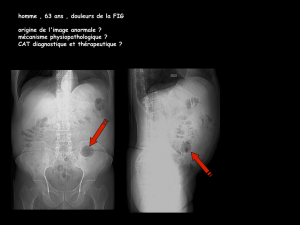
Traitement de la lithiase intradiverticulaire par abord percutané (à

RESUME
Dix neuf diverticules caliciels (chez 18 patients)
contenant une lithiase ont été traités.Tous les
patients étaient symptomatiques, 12 d’entre eux
ont été traités après échec de la lithotritie extra-
corporelle(LEC).
Les temps essentiels de l’abord percutané com-
p renaient : la ponction (“viser le divert i c u l e
c’est viser la pierre”) et le traitement de la
poche calicielle par coagulation à l’anse à boule,
puis drainage temporaire par sonde à ballonnet
ou lame de caoutchouc permettant d’obtenir
une sclérose irritative.
Aucune complication n’a été observée. Après un
échec de ponction 1 patient a refusé tout traite-
ment. Le drainage était de 48 heures en moyen-
ne, l’hospitalisation de 5 jours. Chez 3 patients
une séance de LEC complémentaire était néces-
saire.
A 1 mois, 13 diverticules sur 18 traités avaient
disparu à l’urographie intraveineuse (72%).
A 3 mois, disparition de la douleur chez 17
patients (94% des cas) et de la lithiase chez 15
patients (84%).
A l’issue de cette étude, la chirurgie per-cutanée
nous paraît être une technique efficace et sûre
dans le traitement de la lithiase intra-diverticu-
l a i re symptomatique surtout après échec de la
LEC.
Mots clés : Chiru rgie percutanée, lithiase, divert i c u l e
caliciel.
Progrès en Urologie (1993), 3, 959-963.
INTRODUCTION
Les diverticules caliciels peuvent être symptoma-
tiques et notamment contenir des calculs [9].
La présence de calculs dans un diverticule, fait
poser le problème de son traitement. Il n’est pas
toujours facile de mettre en évidence le diamètre
du collet du diverticule caliciel sur les explorations
radiographiques.
Lorsque le collet est étroit la lithotritie extra-cor-
porelle est souvent vouée à un échec bien qu’elle
améliore les symptômes tout en laissant la lithiase
en place [10, 14]. En revanche, il est parfois sur-
prenant d’observer l’élimination de la lithiase alors
que le collet apparaissait très étroit. La chirurg i e
p e r-cutanée est un traitement possible de cette
a ffection, permettant le traitement simultané du
calcul et de la poche diverticulaire. Nous avons
revu entre juillet 1987 et janvier 1993 le traitement
de 19 diverticules caliciels chez 18 patients.
MATERIEL ET METHODES
Les 18 patients se répartissaient en 13 femmes, 5
hommes, âgés de 42 ans en moyenne (22 à 69 ans).
Un patient, après échec de la ponction au cours de
la chirurgie percutané a refusé tout traitement com-
plémentaire. Tous les patients présentaient une
lithiase intradiverticulaire et tous étaient sympto-
matiques. Ils se répartissaient ainsi: douleurs lom-
baires chroniques (4 cas); coliques néphrétiques
et/ou associées à des douleurs lombaires chro-
niques ( 12 cas); infection urinaire (8 cas; dont 3
pyélonéphrites aiguës).
Manuscrit reçu le 28 septembre 1993
Adresse pour correspondance : Dr. K . Lagha, 2, Boulevard
Winston Churchill, 63000 Clermont-Ferrand.
Progrès en Urologie (1993), 3, 959-963
959
Traitement de la lithiase intradiverticulaire
par abord percutané (à propos de 19 diverticules caliciels)
Kamel LAGHA, Xavier MARTIN, Béatrice CUZIN, Albert GELET, Jean-Marie MARECHAL,
Olivier DESMETTRE, Jean-Michel DUBERNARD
Service d'Urologie et Chirurgie de la Transplantation, Hôpital Edouard Herriot, Lyon

A l’urographie intra-veineuse, le diverticule était
situé 13 fois à droite, 6 fois à gauche, 1 fois bilaté-
ral. Il était de siège cortical dans 15 cas (pôle supé-
rieur : 6; médio-rénal : 4; pôle inférieur : 5);
médullaire dans 3 cas ( pôle supérieur: 2, médio-
rénal : l ); intrasinusal dans l cas.
