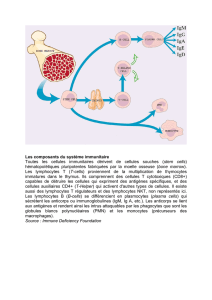
Etat actuel des connaissances sur les mécanismes d

MISE AU POINT Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421
415
Etat actuel des connaissances sur les mécanismes d’action du B.C.G.
Jean-Jacques PATARD (1), François GUILLÉ (1), Bernard LOBEL (1), Clément Claude ABBOU (2),
Dominique CHOPIN (2)
(1) Service d’Urologie, Hôpital Pontchaillou, Rennes, France
(2) Centre de Recherche Chirurgicale, Hôpital Henri Mondor, Créteil, France
RESUME
La connaisance de l’immunité anti-tumorale a per-
mis de progresser dans la compréhension des méca-
nismes d’action du B.C.G.
Il existe trois phases dans la réponse immunitaire
au B.C.G. Tout d’abord, le B.C.G. adhère puis est
phagocyté par les cellules présentatrices d’anti-
gènes mais aussi par les cellules urothéliales. A cette
phase correspond la libération précoce de cytokines
dites inflammatoires (l’IL-1, l’IL-6, l’IL-8). Ces
cytokines pourraient être en cause dans certains
effets indésirables mais elles pourraient également
participer au phénomène cytotoxique.
La deuxième phase est la reconnaissance des anti-
gènes bactériens par les lymphocytes CD4, qui libè-
rent principalement de l’IL-2 et de l’IFN-γ(réponse
TH1). Cette activation cellulaire va aboutir à la
troisième phase qui est l’amplification de popula-
tions cytotoxiques: CD8, Lymphocytes γδ, macro-
phages, NK, LAK, BAK. Toutes ces cellules lar-
guent elles aussi des cytokines qui vont réguler la
réponse. La connaissance de ces modulations rend
possible la rationalisation des protocoles d’instilla-
tions, mais l’identification des éléments réellement
cytotoxiques permettrait de proposer des protocoles
d’immunisation plus efficaces.
Mots clés : Cancer de vessie, vaccin B.C.G.
Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421.
Les tumeurs superficielles de vessie sont caractérisées
par leur fort potentiel de récidive et de progression [41].
Cependant le terme «superficiel» englobe un spectre bio-
logique de tumeurs très large. En effet, certaines tumeurs
peuvent récidiver mais progressent rarement. Ainsi une
tumeur TaG1 a un risque de progression évalué à 2%
[27]. En revanche, une tumeur T1G3 a au moins 40% de
risque de progresser [28] et un carcinome in situ (CIS) a
de 60 à 80% de risque de progression [30].
Le B.C.G. est à la fois un traitement préventif de la
récidive et de la progression des tumeurs superficielles
à haut risque [14] mais aussi un traitement curatif hau-
tement efficace du carcinome in situ [30].
De nombreuses études ont été faites afin d’élucider les
mécanismes d’action anti-tumorale du B.C.G. Elles ont
concerné essentiellement : les infiltrats inflammatoires
vésicaux après traitement [7, 20, 40, 56], les cytokines
urinaires [5, 8, 17, 23, 49, 52] et plus récemment les
mécanismes de cytotoxicité induits in vitro par le
B.C.G. [9, 63, 64]. En l’état actuel des connaissances
on ne peut cependant toujours pas dire si la cytotoxici-
té induite par le B.C.G. est une cytotoxicité spécifique
dirigée contre des antigènes bactériens ou des anti-
gènes tumoraux ou complètement aspécifique du fait
d’une réponse immunitaire large.
On sait cependant qu’il existe schématiquement trois
phases à la mise en action des mécanismes anti-tumo-
raux du B.C.G. : une phase d’adhésion et d’internalisa-
tion, une phase de présentation antigénique, et enfin
une phase de cytotoxicité.
Le but de cet article est de faire le point sur l’état des
connaissances des mécanismes d’action anti-tumoraux
du B.C.G. au travers de ces trois phases et de suggérer
les implications de la connaissance de ces mécanismes
dans le cadre de l’immunothérapie anti-tumorale.
