Les Critères de notation bancaire

Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this presentation requires the prior written approval of Standard & Poor’s.
Copyright © 2012 Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Les Critères de notation bancaire
Bernard de Longevialle
Responsable de la notation des banques & assurances pour la zone EEMEA &
Russie CEI (Communauté des Etats indépendants)
Notations - Institutions Financières
Avril 2012

2. Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this presentation requires the prior written approval of Standard & Poor’s.
Agenda
•Notre nouvelle méthodologie: Une interconnexion accrue entre
les notes souveraines et bancaires
–Analyse des risques de l’industrie bancaire et de l’économie (BICRA)
–Facteurs spécifiques à la banque
–Soutien externe
•Tendances des notations en France et en Europe

3. Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this presentation requires the prior written approval of Standard & Poor’s.
Critères de notation bancaire

4. Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this presentation requires the prior written approval of Standard & Poor’s.
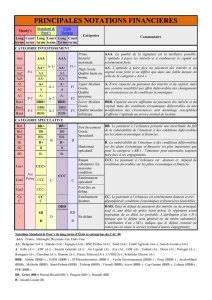
Bank Ratings Framework
Méthodologie
BICRA
Score BICRA
Evaluation du
risque de
l’industrie et de
l’économie
Méthodologie
bancaire
Facteurs macro
économiques Facteurs de notations
propres à la banque Soutien externe
Ancre SACP
Analyse
intrinsèque
ICR
Note de
crédit de
l’émetteur
Notation de la dette
hybride et des
actions de
préférence
Notation de la
dette senior non
sécurisée
Risque de l’économie
Risque de l’industrie
Soutien du
groupe
Soutien du
gouvernement
Profil de
l’activité
Capital et
rentabilité
Profil de
risque
Financement
et liquidité

5. Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this presentation requires the prior written approval of Standard & Poor’s.
BICRA: Analyse du risque économique et du risque
liéàl’industrie
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
1
/
24
100%