La lithiase était de diamètre supérieur à 20mm
dans 1 cas, de15 à 20 mm dans 4 cas, inférieur à 15
mm dans 14 cas.
Le diamètre de la lithiase correspondait le plus
souvent au diamètre du diverticule.
Des malformations ou anomalies urologiques asso-
ciées étaient observées : duplicité urétérale bilaté-
rale ( 1 cas); maladie de Cacchi-Ricci (1 cas); rein
unique congénital (l cas); lithiase coralliforme
associée (l cas).
1. Intervention
Pour le traitement par voie percutanée, tous les
patients étaient apyrétiques, ECBU stérile, créatini-
némie normale.
La technique comportait:
Montée de sonde urétérale (position de la taille),
habituellement bout biseau ch. 7, permettant l’opa-
cification des cavités excrétrices par du produit de
contraste dilué, ce qui facilite la ponction calicielle
sous amplificateur de brillance.
Ponction (patient en décubitus ventral): avec une
aiguille cathéter ( permettant l’aspiration continue)
ou loretto métallique mise au point par KORTH.
- Facile dans les diverticules caliciels periphe-
riques (pôle inférieur ou convexité).
- Difficile pour les diverticules caliciels médul-
laires, du pôle supérieur ou intrasinusaux nécessi-
tant une ponction au-dessus de la douzième côte ou
plus interne ( geste effectué de préférence sous
anesthésie générale, en raison du risque de pneu-
mothorax ). La ponction du diverticule s’eff e c t u e
en “visant” le calcul, au contact de celui-ci, l’on
injecte par la sonde urétérale du produit de contras-
te coloré au bleu de méthylène, dont l’issu par le
trajet de ponction confirme la bonne position de
l’aiguille. Cette ponction est guidée par l’amplifi-
cateur de brillance à bras permettant le repérage de
face et de profil.
Dilatation souvent hasardeuse car il est difficile
de travailler dans une petite cavité (inférieure à 15
mm en moyenne), le guide métallique s’enroulant
dans le diverticule . L’on peut très vite se retrouver
à dilater en “fausse route”
Mise en place du néphroscope : le repérage est
parfois difficile, car la cavité est petite. L’observa-
tion d’une muqueuse lisse est parfois le seul critère
objectif confirmant que l’on se trouve bien dans la
voie excrétrice du rein. Il faut alors rechercher le
calcul, qui est parfois situé en arrière de l’objectif
du néphroscope.
La fragmentation est en général facile car il
s’agit le plus souvent de calculs de phosphate, sou-
vent déjà fragilisés par les ondes de choc. Les ins-
truments utilisés le plus souvent sont la sonotrode,
le lithotriteur hydropneumatique ou la pince méca-
nique.
Traitement de la cavité : le pertuis de communi-
cation avec la voie excrétrice peut parfois être intu-
bé si l’on a la chance de pouvoir introduire un
guide. En cas de difficulté de repérage de ce per-
tuis l’injection de bleu de méthylène peut aider.
Lorsqu’il est possible de passer un guide jusque
dans le bassinet, le trajet peut être dilaté jusqu’à 26
ou 28 Charrière. Une sonde est laissée en place
quelques jours pour modelage. Lorsqu’il n’est pas
possible de cathétériser le chenal de communica-
tion, il faut tenter d’obtenir l’affaissement de la
poche, en provoquant une sclérose irritative par
coagulation de la paroi à l’anse à boule du résec-
teur et par positionnement d’une sonde en caout-
chouc au contact des parois de la poche.
2. La lithotritie extracorporelle.
En pré-opératoire: 12 lithiases intradiverticu-
laires ont été traitées par lithotritie extra-corporelle
première (l à 6 séances par calcul) sans effet sur
l’évacuation des calculs ou/et les douleurs.
Après chirurgie percutanée un traitement par
lithotritie extracorporelle complémentaire a été
réalisé chez 3 patients.
RESULTATS
Aucune complication liée à l’abord percutané n’a
été observée. Chez un patient la ponction a été
impossible et aucun autre traitement n’a été tenté.
