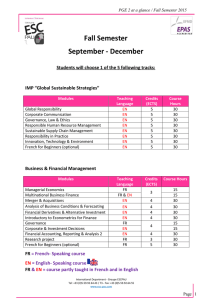
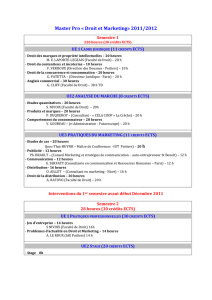
marketing

Last Update:01
/
03/06 Mark Thomas: [email protected]
Page 1 sur 108
Programme
des Cours
Course
Catalogue
Programme Ecole de Commerce
Marketing Management Européen
1° et 2° Année
Business School Programme
European Marketing and Management
Undergraduate
Year 1 & 2
Paris • Lyon • Montpellier • Nantes • Nice • Toulouse

Last Update:01
/
03/06 Mark Thomas: [email protected]
Page 2 sur 108
Introduction
Ce document est une présentation de notre programme Ecole de Commerce, avec les différents cours dispensés
ainsi que leur valorisation en volume et crédits ECTS.
En 1999, 29 pays, y compris la France ont signé la Déclaration de Bologne qui pose les fondations d’une
coopération académique en Europe et à travers le monde. Aujourd’hui 40 pays adhèrent à cet accord qui a pour
objectif de:
• Créer un système de diplômes qui serait lisible et comparable à travers l’Europe
• Etablir une distinction claire entre le niveau Licence et le niveau Master en Europe
• Promouvoir la mobilité académique internationale des étudiants
• Mettre en place un système de contrôle de qualité de l’Education Supérieure afin de maintenir la qualité de
l’enseignement dans les pays participants
Source : http://www.gmac.com/
Avec un long historique d’excellence académique et de mobilité de ses étudiants, IDRAC International
School of Management adhère pleinement aux principes du processus de Bologne.
Une partie fondamentale de cet accord est la création d’un système d’évaluation transparent à travers la mise en
place du European Credit Transfer System (ECTS). Ce document contient donc le descriptif des cours du
programme école de commerce avec les crédits ECTS afin de permettre aux étudiants et aux institutions
partenaires de comparer les modules.
Selon les principes établis par l’Accord de Bologne, ce document est écrit en Français et en Anglais.
Introduction
This document is a presentation of the Business School Programme with the courses offered and their ECTS
value.
In 1999, 29 countries, including France signed the Bologna Declaration which laid down the foundations for
education cooperation within Europe and worldwide. Today some 40 countries adhere to this agreement which
aims to:
• create a system of comparable and understandable degrees throughout the European Union
• establish a clear and standard division between undergraduate and graduate studies
• promote student mobility among different fields of study, institutions, and nations
• develop a quality-assurance process and governing body to ensure standard qualifications and quality throughout
participating countries
Source : http://www.gmac.com/
With a long history of academic achievement and student mobility, IDRAC, International School of
Management adheres fully to principles the system laid down by the Bologna Accord.
A fundamental part of the agreement is the creation of a transparent system of evaluating students through the
establishment of a European Credit Transfer System (ECTS). This document provides a catalogue of courses
provided by the business school programme to enable exchange students and partner institutions to compare
modules.
In accordance with the Bologna Accord, this document is written in French & English.
Mark Thomas
Directeur du Programme Ecole de Commerce
& Relations Internationales, IDRAC Group
Mars / March 2006

Last Update:01
/
03/06 Mark Thomas: [email protected]
Page 3 sur 108
European Credit Transfer System (ECTS)
Le système des crédits ECTS a été mis en place par la commission européenne afin de garantir un
transfert des Crédits dans leur totalité pour les Universités et l’enseignement supérieur en général ;
l’objectif étant de rapatrier l’ensemble des crédits validés à l’extérieur, dans l’université d’origine. Ce
système permet de qualifier et comparer les formations d’un établissement à l’autre.
Il est basé sur 3 axes : l’information (sur les programmes, et les résultats de l’étudiant), un accord (entre
les établissements partenaires et l’étudiant) et l’utilisation des crédits ECTS (afin d’indiquer la charge
de travail). Ce système n’a pas pour objectif de contrôler le contenu des formations ou l’équivalence des
diplômes, les crédits sont simplement un coefficient appliqué à chaque module afin de déterminer la
charge de travail qu’il génère. En ECTS 60 Crédits correspondent à une année d’étude à plein temps, 30
Crédits correspondent à un semestre et 20 pour les systèmes académiques au trimestre.
Le programme école de commerce de l’IDRAC offre la possibilité de valider 30 crédits ECTS par
semestre.
European Credit Transfer System (ECTS)
The European Course Credit Transfer System, ECTS, was developed by the European Commission to
provide common procedures to guarantee the full transferability of credits for university & higher
education studies abroad in order that they might count towards a final qualification in the home
institution.
It provides a way of measuring and comparing academic merits and transferring them from one
institution to another. The system is based on three core elements: information (on study programmes
and student achievement), mutual agreement (between the partner institutions and the student) and the
use of ECTS credits (to indicate student workload). In itself, ECTS in no way regulates the content,
structure or equivalence of study programmes, the credits are simply a value allocated to course units as
a means of describing the workload required to complete the course/module. In ECTS, 60 credits
normally represent the workload required for one year's full-time study, 30 credits per semester or 20
credits per term (in a tri-semester system).
The 4 year business programme at IDRAC provides students with 30 ECTS credits per semester.

