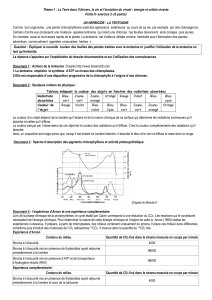
Projet : Biologie des Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts, Matrice

Projet : Biologie des Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts, Matrice extracellulaire, et
Adénocarcinome Pancréatique
Stage encadré par Corinne Bousquet (DR2 Inserm) et co-encadré par Christine Jean (CR2) -
CRCT-Equipe 6
Financement de 3 ans
Dépôt de candidature par mail (corinne.bousquet@inserm.fr) au plus tard le 27 juin pour
audition entre le 1er et 5 juillet 2016.
Résumé :
L’adénocarcinome canalaire pancréatique (PDA) présente un pronostic sombre et a la particularité
d’être constitué d’un stroma fibrotique exubérant. Les CAF (cancer-associated fibroblasts), cellules
majoritaires de ce stroma, sont responsables de la sécrétion abondante de facteurs solubles (de
croissance, cytokines, chimiokines) et insolubles (matrice), activant des voies de survie
chimioprotectrices dans les cellules cancéreuses, limitant la perfusion et donc l’accès des drogues, et
favorisant une réponse immune pro-tumorale.
L’équipe d’accueil développe des projets visant à comprendre la biologie des CAFs afin de développer
des stratégies thérapeutiques innovantes visant à les cibler. L'équipe a d'ores et déjà montré qu’une
nouvelle molécule (partenariat Industrie Pharmaceutique) inhibe les effets délétères des CAF
(primocultures humaines isolées à partir d’exérèse chirurgicale) en réduisant la sécrétion de facteurs
solubles chimioprotecteurs, et présente un fort potentiel chimiosensibilisant in vivo sur des modèles
de cancérogenèse pancréatique.
Le stroma fibrotique n'est certainement pas inerte. Les protéines de la matrice extracellulaire (MEC),
sécrétées par les cellules tumorales mais surtout par les CAFs affectent, au sein de la tumeur et des
métastases, la biologie des cellules, que ce soit des cellules cancéreuses ou des cellules stromales
(fibroblastes, CAFs, cellules endothéliales, cellules immunitaires). Toutefois, les mécanismes de
régulation de la production de MEC (composition qualitative et quantitative) par les CAFs et l'impact
de cette composition sur la chimiorésistance des cellules cancéreuses restent mal connus.
Ce projet propose d'étudier ces aspects en utilisant des modèles murins d'adénocarcinome
pancréatique mais également en développant des cultures organotypiques pancréatiques
tridimensionnelles.
Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Biology, Extracellular Matrix & Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) presents a dismal prognosis and the specificity to be
composed of an exuberant fibrotic stroma. CAF (cancer-associated fibroblasts) are the most
abundant stromal cells, responsible for the large secretion of soluble (growth factors, cytokines,
chemokines) and unsoluble (matrix) proteins that activate survival chemoprotective pathways in
cancer cells, limit tumor perfusion and thereby drug access, and favor a pro-tumoral immune
response.
The recruiting team has recently uncovered a novel molecule (in partnership with the Pharmaceutical
Industry) that is able to inhibit CAF deleterious effects (human primocultures isolated from surgery

PDA resection) by reducing the secretion of chemoprotective factors, and presents a potent
chemosensitization potential in vivo on pancreatic cancer models (Duluc et al, EMBO Mol Med,
2015).
Fibrotic stroma is certainly not inert. Proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM), secreted by tumor
cells but abundantly by CAFs, affect, in the tumor and metastases, the biology of cancer cells but also
of stromal cells (fibroblasts, CAFs, endothelial and immune cells). Nevertheless, mechanisms of
regulation of ECM production (qualitative and quantitative composition) by CAFs, and the impact of
this composition on cancer cell chemoresistance are yet poorly understood.
This project aims at studying those aspects by using murine models of pancreatic cancer as well as by
developing tridimensional organotypic cultures of pancreas.
Methods:
Experimentation on mice: genotyping, phenotyping (survival, blood analyses, cytokines ELISA,
histology and immunohistochemistry / immunofluorescence on pancreas, and other organs), bone
marrow transfer, surgery with intra-pancreatic grafting of cancer cells, in vivo exploration (imaging) ;
Immunophenotyping (bone marrow, blood, spleen, pancreas) by FACS
Molecular biology and Biochemistry: RT-qPCR, in situ hybridization, Western-blot, ELISA
Cell biology and associated techniques (transfection, si/shRNA lentivectors) – 2D and 3D
invasion assay, 3D culture of organoids
Quantitative proteomic analyses by mass spectrometry (Proteomic platform IPBS Toulouse)
Recent publications:
Laval S, Laklai H, Fanjul M, Pucelle M, Laurell H, Billon-Galés A, Le Guellec S, Delisle MB,
Sonnenberg A, Susini C, Pyronnet S, Bousquet C. Dual roles of hemidesmosomal proteins in the
pancreatic epithelium: the phosphoinositide 3-kinase decides. Oncogene. 2014, 33(15):1934-44.
Chalabi M, Duluc C, Caron P, Vezzosi D, Guillermet-Guibert J, Pyronnet S, Bousquet C.
Somatostatin analogs: does pharmacology impact antitumor efficacy? Trends Endocrinol Metab.
2014, 25(3):115-27. Review
Chalabi-Dchar M, Cassant-Sourdy S, Duluc C, Fanjul M, Lulka H, Samain R, Roche C, Breibach
F, Delisle MB, Poupot M, Dufresne M, Shimaoka T, Yonehara S, Mathonnet M, Pyronnet S, Bousquet
C. Loss of Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Promotes Growth of KRAS-induced Pancreatic Tumors in
Mice by Activating PI3K Signaling and Overexpression of CXCL16. Gastroenterology. 2015
Jun;148(7):1452-65. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Feb 13.
Duluc C, Moatassim-Billah S, Chalabi-Dchar M, Perraud A, Samain R, Breibach F, Gayral M,
Cordelier P, Delisle MB, Bousquet-Dubouch MP, Tomasini R, Schmid H, Mathonnet M, Pyronnet S,
Martineau Y, Bousquet C. Pharmacological targeting of the protein synthesis mTOR/4E-BP1 pathway
in cancer-associated fibroblasts abrogates pancreatic tumour chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med.
2015 Apr 1;7(6):735-53. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404346.
Moatassim-Billah S, Duluc C, Samain R, Jean C, Perraud A, Decaup E, Cassant-Sourdy S, Bakri
Y, Selves J, Schmid H, Martineau Y, Mathonnet M, Pyronnet S, Bousquet C. Anti-metastatic potential
of somatostatin analog SOM230: Indirect pharmacological targeting of pancreatic Cancer-Associated
Fibroblasts. Oncotarget. 2016 May 12. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9296.
More informations at:
http://www.crct-inserm.fr/06-s-pyronnet-c-bousquet-protein-synthesis-secretion-in-carcinogenesis-
548.html
http://cvscience.aviesan.fr/cv/1222/corinne-bousquet
1
/
2
100%




![Poster CIMNA journée CHOISIR [PPT - 8 Mo ]](http://s1.studylibfr.com/store/data/003496163_1-211ccc570e9e2c72f5d6b6c5d46b9530-300x300.png)