960

Pour un autre patient un deuxième temps percuta-
né pour calcul résiduel intradiverticulaire a été
nécessaire. La lithotritie extracorporelle réalisée en
complément chez 3 patients pour calcul résiduel a
été un succès dans deux cas. La durée moyenne de
séjour des patients a été de 5 jours.
A 1 mois, absence de diverticule à l’urographie de
contrôle dans 13 cas sur 18 (72%).
A 3 mois, 17 patients sur 18 étaient asymptoma-
tiques (94%), avec absence de lithiase (abdomen
sans préparation et/ou échographie rénale) dans 15
cas (84%).
DISCUSSION
La revue de notre série, montre que l’on peut obte-
nir par abord percutané une disparition complète
de la lithiase dans environ 85% des cas, alors que
la disparition des symptômes est observée dans
prés de 95% des cas. La disparition de la poche
diverticulaire est, quant à elle obtenue dans plus de
70% des cas. Ces données sont semblables à celles
d’autres séries de la littérature [1, 4, 5]. Il est sur-
prenant de constater que même en présence de
fragments résiduels, les symptômes sont souvent
soulagés pour autant que la lithiase ait été frag-
mentée ou réduite en taille. Les résultats sur l’abla-
tion de la lithiase, sont similaires à ceux obtenus
sur des calculs rénaux non compliqués situés dans
des cavités rénales normales [8]. Ils sont très supé-
rieurs à ceux obtenus avec la lithotritie extracorpo-
relle (25 à 35% d’élimination complète) [4, 13]. La
morbidité associée à la chirurgie percutanée dans
ces cas est très faible et n’est pas spécifique de la
situation intra-diverticulaire du calcul [5].
En revanche la technique de ponction, de dilatation
et d’extraction des calculs intradiverticulaires est
plus délicate. Il est en effet difficile de ponctionner
ces cavités, surtout lorsqu’elles sont de petite
taille. Le siège polaire supérieure et médullaire est
aussi un critère de difficulté technique. Le passage
du guide est rendu difficile du fait de l’absence
d’espace entre la pierre et la paroi, et du fait de la
petite taille de la cavité qui impose d’enrouler le
guide dans celle-ci. La dilatation est aussi délicate
puisque elle peut facilement se poursuivre dans
une fausse route en dehors du rein. Ceci est
d’autant plus facile que le diverticule est superfi-
ciel et que la couche de parenchyme rénal le
recouvrant est mince.
Le cathétérisme du pertuis reliant le diverticule
aux voies excrétrices est souvent très diff i c i l e ,
même si on utilise des substances colorantes. Dans
le cas ou il est possible de passer un guide dans ce
pertuis il semble que la dilatation de celui-ci per-
mette un bon drainage et soit un bon moyen théra-
peutique. Dans la majorité des cas il est impossible
de retrouver l’orifice et l’on peut coaguler à l’anse
à boule la muqueuse du diverticule pour obtenir
son affaissement et l’accolement des parois. Cette
technique donne de bons résultats dans 80% des
cas [5 ].
CONCLUSION
Le traitement des calculs inclus dans des diverti-
cules caliciels ne doit s’adresser qu’aux cas symp-
tomatiques. La lithotritie extracorporelle permet
dans la majorité des cas de diminuer les symp-
tômes, mais n’obtient que 25 à 30% d’élimination
des fragments. Elle peut être tentée en première
intention surtout si l’analyse de la poche montre
un diverticule à collet court et large. L’abord per-
cutané de ces lithiases permet l’ablation de celles-
ci et le traitement de la cavité dans le même temps
opératoire avec un taux de réussite de l’ordre de
80%. La chirurgie ouverte, quant à elle, n’a pas été
utilisée dans cette série, elle pourrait s’adresser
aux diverticules géants qui sont en fait très rares.
REFERENCES
1. AMPLATZ K., LANGE PH. Atlas of endourologie-Ye a r
Book Medical Publishers, ed. Chicago, l984, 267-270.
2. CLAYMAN R.V.,SURYA V.,MILLER R.P., CASTANEDA-
ZUNIGA W.R., SMITH A.D., HUNTER D.H., AMPLATZ
K.:Percutaneous nephrolithotomy : extraction of rénal and
ureteral calculi from 100 patients. J.Urol., 1984, 131, 868-
871.
