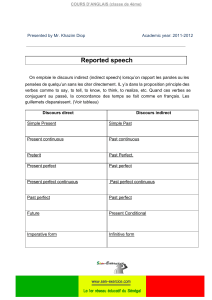
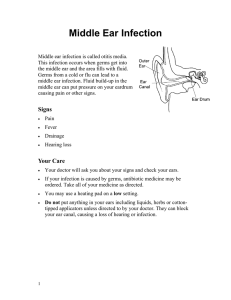
NosoVeille Août 2011

NosoVeille – Bulletin de veille Avril 2015
1 / 28
NosoVeille n°4
Avril 2015
Rédacteurs : Nathalie Sanlaville, Sandrine Yvars, Annie Treyve
Secrétariat de rédaction : Nathalie Vincent
Ce bulletin de veille est une publication mensuelle qui recueille les publications scientifiques publiées au
cours du mois écoulé.
Il est disponible sur le site de NosoBase à l’adresse suivante :
http://nosobase.chu-lyon.fr/RevuesBiblio/sommaire_biblio.html
Pour recevoir, tous les mois, NosoVeille dans votre messagerie :
Abonnement / Désabonnement
Sommaire de ce numéro :
Acinetobacter baumannii
Antibiotique / Antibiorésistance
Antiseptique
Bactériémie
Chirurgie
Clostridium difficile
Ebola
EHPAD
Environnement
Epidémie
Grippe
Hépatite
Hygiène des mains
Infection fongique
Infection urinaire
Légionellose
Néonatologie
Norovirus
Personnel
Pneumonie
Prévention
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Réglementation
Staphylococcus aureus
Stérilisation
Surveillance
Tuberculose
Vaccination

NosoVeille – Bulletin de veille Avril 2015
2 / 28
Acinetobacter baumannii
NosoBase ID notice : 393743
Acinetobacter baumannii producteurs de biofilm multirésistant aux antibiotiques : un défi émergent
Badave GK; Dhananjay K. Biofilm producing multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: an emerging
challenge. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research 2015/01; 9(1): 8-10.
Mots-clés : ACINETOBACTER BAUMANNII; MULTIRESISTANCE; BIOFILM
Aim: To study the quantitative method for biofilm formation and examine the correlation between biofilm
formation and antibiotic resistance among the clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii.
Materials and methods: A total of 72 A. baumannii isolates from different clinical specimens were processed
and confirmed by conventional microbiological methods. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed by
Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method using six antibiotics. Biofilm formation was studied by microtitre plate
assay.
Results: Forty five (62.5%) of 72 isolates produced biofilm. Resistance to ampicillin-sulbactam was least.
36.1% isolates were resistant to imipenem, 66.6% to ceftazidime, 72.2% to ciprofloxacin, 80.5% to amikacin
and 84.7% to piperacillin. Biofilm formers showed greater resistance to ampicillin- sulbactam, amikacin,
ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime as compared to imipenem and piperacillin. In all 65 (90.3%) isolates showed
multiple drug resistance. Correlation between multidrug resistance and biofilm formation was analysed
statistically and p-value was found to be significant (p-value =0.0004; p-value <0.05 is significant by Chi -
Square Test).
Conclusion: The study concludes that there a positive correlation between biofilm formation and multiple drug
resistance in A. baumannii.
Antibiotique / Antibiorésistance
NosoBase ID notice : 393272
La procalcitonine est-elle un marqueur efficace en termes de coût-efficacité pour mettre en place et
réévaluer l’antibiothérapie de patients adultes suspectés d’infection bactérienne et de sepsis ?
Harrison M; Collins CD. Is procalcitonin-guided antimicrobial use cost-effective in adult patients with
suspected bacterial infection and sepsis? Infection control and hospital epidemiology 2015/03; 36(3): 265-
272.
Mots-clés : ANTIBIOTIQUE; PRESCRIPTION; PROCALCITONINE; SOIN INTENSIF; COUT-EFFICACITE;
COUT; COHORTE; INFECTION; SYNDROME SEPTIQUE
Objective: Procalcitonin has emerged as a promising biomarker of bacterial infection. Published literature
demonstrates that use of procalcitonin testing and an associated treatment pathway reduces duration of
antibiotic therapy without impacting mortality. The objective of this study was to determine the financial impact
of utilizing a procalcitonin-guided treatment algorithm in hospitalized patients with sepsis.
Design: Cost-minimization and cost-utility analysis.
Patients: Hypothetical cohort of adult ICU patients with suspected bacterial infection and sepsis.
Methods: Utilizing published clinical and economic data, a decision analytic model was developed from the
U.S. hospital perspective. Effectiveness and utility measures were defined using cost-per-clinical episode and
cost per quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Upper and lower sensitivity ranges were determined for all
inputs. Univariate and probabilistic sensitivity analyses assessed the robustness of our model and variables.
Incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were calculated and compared to predetermined willingness-to-
pay thresholds.
Results: Base-case results predicted the use of a procalcitonin-guided treatment algorithm dominated
standard care with improved quality (0.0002 QALYs) and decreased overall treatment costs ($65). The model
was sensitive to a number of key variables that had the potential to impact results, including algorithm
adherence (<42.3%), number and cost of procalcitonin tests ordered (≥9 and >$46), days of antimicrobial
reduction (<1.6 d), incidence of nephrotoxicity and rate of nephrotoxicity reduction.
Conclusion: The combination of procalcitonin testing with an evidence-based treatment algorithm may
improve patients' quality of life while decreasing costs in ICU patients with suspected bacterial infection and
sepsis; however, results were highly dependent on a number of variables and assumptions.

NosoVeille – Bulletin de veille Avril 2015
3 / 28
NosoBase ID notice : 393269
Mise en place de politiques de gestion des antibiotiques dans les hôpitaux américains : résultats
d’une enquête nationale
Pogorzelska-Maziarz M; Herzig CT; Larson EL; Furuya EY; Perencevich EN; Stone PW. Implementation of
antimicrobial stewardship policies in U.S. hospitals: findings from a national survey. Infection control and
hospital epidemiology 2015/03; 36(3): 261-264.
Mots-clés : ANTIBIOTIQUE; PRESCRIPTION; CONSOMMATION; ENQUETE; RESEAU
Objective: To describe the use of antimicrobial stewardship policies and to investigate factors associated with
implementation in a national sample of acute care hospitals.
Design: Cross-sectional survey.
Participants: Infection Control Directors from acute care hospitals participating in the National Healthcare
Safety Network (NHSN).
Methods: An online survey was conducted in the Fall of 2011. A subset of hospitals also provided access to
their 2011 NHSN annual survey data.
Results: Responses were received from 1,015 hospitals (30% response rate). The majority of hospitals (64%)
reported the presence of a policy; use of antibiograms and antimicrobial restriction policies were most
frequently utilized (83% and 65%, respectively). Respondents from larger, urban, teaching hospitals and
those that are part of a system that shares resources were more likely to report a policy in place (P<.01).
Hospitals located in California were more likely to have policy in place than in hospitals located in other states
(P=.014).
Conclusion: This study provides a snapshot of the implementation of antimicrobial stewardship policies in
place in U.S. hospitals and suggests that statewide efforts in California are achieving their intended effect.
Further research is needed to identify factors that foster the adoption of these policies.
NosoBase ID notice : 395061
Endocardite infectieuse sur pacemaker à Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Reynaud Q; Weber E; Gagneux-Brunon A; Suy F; Lucht F; Botelho-Nevers E. Late Stenotrophomonas
maltophilia pacemaker infective endocarditis. Médecine et maladies infectieuses 2015/03; 45 (3): 95-97.
Mots-clés : ENDOCARDE; INFECTION; STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE; ANTIBIORESISTANCE;
MORTALITE; STENOTROPHOMONAS MALTOPHILIA
Antiseptique
NosoBase ID notice : 395020
Evaluation de l’activité bactéricide de 3 antiseptiques cutanéomuqueux en présence de substances
interférentes : peut-on compléter la norme NF EN 13727 ?
Salvatico S; Feuillolay C; Mas Y; Verrière F; Roques C. Bactericidal activity of 3 cutaneous/mucosal
antiseptic solutions in the presence of interfering substances: Improvement of the NF EN 13727 European
Standard? Médecine et maladies infectieuses 2015/03; 45(3): 89-94.
Mots-clés : ANTISEPTIQUE; BACTERICIDIE; TEST; PEAU; CONTACT MUQUEUX; NORME;
CHLORHEXIDINE; POLYVIDONE IODEE; GYNECOLOGIE; DERMATOLOGIE
Objectifs : L’évaluation des antiseptiques à visée cutanéomuqueuse, en présence de substances
interférentes, ne fait l’objet d’aucun protocole normatif. Notre objectif était de proposer des conditions d’essai
adaptées de la norme NF EN 13727 pour l’évaluation d’antiseptiques utilisés en gynécologie et dermatologie.
Méthode : Trois antiseptiques : une association chlorhexidine-benzalkonium (CB), une association
hexamidine-chlorhexidine-chlorocrésol (HCC) et la povidone iodée (P) ont été testés in vitro. L’adaptation des
conditions d’essai de la norme a concerné le choix des dilutions, du diluant et des substances interférentes.
