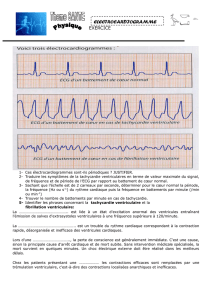
[pastel-00939082, v1] Estimation du risque de mort subite par arrêt

THÈSE DE DOCTORAT DE
L’UNIVERSITÉ PIERRE ET MARIE CURIE
École doctorale :
École doctorale Informatique, Télécommunications et Électronique (Paris)
Présentée par
M. Charles-Henri CAPPELAERE
Pour obtenir le grade de
DOCTEUR de l’UNIVERSITÉ PIERRE ET MARIE CURIE
Spécialité
Électronique
Sujet de la thèse :
Estimation du risque de mort subite par arrêt cardiaque
à l'aide de méthodes d'apprentissage artificiel
soutenue le 31 janvier 2014
devant le jury composé de :
M. Gérard Dreyfus Co-directeur de thèse
M. Rémi Dubois Co-directeur de thèse
M. Guy Carrault Rapporteur
M. Olivier Meste Rapporteur
Mme Sylvie Thiria Examinateur
M. Patrick Gallinari Examinateur
M. Ghassan Moubarak Examinateur
Mme Amel Amblard Examinateur
pastel-00939082, version 1 - 30 Jan 2014

Page 2
pastel-00939082, version 1 - 30 Jan 2014

Page 3
Résumé
On dénombre plus de 40 000 cas de morts subites en France, chaque année. Depuis le
début des années 2000, le défibrillateur automatique implantable (DAI) est prescrit de manière
prophylactique aux populations à risque. Nombre de ces implantations semblent prématurées :
une étude récente a révélé que
délivré de thérapie pendant le
problème en raison des complications post-un
défibrillateur implantable. Avec la rupture de sonde, les chocs électriques engendrés inutilement
-à- les
complications les plus fréquentes : des études ont montré que 13% à 17% des patients porteurs
ceptible de fragiliser le tissu
cardiaque. Il apparaît donc important de mieux définir la population à risque de mort subite, afin
Le pouvoir prédictif de mort subite des différents descripteurs des enregistrements
mémoire, nous présentons
lter que nous avons menée. Nous
mettant à profit les connaissances ph
originale de conception
es
()
pas opportune.
exposée dans la présente étude à une base de données de plus grande dimension, et de contenu
mieux adapté à nos objectifs.
Mots clés :
mort subite, défibrillateur automatique implantable, prévention primaire, triangle de
Coumel, apprentissage statistique, sélection de variables, réseau de neurones.
pastel-00939082, version 1 - 30 Jan 2014

Page 4
pastel-00939082, version 1 - 30 Jan 2014

Page 5
Abstract
Over 40,000 sudden cardiac deaths (SCD) occur per year in France. Implantable
patients at high risk of SCD. Unfortunately, most implantations to date appear unnecessary:
according to a recent study, 81% of the implanted ICDs were not used during the first five years
following the implantation. This result raises an important issue because of the perioperative and
postoperative risks. It has been shown in two studies that 13% to 17% of ICD-implanted
patients have undergone at least one inappropriate shock (i.e. a shock generated by the
-up periods; these shocks
are known to be detrimental to the cardiac muscle. Thus, it is important to improve the selection
of the candidates to ICD implantation in primary prevention.
Risk stratification for sudden cardiac death based on long-term electrocardiographic
(Holter) recordings has been extensively performed in the past, without resulting in a significant
improvement of the selection of candidates to ICD implantation. The present report describes a
nonlinear multivariate analysis of Holter recording indices. We computed all the descriptors
available in the Holter recordings present in our database. The latter consisted of labelled Holter
recordings of patients equipped with an ICD in primary prevention; a fraction of these patients
received at least one appropriate therapy from their ICD during a 6-month follow-up. Based on
physiological knowledge on arrhythmogenesis, feature selection was performed, and an
innovative procedure of classifier design and evaluation was proposed. The classifier is intended
to discriminate patients who are really at risk of sudden death from patients for whom ICD
implantation does not seem necessary. In addition, we designed an ad hoc classifier that
capitalizes on prior knowledge on arrhythmogenesis.
We conclude that improving prophylactic ICD-implantation candidate selection by
automatic classification from Holter recording features may be possible. Nevertheless, that
statement should be supported by the study of a more extensive and appropriate database. This is
mandatory for decreasing the rate of false negatives (i.e. the proportion of patients who are not
deemed to be at risk although they actually are), hence increasing the negative predictive value of
our method.
Keywords:
sudden cardiac death, implantable cardioverter defibrillator, primary prevention,
, machine learning, feature selection, neural network.
pastel-00939082, version 1 - 30 Jan 2014
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
 101
101
 102
102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
 109
109
 110
110
 111
111
 112
112
 113
113
 114
114
 115
115
 116
116
 117
117
 118
118
 119
119
 120
120
 121
121
 122
122
 123
123
 124
124
 125
125
 126
126
 127
127
 128
128
1
/
128
100%