ADHESION ET INTERNALISATION
BACTERIENNE
Le B.C.G. adhère aux cellules urothéliales et la fibro-
nectine semble être le principal agent liguant du B.C.G.
sur les cellules épithéliales [1, 53, 54]. Il a été démon-
tré que l’adhésion à la fibronectine était nécessaire à
l’activité anti-tumorale du B.C.G. et que l’augmenta-
tion de la liaison à la fibronectine pouvait également
augmenter l’effet anti-tumoral du B.C.G. [29, 53]. Ce
site est situé sur la chaîne carboxyterminale de la fibro-
nectine [12]. Les glycosaminoglycanes pourraient éga-
lement être un autre site de fixation [60].
Il a été montré que des cellules autres que les macro-
phages et les cellules présentatrices pouvaient présen-
ter des antigènes aux cellules lymphocytaires T. Par
exemple les cellules urothéliales activées qui expri-
ment les molécules du complexe majeur d’histocompa-
Manuscrit reçu : janvier 1998, accepté : mars 1998.
Adresse pour correspondance : Dr.J . J . Patard, Service d’Urologie, Hôpital
Pontchaillou, 2, rue Le Guilloux, 35000 Rennes.

416
tibilité (CMH) de classe II peuvent présenter des anti-
gènes mycobactériens aux cellules CD4. LATTIME a
montré dans un modèle de tumeur de vessie murin que
les cellules urothéliales tumorales étaient capables de
présenter des antigènes du B.C.G. à des cellules T CD4
spécifiques dans le cadre d’une restriction du CMH de
classe II [38]. D’ailleurs les cellules urothéliales
comme les cellules présentatrices peuvent libérer des
cytokines telles que l’IL-1, l’IL-6 [22, 26]. Par ailleurs
l’expression des molécules d’histocompatibilité de
classe I et de classe II sur les cellules urothéliales est
augmentée après BCGthérapie augmentant par là
même la capacité des cellules urothéliales à présenter
l’antigène [48, 57].
Il a également été montré que les cellules urothéliales
tumorales étaient capables d’internaliser le B.C.G.
[4, 37]. D’autres cellules tumorales comme les sar-
comes sont également capables de phagocyter le
B.C.G. [19].
LA PRESENTATION ANTIGENIQUE
Le concept de présentation antigénique
Les antigènes exogènes sont habituellement présentés
aux cellules T par les molécules de classe II du com-
plexe majeur d’histocompatibilité alors que les anti-
gènes endogènes sont présentés par les molécules
d’histocompatibilité de classe I. Les molécules d’his-
tocompatibilité de classe II sont exprimées unique-
ment par des cellules présentatrices d’antigènes spé-
cialisées : macrophages, lymphocytes B, cellules den-
dritiques et cellules de Langerhans. Les molécules
d’histocompatibilité de classe I sont exprimées par
toutes les cellules. Les cellules présentatrices d’anti-
gènes apprêtent et présentent les antigènes exogènes
qui sont dégradés en petits fragments dans les lyso-
somes qui se lient ensuite aux molécules de classe II,
avant de migrer à la surface de la cellule. Le complexe
CMH de classe II-peptide est alors reconnu par les
lymphocytes CD4 T Helper [2]. Les antigènes endo-
gènes sont apprêtés dans le cytoplasme où ils sont cli-
vés en peptides et transportés dans le réticulum endo-
plasmique avant d’être lié aux molécules d’histocom-
patibilité de classe I. Le complexe molécule d’histo-
compatibilité de classe 1 et peptide arrive à la surface
de la cellule où il est reconnu par les lymphocytes T
cytotoxiques CD8 [6, 10].
Le rôle des macrophages dans la présentation antigé-
nique aux cellules CD4 est essentiel dans l’activité
anti-tumorale induite par le B.C.G. En eff e t ,
THANHAUSER a montré que la déplétion du sang péri-
phérique en cellules mononuclées aussi bien qu’en
CD4 était capable d’abolir la cytotoxicité médiée par le
B.C.G. [64].