Last Update:01
/
03/06 Mark Thomas: [email protected]
Page 4 sur 108
Codification
Le système de crédits ECTS pour le programme Ecole de Commerce à l’IDRAC est présenté sous la forme d’un
catalogue de cours. Selon la norme ECTS chaque cours/module est valorisé en durée, en contenu et suivant un
système d’évaluation. Un module peut prendre la forme d’un cours, d’un stage ou d’un projet. Un module peut
aussi être composé de plusieurs cours (cas des dominantes de 4
ème
année).
Classification
The ECTS system pour the Business School Programme at IDRAC is presented in the form of a catalogue of
modules & courses. In accordance with ECTS norms, each course or module is attributed a duration, work load,
the contents and the evaluation method. A module may consist of a standard academic course, an internship or a
project. A module may also consist of several courses (e.g. Year 4 specialisations or majors).
Les abréviations suivantes sont utilisées pour la codification des modules :
The following abbreviations are used for the codification of modules:
MKTF Marketing Fondamental
Fundamental Marketing CDP Culture et Développement Personnel
Cultural and Personnel Development
MKTA Marketing Appliqué
Applied Marketing DVI Développement International
International Development
MKTE Marketing Etudes
Marketing studies MRH Management des Ressources Humaines
Human Resource Management
MKTC Marketing Cas
Marketing Case MAST Management Stratégique
Strategic Management
MKTS Marketing Stratégique
Strategic Marketing STP Simulation et travaux Professionnels
Business Simulation and professional work
MKTI Marketing International
International Marketing
Dominantes
Specialisations or Majors
INFO Informatique/Bureautique
Computing and Office skills MKT Marketing
Major in Marketing
TQG Techniques Quantitatives de Gestion
Financial Management Skills ACH Achats
Major in Purchasing
GFC Finance/Comptabilité
Financial Management/Accounting PME PME
Major in SME (Small Medium Enterprises)
ECO Economie/Géopolitique
Economics/ Geopolitics AI Affaires Internationales
Major in International Trade
MKTF Marketing Fondamental
Fundamental Marketing FIN Finance
Major in Finance
DRO Droit
Law COM Communication
Major in Communication
La CODIFICATION des modules est fondée sur les principes suivants :
The classification for the courses is based on the following principles:
Matière/Année/Numéro d’ordre si nécessaire. Exemple (en 4
ème
année)
Subject / Year / number and order if necessary (e.g. Year 4 courses)
Mémoire
Dissertation STP 4 0
Stage d’Insertion Professionnelle
Work Placement / Internship STP 4 1
Projet Système d’Information
Information Systems Project STP 4 2

Last Update:01
/
03/06 Mark Thomas: [email protected]
Page 5 sur 108
Une synthèse du programme Ecole de Commerce
Le programme Ecole de Commerce à IDRAC International School of Management a été soigneusement étudié
afin de diplômer des jeunes professionnels qui ont prouvé leurs compétences académiques et leurs compétences
managériales dans un contexte multi culturel. En parallèle des cours académiques enseignés au cours des
différentes années, l'Idrac laisse également une grande place au développement personnel de chacun.
Notre programme comprend :
Un programme académique sur 4 années
15 à 18 mois de stage en entreprise dont au moins 1 stage à l’étranger (pays non francophone)
1 semestre au moins de cours dans l’une de nos université partenaires (45 universités réparties sur 20
pays). 70% des étudiants partent une année et obtiennent un double diplôme.
Une troisième année enseignée totalement en anglais.
Un enseignement de haut niveau de 2 langues étrangères dont l’Anglais. Nous encourageons nos étudiants
à suivre une 3eme langue (parmi un choix 10 langues étrangères)
Le choix de 6 dominantes en 4eme année :
Marketing,
Communication et Publicité,
Affaires Internationales (en anglais),
Création d’entreprise,
Finance,
Management des Achats
Overview of the 4 Year Business Programme
The business programme at IDRAC International School of Management has been carefully designed in order to
create well balanced business graduates that have had the opportunity to prove their academic capabilities and to
show their managerial skills in a mutli-cultural environment. Whilst certain courses are taught throughout the
programme each academic year aims to give the students specific aims and objectives to enhance their personal
& career development.
Programme highlights include:
•
A standard academic workload for a four year business programme.
•
15-18 months working in companies on internships or work placements. At least one of these internships
must be completed in a non French speaking country.
•
At least one semester of study in a partner university or business school outside of France (45 partners in
20 countries). 70% of IDRAC students complete a joint degree programme after one year studying a
partner university.
•
A Year 3 programme that is taught entirely in English.
•
An excellent working level of 2 foreign languages one of which must be English. Students are strongly
advised to begin a third foreign language from the 10 different languages that are taught at IDRAC.
•
The choice of 6 specialisations in Year 4:
Marketing,
Supply Chain Management
SME Management
Communication
Finance
International Trade (taught entirely in English)
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77
 78
78
 79
79
 80
80
 81
81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 85
85
 86
86
 87
87
 88
88
 89
89
 90
90
 91
91
 92
92
 93
93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
 101
101
 102
102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
1
/
108
100%