Phylum - Adam Oliver Brown

1
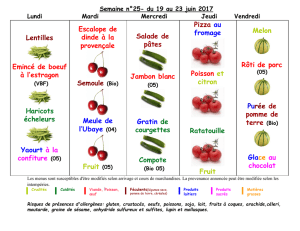
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
1
Bryozoa (Ectoprocta)
Hickman et al., Chap. 9
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
2
Évidence moléculaire!
Protista!
Animalia!
Porifera!
Cnidaria!
Ctenophora!
Platyhelminthes!
Gastrotricha!
Gnathostomulida!
Cycliophora!
Rotifera!
Annelida!
Mollusca!
Sipuncula!
Nemertea!
Bryozoa!
Brachiopoda!
Phoronida!
Arthropoda!
Onychophora!
Tardigrada!
Nematomorpha!
Nematoda!
Priapulida!
Kinorhyncha!
Loricifera!
Echinodermata!
Hemichordata!
Chordata!
Ecdysozoa!
Lophotrochozoa!
Platyzoa!
Lophophora!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
3
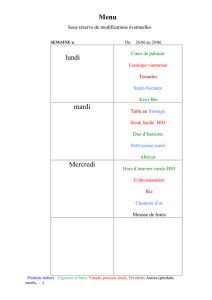
Taxonomie Lophophore
• Phylum Bryozoa
(Ectoprocta)
• Phylum
Brachiopoda
• Phylum Phoronida
Bryozoa (Canda)!

2
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
4
Coelome triparti
Bouche!
Protocoel!Mésocoel!Métacoel!
Anus!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
5
Coelome triparti
Lophophore!
(Mésocoel)!
Épistome!
(Protocoel)!
Cavité!
(Métacoel)!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
6
Avantages d’un coelome
• Espace pour de plus gros organes
• Les fluides peuvent être utilisés pour le transport
• Agit en tant que squelette hydrostatique
• Le tube digestif peut bouger indépendamment de
la paroi corporelle
• Ce n’est pas le cas chez les pseudocoelomates

3
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
7
Lophophore
Tentacules ciliées!
Bouche!
Anus!
Ganglion!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
8
Tube digestif en U (complet)
Bouche!
Pharynx!
Estomac pylorique!
Cecum!
Estomac cardiaque!
Rectum!
Anus!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
9
Termes uniques aux Bryozoa
• Zoarium: colonie
• Zoécium:
exosquelette non
vivant
• Polypide: lophophore
et masse viscérale,
peut être rétracté
dans le cystide
• Cystide: exosquelette
et partie vivante qui le
sécrète

4
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
10
Lophophore!
Zoarium des Bryozoa (colonie)
Zoécium ou!
cystid!
Polypide!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
11
Bryozoa dulcicole
Funicule!
Statoblaste!
Testicule!
Statoblaste: bourgeon produit asexuellement pour résister aux mauvaises conditions!
Funicule: connection entre les individus de la colonie!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
12
Bugula colonie!
Lophophore!
Bouche!
Zoécium!
Bourgeon polypide!
Avicularia!
Ovicell!

5
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
13
Avicularia
Pédicel!
Mandibule!
Vieux !
polypide!
Bec!
Muscle abducteur!
Muscle!
adducteur!
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
14
Alimentation bryozoaire
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
BIO 2535 - Animaux: Structures et fonctions
15
Ecologie
• Se nourrissent par
filtration
• Forment des
croûtes sur les
matières solides,
incluant les
coques de bateaux
 6
6
1
/
6
100%