L’activité des produits a été évaluée sur les souches de la norme aux concentrations de 97 % (utilisation
pure), de 50 % et 10 % (utilisation diluée) et de 1 %. Pour répondre aux exigences de bactéricidie, une
réduction logarithmique ≥ 5 était attendue pour 60 secondes de contact.
Résultats : HCC n’avait pas d’activité bactéricide à l’exception de la concentration à 97 % sur P. aeruginosa .
P n’avait pas d’activité bactéricide sur E. hirae , quelle que soit la concentration testée, ni sur S. aureus à 97

NosoVeille – Bulletin de veille Avril 2015
4 / 28
%. CB avait l’activité bactéricide la plus homogène avec réduction>5 log sur les 4 souches bactériennes à 97
%, 50 % et 10 %.
Conclusion : L’adaptation de la norme NF EN 13727 permet de discriminer les 3 produits testés : seul CB
était bactéricide en conditions de saleté. Ce travail souligne la possibilité de valider le choix des antiseptiques
in vitro dans des conditions représentatives de la pratique, dans le traitement d’appoint des affections
cutanéomuqueuses primitivement bactériennes ou susceptibles de se surinfecter.
Bactériémie
NosoBase ID notice : 395001
Les bactériémies associées aux soins à Staphylococcus aureus : un indicateur des infections
associées aux cathéters
Bonnal C; Birgand G; Lolom I; Diamantis S; Dumortier C; L'Hériteau F; et al. Staphylococcus aureus
healthcare associated bacteraemia: An indicator of catheter related infections. Médecine et maladies
infectieuses 2015/03; 45(3): 84-88.
Mots-clés : INFECTION NOSOCOMIALE; CATHETER VEINEUX; STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS;
BACTERIEMIE; INDICATEUR; CATHETER VEINEUX PERIPHERIQUE; CATHETER VEINEUX CENTRAL;
METICILLINO-RESISTANCE; SARM; SURVEILLANCE; INCIDENCE; ETUDE PROSPECTIVE
Objectifs : Les établissements de santé doivent disposer d’indicateurs pertinents permettant d’évaluer et de
surveiller les infections associées aux soins dites évitables et en particulier celles liées aux cathéters. Le but
de ce travail était de montrer que la surveillance des bactériémies nosocomiales à Staphylococcus aureus
pouvait être un de ces indicateurs.
Patients et méthode : Nous avons réalisé une surveillance prospective sur 10 ans des bactériémies
associées aux soins à S. aureus dans notre hôpital de 940 lits en nous basant sur les définitions standard.
Résultats : Entre 2002 et 2012, 2784 bactériémies associées aux soins ont été identifiées, dont 573 (18 %)
étaient dues à S. aureus. Parmi ces 573 bactériémies, 189 (32,8 %) avaient pour origine un cathéter
vasculaire et 84 % (158/189) survenaient en dehors des services de réanimation. S. aureus était associé à 56
% (61/109) des bactériémies liées à un cathéter veineux périphérique (CVP) et à 34 % (103/301) de celles
dues à un cathéter veineux central (CVC). Les souches de S. aureus résistantes à la méticilline isolées des
bactériémies ont diminué de 50,3 % à 18,4 % entre 2002 et 2012. Les bactériémies sur CVP ont baissé de 20
à 7 par an pendant l’étude.
Conclusion : Dans notre expérience, la surveillance des bactériémies associées aux soins à S. aureus serait
donc un indicateur simple et efficace des infections sur cathéter et donc de la qualité des soins, en particulier
dans des secteurs non couverts habituellement par d’autres types de surveillance.
NosoBase ID notice : 393276
Comparaison entre connecteurs sans aiguille imprégnés d'argent et connecteurs sans aiguille
standard dans la prévention des bactériémies sur voie centrale
Jacob JT; Tejedor SC; Reyes MD; Lu X; Easley KA; Aurand WL; et al. Comparison of a silver-coated
needleless connector and a standard needleless connector for the prevention of central line-associated
bloodstream infections. Infection control and hospital epidemiology 2015/03; 36(3): 294-301.
Mots-clés : CATHETER VEINEUX CENTRAL; BACTERIEMIE; MATERIEL MEDICO-CHIRURGICAL; TAUX;
ETUDE PROSPECTIVE; CONNECTEUR
Objective: To assess the impact of a novel, silver-coated needleless connectors (NCs) on central-line-
associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) rates compared with a mechanically identical NCs without a silver
coating.
Design: Prospective longitudinal observation study
Setting: Two 500-bed university hospitals
Patients: All hospitalized adults from November 2009 to June 2011 with non-hemodialysis central lines
Interventions: Hospital A started with silver-coated NCs and switched to standard NCs in September 2010;
hospital B started with standard NCs and switched to silver-coated NCs. The primary outcome was the
difference revealed by Poisson multivariate regression in CLABSI rate using standard Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention surveillance definitions. The secondary outcome was a comparison of organism-
specific CLABSI rates by NC type.

