L’ EVOLUTION Lycée-Collège de la Planta, Sion

Lycée-Collège de la Planta, Sion
Biologie
Option spécifique (OS) 4
ème
année (programme maturité)
L’EVOLUTION
Julien Dubuis

2
Table des matières
1
1 I
IN
NT
TR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CT
TI
IO
ON
N
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
4
4
2
2 T
TH
HE
EO
OR
RI
IE
ES
S
D
DE
E
L
L’
’E
EV
VO
OL
LU
UT
TI
IO
ON
N
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
7
7
2.1 Avant le Darwinisme ............................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Le lamarckisme ....................................................................................................................... 8
2.3 Le Darwinisme ...................................................................................................................... 10
2.4 La théorie synthétique ........................................................................................................... 15
2.5 Le créationnisme et le dessein intelligent .............................................................................. 16
3
3 «
«
P
PR
RE
EU
UV
VE
ES
S
»
»
O
OU
U
I
IN
ND
DI
IC
CE
ES
S
D
DE
E
L
L’
’E
EV
VO
OL
LU
UT
TI
IO
ON
N
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
1
18
8
3.1 Anatomie et morphologie ...................................................................................................... 18
3.1.1 Homologie ..................................................................................................................... 18
3.1.2 Analogie ........................................................................................................................ 20
3.2 Biochimie et cytologie ........................................................................................................... 21
3.2.1 Cytologie ....................................................................................................................... 21
3.2.2 Biochimie ...................................................................................................................... 22
3.3 Embryologie et génétique ...................................................................................................... 23
3.3.1 Embryologie .................................................................................................................. 23
3.3.2 Génétique ....................................................................................................................... 24
3.4 Biogéographie ....................................................................................................................... 26
3.5 Géologie (dérive des continents) ........................................................................................... 27
3.6 Paléontologie ......................................................................................................................... 28
4
4 L
LE
ES
S
M
ME
EC
CA
AN
NI
IS
SM
ME
ES
S
D
DE
E
L
L’
’E
EV
VO
OL
LU
UT
TI
IO
ON
N
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
3
30
0
4.1 Les niveaux d’intervention .................................................................................................... 30
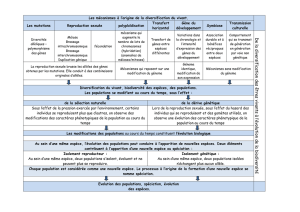
4.2 Les causes de la microévolution ............................................................................................ 30
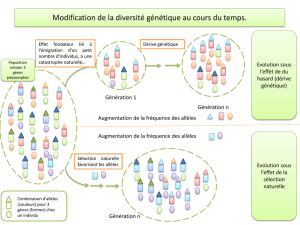
4.2.1 La dérive génétique ....................................................................................................... 32
4.2.1.1 L’effet d’étranglement ............................................................................................... 32
4.2.1.2 L’effet fondateur ........................................................................................................ 33
4.2.2 Le flux génétique (= migration) .................................................................................... 34
4.2.3 La mutation .................................................................................................................... 34
4.2.4 L’accouplement non aléatoire ....................................................................................... 35
4.2.5 La sélection naturelle ..................................................................................................... 35
4.2.6 L’évolution adaptative ................................................................................................... 36
4.2.6.1 La valeur adaptative .................................................................................................. 36
4.2.6.2 L’objet de la sélection naturelle ................................................................................ 36
4.2.6.3 Les modes de sélection naturelle ............................................................................... 37
4.2.6.4 La sélection sexuelle.................................................................................................. 38
4.3 L’origine des espèces ............................................................................................................ 39
4.3.1 Le problème de l’espèce ................................................................................................ 39
4.3.2 L’isolement reproductif ................................................................................................. 39
4.3.2.1 L’isolement reproductif prézygotique ....................................................................... 40
4.3.2.2 L’isolement reproductif postzygotique ...................................................................... 41
4.3.3 La biogéographie de la spéciation ................................................................................. 41
4.3.3.1 La spéciation allopatrique .......................................................................................... 42

3
4.3.3.2 La spéciation sympatrique ......................................................................................... 43
5
5 L
LA
A
G
GE
EN
NE
ET
TI
IQ
QU
UE
E
D
DE
ES
S
P
PO
OP
PU
UL
LA
AT
TI
IO
ON
NS
S
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
4
46
6
5.1 Patrimoine génétique ............................................................................................................. 46
5.2 La loi de Hardy-Weinberg ..................................................................................................... 48
5.2.1 Démonstration de la loi Hardy-Weinberg ..................................................................... 48
5.2.2 Généralisation de la loi de Hardy-Weinberg ................................................................. 49
5.2.3 Application 1 ................................................................................................................. 49
5.2.4 Application 2 ................................................................................................................. 50
5.3 Les conditions d’application de la loi d’Hardy-Weinberg .................................................... 50
5.4 L’équilibre d’Hardy-Weinberg n’existe pas mais est utile .................................................... 50
6
6 S
SY
YS
ST
TE
EM
MA
AT
TI
IQ
QU
UE
E
E
ET
T
P
PH
HY
YL
LO
OG
GE
EN
NE
ES
SE
E
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
5
52
2
6.1 La taxonomie ......................................................................................................................... 52
6.2 La phylogénie classique ........................................................................................................ 55
6.2.1 Les arbres phylogénétiques ........................................................................................... 59
6.2.1.1 Les caractères dérivés ................................................................................................ 59
6.2.1.2 Homologie et analogie ............................................................................................... 59
6.2.1.3 Exemple ..................................................................................................................... 61
6.2.2 L’extra-groupe ............................................................................................................... 62
6.2.3 Pratique - exercice ......................................................................................................... 63
6.3 La phylogénie moléculaire .................................................................................................... 65
6.3.1 Les protéines .................................................................................................................. 65
6.3.2 L'ADN (Acide DésoxyriboNucléique) .......................................................................... 65
7
7 L
L’
’E
EV
VO
OL
LU
UT
TI
IO
ON
N
D
DE
E
L
L’
’H
HO
OM
MM
ME
E
.
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
..
.
6
67
7
7.1 L’homme et ses proches cousins ........................................................................................... 67
7.2 Origines de l’Homme ............................................................................................................ 68
7.3 Origines et diversité des Hommes modernes ........................................................................ 71
7.4 Evolution intellectuelle et culturelle de Hommes.................................................................. 72

