercier Dieu, le tout-puissant, qui m’a aidé à réaliser ce travail.
Ce travail a été effectué au Laboratoire unité des recherches (DRA) à l’usine
ARCELOR MITTAL ANNABA, au laboratoire de Métallurgie physique &
métallographie de l’université de BADJ Mokhtar Annaba.
J’exprime mes remerciements les plus distingués à mon professeur et encadreur
BELIARDOUH Nasser Eddine, professeur à l'université BADJ Mokhtar Annaba, en
reconnaissance de sa compétence, de son dévouement et de ses conseils judicieux qui
m’ont été d’un grand soutien moral et qui m’ont amené à réaliser ce travail.
J’exprime mes grands remerciements à Monsieur LEGUERA Messaoud,
professeur à l'université 20 Aout 1955 Skikda de m'avoir fait l'honneur de présider le jury
de cette thèse.
Je voudrais remercier très sincèrement Madame ABDERRAHMANE Sihem,
professeur à l'université BADJ Mokhtar Annaba, d’avoir accepté d’examiner ce travail.
Je tiens à remercier très vivement Monsieur ASSALA Omar, Maître de conférence à
universitaire BADJ Mokhtar Annaba, pour avoir accepté de faire partie du jury et juger
ce travail.
Mes remerciements vont également à tous les enseignants du département des
Génie mécanique, surtout chef de département Monsieur METATLA Abderrazak,
Maître de conférence à université de 20 Aout 1955, d’avoir accepté d’examiner ce travail.
Je tiens à exprimer ma profonde reconnaissance à toutes les personnes ayant aidé de
prés ou de loin à l’achèvement de cette thèse et plus particulièrement : Bilal Labo,
Monsieur BELACHIA.M et ma sœurs Sihem, Noura, etc …

Dédicace
A mon père
A ma très chère mère
A tous ceux qui me sont chers:
Mes frères (Sabar, Fouzi, Adel, Bilal, Salah)
Ma sœur (Sara)
A (Mohamed,Nessrin,Manar,Nounousa)
A tous mes amis
A tous mes collègues

Résumé
La protection contre la corrosion du matériau constituant le radiateur est habituellement assuré
par une formulation adaptée du liquide de refroidissement des moteurs.
Les mécanismes de corrosion et de protection sont complexes. Ils dépendent des conditions
physico-chimiques de service (nature de l’inhibiteur) et des caractéristiques du matériau. Le
marché national est inondé par une large gamme de produits.
L’étude entreprise a consisté en une caractérisation physico-chimique, par méthodes
électrochimiques stationnaires de l’efficacité protectrice d’un liquide de refroidissement constitué
principalement de l’eau déminéralisée contenant l’éthylène glycol et 2 types d’inhibiteurs
organique et minéral à savoir le benzoate de sodium et le phosphate de sodium.
La formulation a été mise au point en combinant les 3 produits avec leurs concentrations ayant
donné le meilleur d’inhibition à la température ambiante.
L’influence de l’agitation, de la température, des cycles thermiques (simulant les périodes de
fonctionnement et l’arrêt).
Le mécanisme d’interaction de ces inhibiteurs a été proposé.
Mots-clés : alliage aluminium, Corrosion, inhibiteurs
Abstract
The protection against corrosion in the material of the radiator is usually carried out by a
formulation of suitable coolant engines.
The mechanisms of corrosion and protection are complex. They depend on the physicochemical
conditions of service (nature of the inhibitor) and the characteristics of the material. The domestic
market is flooded with a wide range of products.
The study undertaken consisted of a physical and chemical characterization by electrochemical
stationary methods protective efficacy of a coolant consisting mostly of deionized water
containing ethylene glycol and 2 types of inhibitors organic and mineral namely, sodium benzoate
and sodium phosphate.
The formulation has been developed by combining these products with 3and4 concentrations
giving the highest level of inhibition at room temperature.
The influence of agitation, temperature, thermal cycles (periods of simulating operation and stop).
The mechanism of interaction of these inhibitors was proposed...
Keywords: Corrosion, aluminum alloy, inhibitors, electrochemistry.

ا و ارا ه م آا دا ةد م تآا. ت
ا آا ة. هو نو طو آ ا ( ا و داا. و
أ قا ا او تا.
ارا ا ن آ وآوآ أ ا
ةءآ و ا يا أ ءا ا ن يا ي ا ل و
2عاأ ت ا او هو تاو مدا و ت مدا.
ا و ا ءإ 3و4 آا ءإ ى رد
ةرا ا ) ،لا ردو ةراا ، تارود راا (تا ةآ فإوو ا
ه ت.
تﻝا ﻝا : آا ، ما ، تو ، ءآ آ .
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
 101
101
 102
102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
 109
109
 110
110
 111
111
 112
112
 113
113
 114
114
 115
115
 116
116
 117
117
 118
118
 119
119
 120
120
 121
121
 122
122
 123
123
 124
124
 125
125
 126
126
 127
127
1
/
127
100%