NosoVeille – Bulletin de veille Avril 2015
5 / 28
Results: Among 15,845 hospital admissions, 140,186 central-line days and 221 CLABSIs were recorded
during the study period. In a multivariate model, the CLABSI rate per 1,000 central-line days was lower with
silver-coated NCs than with standard NCs (1.21 vs 1.79; incidence rate ratio=0.68 [95% CI: 0.52-0.89],
P=.005). A lower CLABSI rate per 1,000 central-line days for the silver-coated NCs versus the standard NCs
was observed with S. aureus (0.11 vs 0.30, P=.02), enterococci (0.10 vs 0.27, P=.03), and Gram-negative
organisms (0.28 vs 0.63, P=.003) but not with coagulase-negative staphylococci (0.31 vs 0.36) or Candida
spp. (0.42 vs 0.40).
Conclusions: The use of silver-coated NCs decreased the CLABSI rate by 32%. CLABSI reduction efforts
should include efforts to minimize contamination of NCs.
NosoBase ID notice : 393741
Comparaison des bactériémies à Acinetobacter pittii et à Acinetobacter nosocomialis
Liu YM; Lee YT; Kuo SC; Chen TL; Liu CP; Liu CE. Comparison between bacteremia caused by
Acinetobacter pittii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis. Journal of microbiology, immunology and infection
2015/01/30; in press: 1-6.
Mots-clés : BACTERIEMIE; ACINETOBACTER; ETUDE RETROSPECTIVE; CENTRE HOSPITALIER
UNIVERSITAIRE; APPARIEMENT; MORTALITE; ACINETOBACTER PITTII; ACINETOBACTER
NOSOCOMIALIS
Background/Purpose: Patients with Acinetobacter pittii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis bacteremia have
lower mortality rates than those with Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia. However, it is unknown whether
these organisms differ in outcomes of bacteremic patients. We conducted this study to answer this question.
Methods: In this retrospective study conducted at a teaching hospital in Taiwan, we enrolled all 86 patients
who had developed A. pittii bacteremia and those with A. nosocomialis bacteremia from 2000 to 2008 while
matching for age, sex, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, and appropriate
antimicrobial therapy. After adjustment, we accessed the clinical characteristics and 14- and 28-day
mortalities.
Results: We found that the patients with A. pittii bacteremia had multiple comorbidities less often and received
invasive procedures less frequently. The 14-day mortality rate of patients with A. pittii or A. nosocomialis
bacteremia was 14% and 7%, respectively, whereas their 28-day mortality rate was 17% and 9%,
respectively. Using the mortality rate in patients with A. nosocomialis bacteremia as a reference, the odds
ratios for the 14- and 28-day crude morality in those with A. pittii were 2.16 [95% confidence interval (CI),
0.77-6.05] and 2.06 (95% CI, 0.82-5.15), respectively, whereas the adjusted odds ratios for 14- and 28-day
mortality were 1.89 (95% CI, 0.56-6.14) and 1.67 (95% CI, 0.59-4.78) respectively.
Conclusion: Our 8-year study showed that the mortality rate of A. pittii bacteremia was higher but the
difference was not statistically significant.
NosoBase ID notice : 394304
Impact d’interventions de lutte contre le risque infectieux sur les taux de bactériémies à
Staphylococcus aureus dans des hôpitaux pour soins aigus du NHS, Est des Midlands, Royaume-Uni,
à l’aide d’une analyse de series temporelles interrompues
Newitt S; Myles PR; Birkin JA; Maskell V; Slack RC; Nguyen-Van-Tam JS; et al. Impact of infection control
interventions on rates of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in National Health Service acute hospitals, East
Midlands, UK, using interrupted time-series analysis. The journal of hospital infection 2015/01/15; in press: 1-
10.
Mots-clés : ANALYSE; TAUX; BACTERIEMIE; STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS; PREVENTION;
EFFICACITE; ETUDE MULTICENTRIQUE
Background: Reducing healthcare-associated infection (HCAI) is a UK national priority. Multiple national and
regional interventions aimed at reduction have been implemented in National Health Service acute hospitals,
but assessment of their effectiveness is methodologically challenging.
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of national and regional interventions undertaken between 2004 and 2008
on rates of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and meticillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
(MSSA) bacteraemia within acute hospitals in the East Midlands, using interrupted time-series analysis.
Methods: We used segmented regression to compare rates of MRSA and MSSA bacteraemia in the pre-
intervention, implementation, and post-intervention phases for combined intervention packages in eight acute
hospitals.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
1
/
28
100%