Les Temps du Passé

Les Temps du Passé

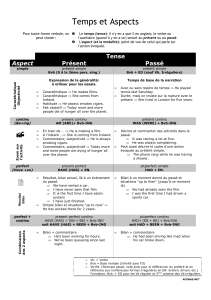
Le Prétérit
Le Prétérit correspond au :
•Passé Composé
•Passé Simple
•Imparfait
…selon le cas.

Le Prétérit
Verbes réguliers : on ajoute –ed à toutes les personnes.
I worked.
Did you work?
I did not (didn’t) work.
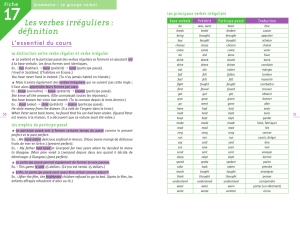
Verbes irréguliers : liste à apprendre par cœur.
I saw him.
Did you see him?
I did not (didn’t) see him.

Le Prétérit
Prétérit Simple
Action datée dans le passé.
-In 1666, a fire destroyed
almost the whole of
London.
Temps de la narration.
-He looked up and then
smiled.
Prétérit en « be + ing »
Description dans le passé.
Action qui était en cours de
déroulement au moment
de l’énonciation.
-When I came in, they were
watching TV.

« have + en » (Present Perfect)
« have + en » correspond au :
•Passé Composé
•Présent
…selon le cas.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
1
/
21
100%