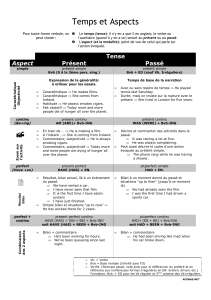
Présent en “ BE+ing” Présent simple Prétérit simple Prétérit en “BE+

Présent en “ BE+ing” Présent simple Prétérit simple Prétérit en “BE+ing”
did / bV (=V à l’inf. sans to)
Auxiliaire
Forme verbale
am
is / V ing
are
do
does / bV (=V à l’inf. sans
to)
( 3° pers sing)
* Attention : cas particulier de BE
was
were / V ing
S + Ved + C
V irrégulier
Forme
affirmative
am
S + is + Ving+ C
are
S + bV+ C
V+s (3° pers sing)
* S + was + C
were
was
S + were + Ving+ C
(Wh)+did+ S+ bV+ C+ ?
Forme
interrogative
am
(Wh)+ is + S+ Ving+ C+ ?
are
do
(Wh)+ does+ S+ bV+ C+ ?
* (Wh)+ was+ S+ C+ ?
were
was
(Wh)+ were+ S+ Ving+ C+ ?
S+ did+ not+ bV+ C
Forme
négative
am
S+ is + not+ Ving+ C
are
S + do+ not+ bV+ C
does
* S+ was+ not+ bV+ C
were
was
S+ were+ not+ Ving+ C
Emploi et
exemples
* Action en train de se dérouler au
moment où l'on parle :
Listen, he's singing.
* Futur (si accompagné d’un C.C.T.
faisant référence à du futur) :
Is Tom getting his new glasses next
week ?
* Action habituelle:
Do you watch TV every evening ?
* Caractéristique :
Cats don't like water .
Water freezes at 32° Farenheit.
Jim lives and works in Barley.
*Programme officiel :
The match starts at three.
* Action passée, datée, terminée,
coupée du moment présent :
I bought this house in 1961.
* Action irréelle (prétérit modal) :
If only I were rich!
* Action en train de se dérouler à
un moment précis du passé :
Were you sleeping yesterday at 11
p.m.?
* Action qui durait, interrompue
par une action brêve, exprimée,
elle, au prétérit simple :
I was reading when the phone
rang.
Indices
now, listen, look ...
usually, every ...often, always...
ago, it's time, yesterday, last X
it's X days/years since... ou toute
justification temporelle faisant
référence à du passé.

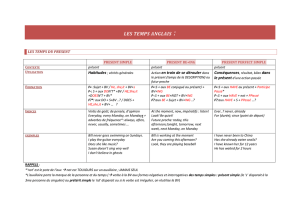
Present perfect Present perfect en “BE+ing” Past-perfect Past-perfect en “BE+ing”
Auxiliaire
Forme verbale
have / participe passé
has du verbe
have / been / Ving
has ( 3° pers sing)
had / p.passé du verbe
had / been / Ving
Forme
affirmative
have
S+ has + p.passé+ C
have
S+ has+ been+ Ving+ C
S+ had+ p.passé+ C
S+ had+ been+ Ving+ C
Forme
interrogative
have
(Wh)+ has + S+ p.passé+ C+ ?
have
(Wh)+ has+ S+ been+ Ving+ C+ ?
(Wh)+ had+ S+ p.passé+ C+ ?
(Wh)+ had+ S+ been+ Ving+ C+ ?
Forme
négative
have
S+ has + not+ p.passé+ C
have
S+ has+ not+ been+ Ving + C
S+ had+ not+ p.passé+ C
S+ had+ not+ been+ Ving + C
Emploi et
exemples
* Action du passé, non datée, ayant
des conséquences sur le présent :
Sorry, I can't pay ! I've forgotten
my wallet.
* Action du passé, non datée
présentant un bilan dans le présent,
un résultat visible, achevé. L'accent
est mis sur le résultat :
What have you done?
I've painted the room. (you can see
it)
*Bilan que l’on fait de sa vie ou de
celle d’un autre (parcours) :
I’ve never been to Australia.
*Evénement venant juste d’arriver :
The President has just been shot at.
* Action non obligatoirement
achevée au moment présent :
I've been reading your book. (I
haven't finished it).
* Action présentant une
conséquence sur le sujet. L'accent
est mis sur le sujet de l'action, et non
sur le résultat de celle-ci (valeur
appréciative):
What have you been doing?
I've been painting the room
(I've got some paint all over my
clothes, but I haven't finished yet.)
* Action qui aurait déjà eu lieu au
moment où l'on parle. Passé dans le
passé :
I explained I had forgotten my keys.
*Bilan à un moment précis du
passé :
We had already seen that film.
* Action ou situation qui s'était
poursuivie jusqu'au moment du
passé évoqué :
When she arrived, I had been
waiting for 3 hours.
*Valeur de commentaire
appréciatif :
He had been driving like mad when
the car broke down.
Indices
Since, for, already, yet, just, ever, ...
Pas de justification temporelle
définie

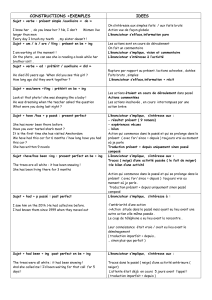
Futur en “will” Futur en “be going to” Conditionnel Conditionnel passé
Auxiliaire
Forme verbale
will / bV (=V à l’inf. sans to)
am
is going to / bV (=V à l’inf. sans to)
are
would / bV (=V à l’inf. sans to)
would have / participe passé du V
Forme
affirmative
S+ will + bV+ C
am
S+ is going to+ bV+ C
are
S+ would + bV+ C
S+ would+ have+ p.passé+ C
Forme
interrogative
(Wh)+will+ S+ bV+ C+ ?
am
(Wh)+ is+ S+ going to+ bV+ C+ ?
are
are
(Wh)+ would+ S+ bV+ C+ ?
(Wh)+would+S+have+p.passé+C+
?
Forme
négative
S+ will + not+ bV+ C
am
S+ is+ not+ going to+ bV+ C
are
S+ would+ not+ bV+ C
S+ would+ not+ have+ p.passé+ C
Emploi et
exemples
* Action prévue mais non certaine,
représente la volonté du sujet, mais
la réalisation de l'action dépend
d'éléments extérieurs; projet :
I will buy a new car next year.
* Action prévue mais indépendante
de la volonté du sujet :
I'm going to buy a new car ( my old
one is broken, I have no choice).
* Prédiction à partir d'indices :
What a mess! He's going to be
furious.
Look at those black clouds ! It is
going to rain soon !
* Action dont on est sûr qu’elle va
se réaliser :
I’m going to spend my holidays in
California ! (I’ve got the plane
tickets)
* Action irréelle qui n'a pas eu lieu
mais qui le pourrait si les choses
étaient différentes :
If I had some money, I would travel
a lot .
* Futur dans le passé :
I was looking for my keys ; I knew it
wouldn't be easy to find them
quickly
* Action irréelle qui aurait pu se
réaliser si les choses avaient été
différentes dans le passé :
If he had given me some money, I
would have bought a ticket for the
concert . (now, it's too late )
1
/
3
100%