Tolérance cardiovasculaire des anticholinestérasiques

Journal Identification = PNV Article Identification = 0335 Date: March 2, 2012 Time: 2:41 pm
Synthèse
Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil 2012 ; 10 (suppl ´
ement 1) : 15-8
Tolérance cardiovasculaire
des anticholinestérasiques
Olivier Hanon
Université Paris Descartes, EA 4468,
Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris,
Hôpital Broca, Service de gériatrie, Paris
<olivier[email protected]>
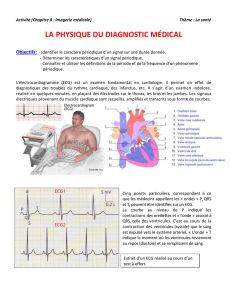
Le cœur possède une innervation parasympathique dont le neurotransmet-
teur est l’acétylcholine. Ces fibres ont un effet dépresseur sur le nœud
sinusal qui ralentit la fréquence des décharges nodales. De même, ces
fibres sont inhibitrices sur la conduction auriculo-ventriculaire par leur action sur
le nœud auriculo-ventriculaire. Cet effet vagotonique se traduit par une brady-
cardie due à une augmentation de la conductance au potassium causant une
hyperpolarisation membranaire. Chez les personnes âgées, l’un des effets du
vieillissement myocardique est associé à une perte cellulaire plus marquée au
niveau du nœud sinusal et du tissu nodal, majorant alors le risque de bradycardie.
Ainsi, la réalisation d’un holter ECG, chez des sujets âgés de plus de 75 ans [1]
indique l’existence d’épisodes de bradycardie sinusale (FC <60/min) chez 13 %
des sujets, en revanche les troubles conductifs sévères (BAV 2 et 3) apparaissent
rares (<2 %).
Les anticholinestérasiques sont susceptibles d’augmenter l’acétylcholine au
niveau du cœur et de favoriser un effet vagotonique. La traduction clinique de
cet effet fait l’objet de cette revue de la littérature.
Cas cliniques
Dans l’ensemble de la littérature on note 14 cas de mauvaise tolérance cardiovas-
culaire rapportés chez des patients recevant des anticholinestérasiques. La grande
majorité concerne des bradycardies et des troubles de conduction. Parfois une tor-
sade de pointes est décrite, le plus souvent, dans ces cas, d’autres circonstances
cliniques telles que des hypokaliémies ou la prise de médicaments allongeant
l’espace QT sont présentes. Un certain nombre de ces publications notent que les
traitements anticholinestérasiques étaient parfois donnés avec des doses supé-
rieures à celles recommandées. La complexité dans ce type de «cas rapportés »
est l’impossibilité d’évaluer réellement si l’événement indésirable est imputable
ou non au traitement anticholinestérasique, puisque survenant chez des patients
âgés fragiles qui auraient peut-être fait l’événement sans traitement.
Études rétrospectives
Une étude rétrospective [2] a examiné à partir des codes diagnostiques, la sur-
venue de syncopes chez des patients ayant une maladie d’Alzheimer (n = 19 803)
recevant des anticholinestérasiques ; et chez des patients non déments ne rece-
vant pas d’anticholinestérasiques (n = 61 499). Le groupe traité présentait plus
souvent des syncopes (OR : 3,15 [IC 95% : 1,6-2,0]). Dans cette observation
étaient constatées également plus de bradycardies (1,8 [1,3-2,2]), de poses de
pace maker (1,5 [1,1-2,0]) et de fractures de l’extrémité supérieure du fémur (1,2
[1,0-1,3]) dans le groupe traité.
doi:10.1684/pnv.2012.0335
Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil, vol. 10, suppl ´
ement 1, mars 2012 15
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

Journal Identification = PNV Article Identification = 0335 Date: March 2, 2012 Time: 2:41 pm
O. Hanon
Toutefois, la méthodologie de ce travail (étude
rétrospective) ne permet pas de conclure sur la causa-
lité des traitements anticholinestérasiques vis-à-vis des
complications rapportées. Il n’est notamment pas possible
de déterminer si ces complications sont plus souvent asso-
ciées aux pathologies démentielles et à leurs nombreuses
comorbidités ou bien aux traitements anti-cholinestérasi-
ques.
Dans une autre étude d’observation [3], le risque de
bradycardie de patients atteints d’une maladie d’Alzheimer
sous traitement a été comparé à un groupe de patients
déments non traités. La présence à la fois du code maladie
d’Alzheimer et prise d’un traitement anticholinestérasique
était associée à une augmentation du risque de bradycardie
définie par une fréquence cardiaque <60/min (1,4 [1,1-1,6]).