Les antigènes mycobactériens
Durant une infection mycobactérienne les macrophages
apprêtent les antigènes mycobactériens et libèrent des
cytokines: IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-l0, IL- 12, TNF-α,
I F N -α, IFN-γ. Les antigènes mycobactériens sont pré-
sentés à la surface de la cellule par les molécules du
CMH de classe II aux lymphocytes CD4 qui sont alors
activés. Les infections mycobactériennes induisent pré-
férentiellement une réponse T Helper1 (TH1) : libéra-
tion d’IL-2 et IFN-γ[24]. La réponse immunitaire indui-
te par l’infection mycobactérienne concerne aussi bien
les lymphocytes T α β (CD4 ou CD8), γ δ que des cel-
lules effectrices non spécifiques telles que les cellules
Natural Killer (NK) et les macrophages [32, 34, 43]. Les
antigènes de Mycobactérium tuberculosis qui induisent
une réponse immunitaire protectrice ne sont pas parfai-
tement caractérisés. Néanmoins on connaît un certain
nombre d’antigènes de surfaces tels que les antigènes de
12, 14, 19, 35, 65 et 71 kilodaltons. Les antigènes sécré-
tés ont aussi été identifiés comme étant de 10, 19, 30, 38
et 85 kilodaltons [3]. Z
L O T TA
a montré que les lympho-
cytes sanguins des patients traités par B.C.G. prolifé-
raient significativement plus qu’une population témoin
en réponse à l’antigène 85 in-vitro [68].
Les antigènes tumoraux
La description des antigènes de rejet des tumeurs
(TRA) représente une avancée majeure dans la com-
préhension des mécanismes de rejet des tumeurs.
Classiquement ces antigènes de rejet des tumeurs sont
présentés à la surface de la cellule tumorale par les anti-
gènes de classe I du CMH et sont reconnus par des
lymphocytes T cytotoxiques CD8 (Figure 1). Les gènes
Figure 1. L’antigène de rejet tumoral (TRA) est présenté à la
surface de la cellule par une molécule HLA de classe I.Ce
complexe HLA et TRA est reconnu par un lymphocyte T CD8
cytotoxique spécifique (CTL).Ce CTL est capable de lyser la
cellule tumorale.
J.J. Patard, Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421

codant pour ces antigènes ont été caractérisés et la pre-
mière famille de gènes décrite a été la famille des gènes
MAGE [65]. Ces gènes ne sont pas exprimés dans les
tissus normaux, ils sont exprimés très fréquemment
dans le mélanome mais aussi dans certains autres types
de tumeurs dont les tumeurs de vessie [44].
Le traitement par B.C.G. augmente l’expression des
molécules de classe I et de classe II sur les cellules uro-
théliales [48, 57]. La surexpression des molécules de
classe I sur les cellules urothéliales peut suggérer la
reconnaissance spécifique des antigènes tumoraux à la
surface de la cellule par des cellules CD8. Ceci est étayé
par certains travaux qui ont montré que l’expression des
molécules de classe I était corrélée à la réponse au
B.C.G. [59] et qu’en immuno-histochimie et en fluoro-
cytométrie les cellules type CD8 étaient largement pré-
sentes dans la vessie après BCGthérapie. Néanmoins
aucun argument définitif expérimental n’existe à l’heu-
re actuelle pour penser que le B.C.G. induit une recon-
naissance spécifique d’antigènes tumoraux. Une maniè-
re élégante de faire la synthése des deux théories (anti-
gène bactérien et antigène tumoral) serait d’admettre
comme le suggère Z
LOTTA
qu’il existe des antigènes
croisés entre le B.C.G. et les tumeurs vésicales [69].
CYTOTOXICITE ANTI-TUMORALE
Les cellules cytotoxiques
Les différentes cellules pouvant avoir un effet cytotoxique
sur les cellules tumorales après activation par le B.C.G.
sont les lymphocytes T αβ, γδ, les cellules NK,
Lymphokine activated Killer (LAK), B.C.G. activated
Killer (BAK), et enfin les macrophages. La preuve que la
réponse anti-tumorale du B.C.G. est médiée par une
réponse T a été fournie par une expérimentation de
R
AT L I F F
qui a démontré que la souris athymique n’était
pas capable d’éliminer une tumeur après traitement par
B.C.G. et que la déplétion en cellule CD4 ou en cellule
CD8 chez la souris supprimait également l’effet anti-
tumoral du B.C.G. [52, 55]. Par ailleurs de nombreux
auteurs ont démontré que les lymphocytes CD4 et CD8
étaient présents dans la paroi vésicale après B.C.G. et que
le phénotype de type CD4 était prédominant [7, 20, 40,
4 7 ] .