3. GELET A., DUBERNARD J.M. Atlas de chirurgie urolo-
gique : Chirurgie percutanée de la lithiase rénale. CUKIER
J., DUBERNARD J.M., GRASSET D., ed. Masson, 1991,
223-246.
4. HENDRIKX A.J.M., BIERKENSA F., BOS R., OOSTE-
RHOF G.O.N., DEBRUYNE M.J. : Treatment of stone in
caliceal divercitula : extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
versus percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy. B r.J . Urol., 1992,
70, 478-482.
961

5. HULBERT J.C., REDDY R.K., HUNTER D.W., CASTANE-
DA- ZUNIGA W., AM PLATZ K., LANGE Ph. :
Percutaneous techniques for the management of caliceal
containing calculi. J. Urol., 1986, 135, 225-227.
6. LANG E.K. : Percutaneous infundibuloplasty : management
of caliceal diverticula and infundibular stenosis.Radiology,
1991, 3, 871-877.
7. LE DUC A., CARIOU G., CORTESSE A., TEILLAC P. :
C h i r u rgie percutanée du rein. E.M.C., Paris, France.
Techniques chirurgicales, Urologie-gynécologie, 41088, 4,
10.06, 16p.
8. LINGEMAN J.E., COURY T.A., NEWMAN D.M. :
Comparison of results and morbidity of percutaneous
nephroslithotomy and extra corporeal shock wave lithotrip-
sy. J. Urol., 1987, 138, 485-489.
9. MANGIN PH., MITRE A., PASCAL B., CUKIER J. : Les
diverticules caliciels.J. Urol. (Paris), 1980, 86, 653-664.
10. MARTIN X., MOURIQUAND P., HENRIET M. et al. :
Lithotritie extracorporelle par onde de choc (Premiers résul-
tats 322 patients).J. Urol. (Paris), 1986, 3, 177-181.
11. MOSLI H., MAC DONALD P., SCHILLINGER J. :
Caliceal diverticula developing into simple rénal cyst. J .
Urol., 1986, 136, 658-661.
12. MOLLARD P. : Précis d'urologie de l'enfant. E d . M a s s o n ,
1984, 5-7.
13. PSIHRAMIS K.E., DRETLER S.P. : Extracorporeal shock
wave lithotripsy of diverticula calculi. J . Urol., 1987, 138,
707-711.
14. RITCHIE A.W.S., PARR N.J., MOUSSA S.A., TO L L E Y
D.A. : Lithotripsy for calculi in caliceal diverticula. B r.J .
Urol., 1990, 66, 6-8.
15. WULFSOHN M.A. : Pyelocaliceal diverticula. J . U r o l . ,
1980, 123, 1-8.
____________________
SUMMARY
We reviewed 18 patients with calculi in caliceal diverti -
cula (19 caliceal diverticula). All patients were sympto -
matic; 12 of them were treated after Extracorpore a l
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (E.S.W.L).
The main technical procedures in percutaneous nephro -
lithotomy are the direct puncture of the divert i c u l u m
( p recise puncture may be re q u i red to place the tract
d i rectly on to the stone), and treatement duration the
diverticulum could be coagulated and a large nephrosto -
my catheter could be left in place two days.
No complication was encountered. One patient re f u s e d
the treatement after unsuccessful puncture. The nephro -
stomy tube was left open for two days of drainage. Mean
hospital stay was 5 days. Three patients required E.S.W.L
because of persistent symptoms.
One month after treatement 13 of 18 patients intravei -
nous urography showed obliteration of the diverticulum
(72%); Three monthes after 84% (15/18) of our patients
were stone free and 94% (17/18) symptom free.
P e rcutaneous nephrolithotomy should be performed for
symptomatic patients, it has low complication rate and
should be reserved for patients with persistent symptoms
after E.S.W.L.
Key words : Percutaneous surg e ry, lithiasis, caliceal
diverticulum.
____________________
ZUSAMMENFASSUNG
Perkutane Behandlung von intradivert i k u l ä re n
Konkrementen bei 19 Patienten.
