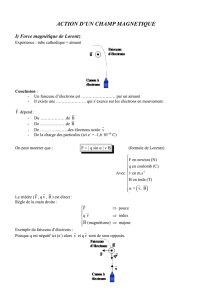
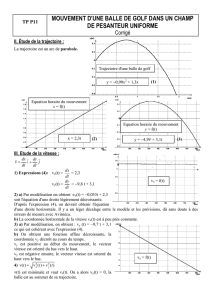
g V α sin g V α α sin . cos .2 g V 2 2 sin .2 α α2 sin .. 2 x g λ λ λ λ λ

Page 1 of 2
Physique Corrigé examen1 Classe de SV
Déc 2015
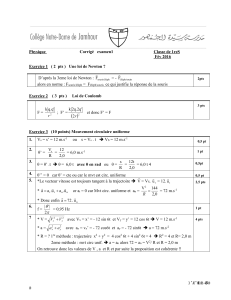
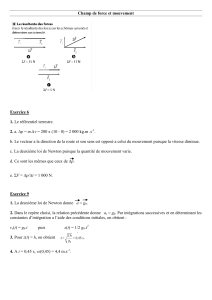
Exercice 1 (6 pts ) Étude d’un plongeon
Exercice 2 (8 pts ) Les quasars, des astres très lointains
1.
* Soit tF l’instant d’arrivée en F
*Les coordonnées de
⃗
sont les équations horaires du mouvement : x(t) et y(t)
* x = (V0.cosα).t alors xF = (V0.cosα).tF (1)
* Vy = y’ = - g.t + V0.sinα
*Au sommet F de la trajectoire : vy = 0
* 0 = - g.tF + V0.sinα ==> tF = g
V
sin
0 ; remplaçons dans (1) nous aurons :
xF = g
V
sin.cos.
2
0 (ou xF = g
V
2
2sin.
2
0
) ; alors V0 =
2sin
..2 F
xg ≈ 4,5 m.s-1
3 pts
2. * En tout point : V = 22
yx VV ; en particulier en H : VH = 22
yenHx VV
* Vx = x’ = V0.cosα = cte indép . de t et alors Vx = 3,447m.s-1 .
Vy = y’ = - g.t + V0.sinα (2)
* yH = 0 or y = ( -
2
1.g.t2 +(V0.sinα ).t + y0 ) ==> 0 = ( -
2
1.g.t2 +(V0.sinα ).t + y0 )
* On trouve tH = 1,44 s ; on remplace dans (2) on aura Vy en H = - 11.219 m.s-1
* Enfin VH = 22
yx VV ≈ 12 m.s-1
3pts
1.
En = - 2
0
n
E avec E0 = 13,6 eV ; en remplaçant n successivement par 1 ; 2 ; 3 et 4 on trouve :
E1 = - 13,6 eV ; E2 = - 3,40 eV ; E3 = -1,51 eV et E4 = - 0,850 eV
1 pt
2.
a. ΔE = En – E1 =
n
h.c
le tout en S.I. ==> 2
19
010.6,1.E -
n
- ( 2
19
0
1
10.6,1.E -
) =
n
h.c
==> E0 .1,6.10-19 ( 1 - 2
n
1) =
n
h.c
et alors
n
1
=
c
h
.
10.6,1.E 19
0
( 1 - 2
n
1)
D’où RH =
c
h
.
10.6,1.E 19
0
2 pts
b.
D’après l’expression donnée:
n
1
= RH . ( 1 - 2
n
1) ; n sans dimension ==> [RH] = [L]-1 1pt

Page 2 of 2
EXERCICE 3 ( 5 points ) Quantité de mouvement et effet Compton
c.
RH = ch.
10.6,1.E 19
0
avec E0 = 13,6 eV on trouve RH = 1,09.107 m-1
1 pt
d.
On a :
n
1
= RH . ( 1 - 2
n
1) ; λmin n →∞ alors λmin = 1 / RH et donc λmin = 91,7 nm
λmax n = 2 alors λmax = 122 nm
1 pt
e. *D’après le texte pour la raie « Lyman-alpha » on a λ = 121,5 nm ≈122 nm ,
il s’agit donc d’après la question précédente de la transition entre n =1 et n = 2
* ΔE = E
2
– E
1
= 10,6 eV
0,5pt
3.
a. * équation-bilan :
ch. = WS + Ecmax ; pour Ec = 0 on a λS ; on trouve alors : λS = 289.10-9 m = 289 nm
0,5pt
b.
* λ < λS il y a effet photoélectrique et par suite un électron est arraché et aura une vitesse v .
*
ch. = WS + Ecmax on trouve Ec en J et EC = ½.m.V2 ; on calcule v = 14.105 m.s-1 .
1pt
1
/
2
100%