Les lymphocytes de type CD4
Les lymphocytes de type CD4 dit lymphocytes
«T Helper» sont composés de deux sous groupes : les
lymphocytes TH1 et TH2. Cette distinction repose sur
le profil de libération des cytokines. En effet, les lym-
phocytes de type TH1 libèrent de l’IL-2, du TNF-β, de
l’IFN-γet sont principalement recrutés dans la réponse
cellulaire. La réponse TH2 est faite d’une production
d’IL-4, d’IL-5 et d’IL-10 et oriente vers une réponse de
type humorale. Elle peut par ailleurs inhiber la réponse
TH1. l’IL-2 et l’IFN-γont été largement mis en évi-
dence dans les urines après B.C.G. alors que l’IL-4 ne
l’a jamais été [31]. MCAVENEY a étudié sur un modèle
expérimental de tumeur urothéliale murin la modula-
tion des cytokines par le B.C.G. [42]. Il a montré que
l’ARN messager des cytokines après implantation
d’une tumeur de type MB49 était associée à une
expression d’IFN-γet d’IL-4. Le B.C.G. augmentait
significativement l’IFN-γet réduisait l’expression de
l’IL-4, si bien que le phénotype dominant correspon-
dant à la réponse antitumorale médiée par le B.C.G.
était de phénotype TH1. L’IL-10 a cependant été détec-
tée dans les tissus et les urines de patients traités par
B.C.G. [31, 39]. Compte tenu de ce que l’on connaît du
rôle du phénotype TH1 dans la réponse cellulaire il
serait maintenant intéressant de savoir si l’apparition
d’un profil TH2 urinaire après BCGthérapie serait lié à
une mauvaise réponse au traitement [58].
Les lymphocytes T CD8
On a vu que l’expression des antigènes de classe II et
le recrutement des lymphocytes CD4 étaient activés
par le B.C.G. mais il a également été montré que les
lymphocytes T CD8 spécifiques pouvaient reconnaître
des antigènes mycobactériens. Ces lymphocytes T
cytotoxiques (CTL) étaient capables de lyser des cel-
lules infectées par la mycobactérie et produisaient de
l’IFN-γ[34). On sait qu’à l’état basal le phénotype de
type CD8 est prédominant dans la vessie normale et
que le traitement par le B.C.G. renverse le rapport en
rendant le phénotype CD4 prédominant [20]. Là enco-
re ces lymphocytes CD8 présents dans la vessie après
BCGthérapie n’ont pas été parfaitement caractérisés et
on n’est pas actuellement en mesure de dire s’ils recon-
naissent des antigènes bactériens plutôt que des anti-
gènes tumoraux.
Les lymphocytes T γδ
Les lymphocytes T γδ sont également des lymphocytes
cytotoxiques. Ils n’expriment pas habituellement le
phénotype CD4 ni le phénotype CD8 et leur reconnais-
sance de l’antigène n’est pas restreinte par le système
d’histocompatibilité. Les lymphocytes T γδ peuvent
reconnaître les antigènes mycobactériens, des protéines
virales et notamment des «heat-shock» protéines et des
super antigènes [25, 32]. Les lymphocytes T γδ produi-
sent des cytokines comme l’IL-2, l’IL-4 et l’IFN-γ.
Nous avons étudié en immunohistochimie la cinétique
des lymphocytes T γδ avant et à différents moments
après traitement par le B.C.G.. L’expression des lym-
phocytes T γδ était très augmentée trois semaines après
le traitement et était maximale à trois mois [57]. WANG
a bien montré que les lymphocytes T γδ provenant
d’individus sains, activés par mycobactérie in vitro,
étaient capable de lyser des tumeurs de vessie, des
lignées tumorales vésicales sans restriction CMH [67].
417
J.J. Patard, Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421

Les cellules NK, LAK, BAK
Trois groupes de lymphocytes cytotoxiques peuvent
être impliqués dans l’immunité anti-tumorale induite
par le B.C.G. et ce de manière non spécifique : les cel-
lules NK, LAK et BAK. Les cellules NK représentent
un groupe particulier de lymphocytes qui sont distincts
des lymphocytes T, B et des cellules lymphocytaires.
