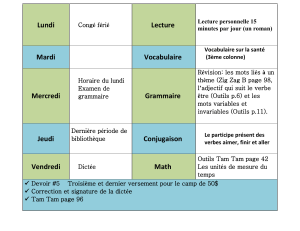
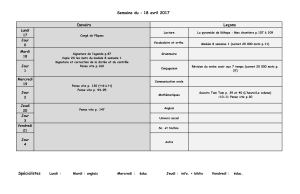
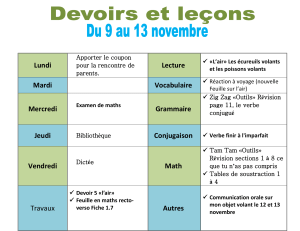
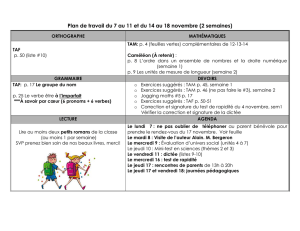
Hormone modulation in women with Hereditary angioedema

Hormones and Hereditary
angioedema benefits
and dangers
Anne Gompel, Isabelle Boccon-Gibod,
Laurence Bouillet, David Launay, Ludovic
Martin, Aurélie DuThan, Olivier Fain, and
CRéAK

Disclosures: none with this talk
•Research Grant CIFRE HRA-Pharma: Antiprogestin
in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers
•Research grant Luteron for Estetrol
•Consultant Pfizer: benzedoxifene/CE
•Consultant Richter: on contraceptive agents
•Shire: Advisory board Firazyr France
•Behring: Advisory board Berinert France
•Lectures given for Bayer, Besins, Novartis,
Viropharma…
•Attendance to congresses: Shire, Viropharma

Hormones and AE
estrogens
antiandrogens
androgens

estradiol Progesterone
androgens
Menstrual cycles: endogenous
estradiol Progesterone
Pregnancy: endogenous
Contraception: exogenous
Estrogens:
Ethinyl-E2
estradiol
Progestins
PR, AR, ER,
MR

Progesterone: PR, AR(-), MR(-)
Normethyltestosterone derivatives:PR, AR(+), ER, GR±
Norethisterone/norethindrone, NET acetate, Lynestrenol : AGP
Etonogestrel, norgestrel : POP
Pregnanes: PR, ±AR, ±GR
MPA: glucocorticoid and androgen agonist
Chlormadinone acetate : no AR, no GR AGP
Cyproterone acetate strong anti AR, GR± AGP
Norpregnane
Nomegestrol acetate PR, AR? AGP
Spironolactone, drospirenone PR, MR(-),AR(-)
Non-selectivity of synthetic progestins
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
1
/
35
100%