Es w urd en 19 K elchdive rtik el mit e iner
K o n k r ementbildung bei 18 Patienten behandelt. A l l e
Patienten waren symptomatisch, 12 von ihnen wurd e n
nach einer misslu ngenen e xtra korporal en
Stos swellenlit hotripsie th er apiert . E s s e n t i e l l e
Bestandteile der perkutanen Operation beinhalteten : die
Punktion (die Darstellung des Divertikels ist eine
Darst ellung des St eines), die B ehand lu ng des
K e l c h d i v e r tikels durch eine Koagulationsschlinge und
die temporäre Drainage des Divertikels mit dem Ziel
einer nachfolgenden Sklerosierung.
Es wurde keine Komplikation beobachgtet?. Ein Patient,
bei dem die Punktion misslang, verweigerte jede weitere
Behnadlung. Die Drainage wurde im Durchschnitt für 48
Stunden belassen, die Krankenhausaufenthaltsdauer
betrug 5 Tage. Bei 3 Patienten war eine komplementäre
ES WL notwendig. Nach ei nem Mon at waren 13
D i v e rtikel bei 18 Patienten in der int ravenösen
Ausscheidungsurographie nicht mehr nachweisbar.Nach
3 Monaten war der Schmerz bei 17 Patienten (94% der
Fälle) und die Konkrementbildung bei 15 Patienten
(84%) verschwunden.
____________________
RESUMEN
Tratamiento de la litiasis intradiverticular por la via
percutanea (a proposito de 19 diverticulos de la pelvis
renal).
F u e ron tratados diecinueve diverticulos de la pelvis
renal (en 18 pacientes) que contenian una litiasis. Todos
los pacientes eran sintomàticos, fueron tratados 12, des -
puès de fracaso de la litotricia extracorporal (LEC).
Los tiempos esenciales de la via percutanea comprendie -
ron : la puncion ("apuntar al diverticulo es apuntar a la
piedra") y el tratamiento de la bolsa de la pelvis renal
962

por coagulacion con el asa de bola, y luego dre n a j e
temporal por sonda de blobito o làmina de caucho que
permita obtener una esclerosis irritativa.
No se ha observado ninguna complicacion. Despuès del
fracaso de 1 puncion, un paciente rechazo cualquier tra -
t a m i e n t o . El drenaje fue de unas 48 horas por termino
medio, la hospitalizacion de 5 dias. En 3 pacientes fue
necesaria una sesion complementaria de LEC.
A 1 mes, 13 diverticulosn de los 18 tratados habian
desaparecido a la urografia intravenosa (un 72%).
A 3 meses, desaparicion del dolor en 17 pacientes (un
94% de los casos) y de la litiasis en 15 pacientes (un
84%).
Al termino del presente estudio, la cirugia perc u t a n e a
nos parece ser una tecnica eficaz y segura en el trata -
miento de la litiasis intradiverticular sintomàtica, sobre
todo despuès de un fracaso de la LEC;
____________________
RIASSUNTO
Trattamento della litiasi intradiverticolare con acces-
so percutaneo (a proposito di 19 diverticoli caliciali).
19 diveticoli caliciali (su 18 pazienti) contentenenti una
litiasi son stati trattati. Tutti i pazienti erano sintomatici.
12 di loro son stati trattati dopo insuccesso della
Litotripsia Extracorporea (LEC). Le fasi essenziali
dell'accesso percutaneo sono : la puntura ("mirare il
d i v e rticolo è mirare la pietra") e il trattamento della
borsa caliciale con coagulazione con "anse à boule",
poi drenaggio temporaneo con sonda a pallonetto o
lamella di caoutchouc che permette una sclerosi irritati -
va.
Nessuna complicazione è stata osserv a t a . Dopo un
insuccesso di puntura, un paziente ha rifiutato ogni
cura. Il drenaggio durava in media 48 ore, l'ospedaliz -
zazione 5 giorni.Su 32 pazienti una seduta complemen -
tare di LEC era necessaria.
Dopo un meso, 13 diverticoli sui 18 trattati erano scom -
parsi all'urografia intravenosa (72%).
Dopo 3 mesi, scomparsa del dolore su 17 pazienti (94%
dei casi) e della litiasi su 15 pazienti (84%).
Al termine di questo studio, la chiru rgia percutanea ci
sembra una tecnica efficace e sicura del trattamento
della litiasi intra-civert i c o l a re sintomatica, sopratutto
dopo insuccesso della LEC.
____________________
963
1
/
5
100%