Les cellules NK n’expriment pas l’antigène CD3 ou les
chaînes α, β, γ ou δdu récepteur T. Leur phénotype est
habituellement CD3-, CD2+/-, CD8+/-, CD16+/-,
CD56+. Les cellules NK constituent le principal pré-
curseur des cellules LAK. Les cellules NK et les cel-
lules LAK sont capables de lyser les cellules tumorales
vésicales après stimulation par B.C.G. in vitro [35].
BÖHLE a testé la capacité des lymphocytes périphé-
riques à lyser des lignées tumorales vésicales dans dif-
férentes conditions expérimentales. Le B.C.G. seul, les
cytokines, les lymphocytes périphériques non stimulés
étaient incapables de tuer les cellules tumorales alors
que les LAK et les lymphocytes incubés avec le B.C.G.
vivant exercaient une lyse significative de certaines
lignées tumorales vésicales [9]. Cependant les expéri-
mentations ont été conduites in-vitro et on ne connaît
pas réellement le rôle des cellules NK et LAK contre
les tumeurs de vessie in vivo. Par étude immunohisto-
chimique des biopsies de la paroi vésicale nous avons
observé peu de cellules NK trois semaines après traite-
ment [57].
Les macrophages
Le rôle des macrophages dans la cytotoxicité induite
par le B.C.G. est suggéré mais non prouvé [21].
Plusieurs études ont montré l’activité cytotoxique des
monocytes et des macrophages contre les tumeurs de
vessie après stimulation in-vitro par le B.C.G. [13, 36,
50]. Par ailleurs la libération de NO-synthétase par les
macrophages a également été documentée après traite-
ment par le B.C.G. [33].
Les cytokines
Les cellules immunocompétentes communiquent entre
elles par des cytokines qui ont des fonctions de crois-
sance, d’immunomodulation et également un rôle cyto-
toxique. De nombreux travaux ont montré que les cyto-
kines étaient présentes dans les urines des patients trai-
tés par le B.C.G. [5, 8, 15, 23, 31, 49, 51]. Cependant
l’origine de ces cytokines est multiple (Tableau 1). Les
macrophages peuvent libérer de l’IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-
10, IL-12, TNF-α, IFN-α, IFN-γ[11]. Les cellules TH1
libèrent classiquement de l’IL-2 et de l’IFN-γet les cel-
lule TH2 libèrent de l’IL-4, de l’IL-5 et de l’IL-10. Les
lymphocytes T CD8 produisent de l’IL-2 et de
l’IFN-γ, les cellules T γδ produisent de l’IL-2, de l’IL-
4 et de l’IFN-γ. Les cellules NK et LAK peuvent éga-
lement produire du TNF-αet de l’ IFN-γ. Les cellules
urothéliales normales peuvent produire de l’IL-6 [66].
Les cellules urothéliales tumorales peuvent produire de
l’IL-1, de l’IL-6, de l’IL-10 et du TNF-α[18, 22, 21, 39].
J
A C K S O N
a étudié la cinétique de certaines cytokines
après traitement par le B.C.G. [31]. L’IL-1, l’IL-6, IL-8,
IL-10 sont détectées tôt dès la première instillation après
BCGthérapie. Les autres cytokines comme l’IL-2, le
T N F -αet l’IFN-γsont détectés plus tard à partir de la
troisième instillation. Nous avons ainsi mis en évidence
que l’IFN-g urinaire après BCGthérapie était maximum
4 à 6 heures après la 5 ème ou 6 ème instillation [45]. On
peut donc penser que les macrophages et les cellules uro-
théliales sont responsables de la production initiale de
cytokines de type inflammatoire; ces cytokines pour-
raient d’ailleurs être responsables des effets indésirables
précoces du B.C.G. [61]. Cependant leur rôle antitumo-
ral n’est pas exclu car leur production, notamment pour
l’IL8, pourrait être corrélée à la réponse [16, 62]. Les
cytokines telles que l’IL-2 et l’IFN-γseraient produites
par les lymphocytes T activés. L’IL-4 n’est pas retrouvé
dans les urines après BCGthérapie ce qui confirme le
recrutement préférentiel de cellules TH1 [31]. Il semble
maintenant établi que le profil de réponse immunitaire
favorable au B.C.G. est le phénotype TH1 [42, 58]. Ainsi
nous avons pu montrer que les patients qui produisaient
plus de 20 pg/ml d’IL-2 ou 100 pg/ml d’IFN-γdans les
urines à la cinquième instillation récidivaient significati-
vement moins que les autres patients [46]. Ceci est une
preuve supplémentaire quoique indirecte de l’importance
de la réponse T dans l’activité antitumorale du B.C.G. La
Figure 2 résume l’ensemble des cellules intervenant dans
la réponse immunitaire au B.C.G. et la modulation excer-
cée par les cytokines.
