Apprentissage symbolique et statistique à l`ère du mariage pour tous

Apprentissage : humain vs. machine
Les apprentissages d’un enfant
marcher : un an
parler : deux ans
raisonner : le reste

Apprentissage : humain vs. machine
Les apprentissages d’un enfant
marcher : un an
parler : deux ans
raisonner : le reste

Apprendre à raisoner

Symbolique et statistique : une opposition historique
Deux visions de l’apprentissage des machines
Expliquer : trouver un model
Prédire : améliorer des performances
Deux disciplines scientifiques concernées
Informatique
Statistique
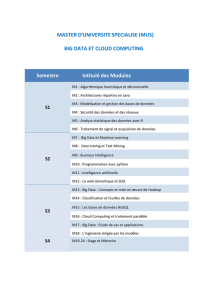
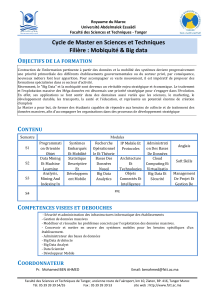
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
1
/
21
100%