4
1
1
I
IN
NT
TR
RO
OD
DU
UC
CT
TI
IO
ON
N
L'idée d'une transformation des êtres vivants au cours du temps a été exprimée à diverses occasions
depuis près de 2500 ans, mais ce n'est qu'au XIX siècle que le concept de descendance avec
transformation - l'évolution telle qu'on la conçoit aujourd'hui - a été formalisé et doté d'un mécanisme
cohérent par Darwin, apportant une vision nouvelle de la vie et de son histoire.
Les processus évolutifs qui s’opèrent depuis que la vie est apparue sur terre, il y a plus de trois
milliards d’années, ont donné naissance aux millions d’espèces actuelles, ainsi qu’au nombre bien plus
grand encore d’espèces qui ont vécu dans le passé mais qui ont aujourd’hui disparu. L'apparition d'une
nouvelle espèce s’appelle une spéciation. Certaines spéciations (chez les bactéries notamment) sont
observables en temps réel, à l'échelle humaine. Toutes ces espèces ont un « ancêtre commun » :
(LUCA = Last Universal Common Ancestor) qui est apparu il y a 3,5 milliards d’années environ.
Evolution signifie donc changement : changement dans la structure et le comportement des
organismes, au fil des générations. L'évolution est donc la transformation des espèces dans le temps.
Les aspects divers des organismes actuels à tous les niveaux depuis la séquence de leur ADN jusqu’à
leurs structures macroscopiques ou jusqu’à leurs comportements sociaux, sont issus de la modification
de ceux de leurs ancêtres. Les modifications évolutives des êtres vivants dépendent d’une part des
changements dans les conditions du milieu et, d’autre part, d’une innovation génétique qui se fait au
hasard.
Pour comprendre l’évolution il faut étudier les mécanismes qui ont présidé à la structuration actuelle
de la biodiversité, et qui ont permis les multiples adaptations des animaux, des végétaux, des
organismes unicellulaires. Les recherches dans le domaine de l’évolution se séparent en deux volets ;
les unes visent la reconstruction de l’histoire de la vie, les autres tendent à comprendre les modalités et
les processus de l’évolution.
L’évolution explique donc :
- la diversité des espèces vivant actuellement (1’200’000 espèces animales et 400’000 espèces
végétales recensées),
- leur multiplication (comment une espèce existante donne naissance à deux ou plusieurs
espèces),
- leur origine commune par les modifications progressives qu’ont subies leurs ancêtres au
cours des temps géologiques.
- les processus de l’évolution.
La théorie générale de l’évolution explique comment les organismes vivants se sont développés et
succédés, mais elle ne peut en aucun cas prédire comment ils évolueront.

5
Il est important de noter que les théories de l’évolution ont émergé grâce à de nombreuses découvertes
faites durant le 18
ème
et le 19
ème
siècle, découvertes faites dans des domaines aussi variés que la
géologie, la paléontologie, l’économie. L’exercice de la page suivante va nous permettre de mettre en
évidence les apportes divers qui ont permis l’élaboration de cette théorie.
Exercice : Attribue chaque affirmation à un personnage évoqué sur la ligne du temps (figure 6).
Figure 6: Contexte historique de la vie et des idées de Darwin
A. Les processus géologiques n’ont pas changé au cours de l’histoire de la planète. Ainsi, les forces
qui ont modelé les montagnes et qui les érodent, ainsi que le rythme de ces phénomènes, sont les
mêmes aujourd’hui que par le passé.
Personnalité : __________________________________
B. Il est possible d’expliquer les divers éléments du relief en observant les phénomènes encore à
l’œuvre dans le monde. Par exemple, les canyons ont été creusés par les fleuves ; les roches
sédimentaires contenant des fossiles marins ont été emportées par les fleuves jusqu’à la mer. Un
changement profond résulte du cumul de processus lents mais continuels.
Personnalité : __________________________________
C. Les espèces fossiles se succèdent dans les couches de sédiments. Chaque strate se distingue par un
groupe unique d’espèces fossiles et plus la strate est profonde, plus les fossiles sont anciens. Les
phénomènes d’extinction sont fréquents dans l’histoire de la vie, car, de strate en strate, des
espèces disparaissent alors que d’autres apparaissent. Toutefois, les limites entre les strates
correspondent à des catastrophes, et les nouveaux organismes sont venus d’ailleurs, sans
transformations.
Personnalité : __________________________________
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
1
/
73
100%