CONCLUSION
Si les différentes étapes de la réponse immunitaire anti-
tumorale générée par le B.C.G. semblent maintenant
bien connues, il reste encore à établir le rôle précis des
médiateurs qui permettent les communications entre
ces différentes étapes (cytokines). En effet on a pu éta-
418
Tableau 1. Cytokines produites par les différentes cellules
intervenant dans la réponse immunitaire au BCG endovési -
cal.
Cellules Cytokines
Macrophages IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL 12,
TNF-α, IFN-α, IFN-γ
Cellules urothéliales normales IL-6
Cellules tumorales IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α
Lymphocytes T CD4 Th1 IL-2, IFN-γ
Lymphocytes T CD4 Th2 IL-4, IL-5, IL-10
Lymphocytes T CD8 IL2, IFN-γ
Lymphocytes T γδ IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ
J.J. Patard, Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421

blir que deux groupes principaux de cytokines étaient
générés dans les tissus et les urines : des cytokines
inflammatoires et des cytokines témoignant de l’activa-
tion lymphocytaire T. De nouvelles expériences sont
nécessaires afin de déterminer si ces cytokines inter-
viennent directement dans la lyse ou si elles ne sont que
des messagers entre les differentes cellules immuno-
compétentes. Par ailleurs, au sein des cytokines corres-
pondant à une activation T, le profil TH1 (IL-2, IFN-γ)
est corrélé à une réponse antitumorale efficace. Cette
donnée mérite d’être mieux explorée afin d’améliorer
et de rationaliser les protocoles d’instillations endové-
sicales.
Les cellules effectrices cytotoxiques sont également un
point d’interrogation : l’étape cytotoxique est-elle sous le
contrôle d’une lyse totalement aspécifique ou d’une
reconnaissance d’antigènes bactériens ou tumoraux?. La
réponse viendra de la caractérisation et du clonage des
d i f férentes populations lymphocytaires activées dans la
vessie après BCGthérapie. La connaissance des cellules
réellement cytotoxiques induites par le B.C.G. pourrait
conduire à des protocoles de traitement plus rationnels et
plus spécifiques d’une population tumorale donnée.
REFERENCES
1. ABOU-ZEID C., RATLIFF T.L., WIKER H.G., HARBOE M.,
BENNEDSEN J., ROOK G.A.W.Characterization of fibronectin-
binding antigens released by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and myco-
bacterium bovis B.C.G.. Infect. Immun., 1988, 56, 3046-3051.
2. ALLEN P.M., STRYDOM D., UNANUE F.R. Processing of lysozy-
me by macrophages: Identification of the determinant recognized by
two T-cell hybridomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 1984, 81, 2489-
2493.
3. AVERILL L.E., CAVALLO U., WALLIS R.S., BOOM W.H., BONA
M., MINCEK M., PASCOPELLA L., JACOBS W.R. JR., ELLNER
J.J. Screening of a cosmid library of Mycobacterium bovis B.C.G. in
Mycobacterium smegmatis for novel T-cell stimulatory antigens.
Res. Microbiol., 1993, 144, 349-362.
4. BECICH M.J., CARROL S., RATLIFF T.L. Internalisation of bacil-
lus Calmette-guerin by bladder tumor cells. J. Urol., 1991, 145,
1316-1324.
5. BETTEX-GALLAND M., STUDER U.E., WALZ A., DEWA L D
B., BAGGIOLINI M. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleu-
kin-8 detection in human urine during acute bladder inflamma-
tion caused by transurethral resection of superficial cancer and
bacillus Calmette-Guerin administration. Eur. Urol.,1991, 19,
1 7 1 - 1 7 5 .
6. BJORKMAN P.J., PARHAM P.Structure, function and diversity of
class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Annu. Rev.
Biochem., 1990, 59, 253-288.
7. BÖHLE A., GERDES A., ULMER A.J., HOFSTETTER A.G.,
FLAD H.D. Effects of local Bacillus Calmette Guerin therapy in
patients with bladder carcinoma on immunocompetent cells of the
bladder wall. J. Urol., 1990, 144, 53-58.
8. BÖHLE A., NOWC C.H., ULMER A.J.,MUSEHOL J., GERDES J.,
HOFSTETTER A.G., FLAD H.D. Elevations of cytokines interleu-
kin-1, interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor in the urine of patients
after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy. J. Urol.,
1990, 144, 59-64.
9. BÖHLE A., THANHAUSER A., ULMER A.J., ERNST M., FLAD
H.D., JOCHAM D. Dissecting the immunobiological effects of
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (B.C.G.) in vitro: evidence of a distinct
B.C.G.-activated killer (BAK) cell phenomenon. J. Urol., 1993, 150,
1932-1937.
10. BUUS S., SETTE A., COLON S., MILES C., GREY H.M. The rela-
tion between major histocompatibility complex (CMH) restriction
and the capacity of Ia to bind to immunogenic peptides. Science,
1987, 235, 1353-1358.
11. C AVAILLON J.M. Cytokines and macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother. ,
1994, 48, 445-453.
12. CHENG D.L., SHU W.P., CHOI J.C., MARGOLIS E.J., DROLLER
M.J., LIU B.C.Bacillus Calmette-Guerin interacts with the car-
boxyl-terminal heparin binding domain of fibronectin: implications
for B.C.G.-mediated antitumor activity. J. Urol., 1994, 152, 1275-
1280.
13. CONTI P., REALE M., NICOLAI M., BARBACANE R.C., PLA-
CIDO F.C., IANTORNO R., TENAGLIA R. Bacillus Calmette-
Guerin potentiates monocyte responses to lipopolysaccharide-indu-
ced tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, but not interleukin-6 in
bladder cancer patients. Cancer. Immunol. Immunother., 1994, 38,
365-371.
14. COOKSON M.S., HERR H.W., ZHANG Z.F., SOLOWAY S.,
SOGANI P.C., FAIR W.R. The treated natural history of high risk
superficial bladder cancer: 15 year outcome. J. Urol., 1997, 158, 62-
67.
15. DE BOER E.C., DE JONG W.E., STEERENBERG P.A., AARDEN
A.A., TETTEROO E., DE GROOT E;R., VAN DER MEIJDEN
P.D.J., BEGT P.D.J., DEBRUYNE F.M.J., RUITENBERG E.J.
Induction of urinary interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL2, IL6, and tumour
necrosis factor during intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus
Calmette-Guerin in superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol.
Immunother., 1992, 34, 306-312.
16. DE BOER E.C., SCHAMHART D.H., KURTH K.H., DE REIJKE
T.M., DE RUITER G.J., SOMOGYI L. Role of interleukin-8 in
onset of the immune response in intravesical B.C.G. therapy for
superficial bladder cancer. Urol. Res., 1997, 25, 31-34.
17. DE JONG W.H., DE BOER E.C., VAN DER MEIDJEN A.P.M.,
VEGT P., STEERENBERG P.A., DEBRUYNE F.M.J., RUITEN-
BERG E.J. Presence of interleukin-2 in patients after intravesical
treatment with bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Cancer Immunol.
Immunother., 1990, 31, 182-186.
419
J.J. Patard, Progrès en Urologie (1998), 8, 415-421
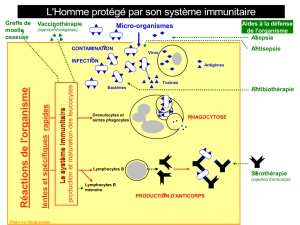
Figure 2. Représentation schématique des trois phases de la
réponse immunitaire au BCG : adhésion-internalisation, pré -
sentation antigénique et cytotoxicité.Les cytokines permettent
la communication entre les cellules immunocompétentes et
ont un rôle de régulation de la réponse immunitaire. La voie
TH1 est associée à une réponse antitumorale efficace.
 6
6
 7
7
1
/
7
100%