L’augmentation de risque était observée pour le donepezil
(essentiellement avec des fortes doses), la rivastigmine et
non pour la galantamine, mais il s’agit d’une étude rétros-
pective qui n’avait pas vocation à comparer les traitements
entre eux.
Études en ouvert
Les études en ouvert ont permis d’effectuer une sur-
veillance des patients recevant des anticholinestérasiques.
Ainsi dans une étude [4] où les sujets sous rivastigmine
ont été suivis pendant 5 ans, les anomalies de l’ECG et
les complications cardiovasculaires graves n’ont été obser-
vées que chez 0,2 % des patients. Avec le donepezil [5]
une extension en ouvert d’une étude de tolérance-efficacité
(n = 763) pendant 2,8 ans observe une fréquence des bra-
dycardies (<50 bpm) de 18 % et des effets secondaires
cardiovasculaires de 1 %, soit des chiffres habituels pour
une population âgée.
Dans les précédentes études, la bradycardie est consi-
dérée sous son aspect d’effet indésirable potentiel des
médicaments à effets cholinergiques. Mais en-soi la bra-
dycardie ne représente pas un facteur de gravité, en
particulier dans l’insuffisance cardiaque ou les coronaro-
pathies, où elle est même bénéfique. Dans une étude
franc¸aise, 19 386 personnes âgées de plus de 55 ans ont
été suivies pendant 20 ans [6]. La mortalité était inférieure
dans le groupe dont la fréquence cardiaque était entre 60
et 80 bpm, par rapport au groupe ayant une fréquence car-
diaque entre 80 et 100 bpm, lequel a une mortalité inférieure
au groupe ayant une fréquence cardiaque supérieure à
100 bpm. De même, dans la récente étude Beautiful menée
chez des coronariens avec dysfonction ventriculaire gauche
(n = 5 438), les patients ayant une fréquence cardiaque infé-
rieure à 70 bpm présentaient une réduction de la mortalité
cardiovasculaire. Dans cette étude une fréquence cardiaque
inférieure à 70 bpm semblait protéger également du risque
de survenue d’une insuffisance cardiaque, d’infarctus du
myocarde ou de la nécessité de réaliser une angioplastie
coronaire [7].
Événements cardiovasculaires
au cours des essais randomisés
Les essais randomisés correspondent au niveau de
preuve le plus élevé pour déterminer la tolérance d’un trai-
tement.
Les bradycardies
Globalement, les anticholinestérasiques diminuent la
fréquence cardiaque de2à3battements par minute en
comparaison au placebo [8]. Dans les études analysant
l’efficacité des anticholinestérasiques (donepezil, rivastig-
mine, galantamine), les bradycardies n’étaient pas plus
fréquentes dans le groupe traité (8). Dans une étude [9]
incluant des sujets en institution, âgés en moyenne de 86
ans (MMS moyen : 14/30), la fréquence cardiaque diminuait
de 2,7 bpm chez les patients traités et de 0,7 bpm dans
le groupe contrôle. Cette différence n’était pas significa-
tive, de même le nombre d’événements cardiovasculaires
et d’anomalies à l’ECG n’était pas différent entre les
2 groupes.
Les troubles de la conduction
Il est parfois évoqué une relation dose-dépendante avec
les effets indésirables cardiovasculaires, mais les études
randomisées ne le montrent pas. Pour la rivastigmine sur un
collectif de 2 791 patients suivis 26 semaines en moyenne
[10], il n’est pas observé de ralentissement de la fréquence
cardiaque entre les valeurs initiales et celles au terme
du suivi. De même l’espace PR sur l’ECG de surface ne
s’allonge pas ni l’espace du complexe QRS, ou encore
l’espace QT. Dans ce même travail en comparaison avec
le groupe placebo, il n’y a pas plus d’anomalie ECG, de BAV
de premier degré, d’allongement du QRS ou de troubles de
la repolarisation.
Une large méta-analyse très récente [11] a regroupé
40 études d’intervention soit 9 882 sujets, les risques de
survenue de chutes, de syncopes, et d’effets indésirables
ont été analysés. Il est noté une augmentation du risque
de syncope (OR ; 1,53 [IC 95% : 1,02-2,30]), mais non
de chutes (0,88 [0,74-1,04]), ni de fractures (1,39 [0,75-
2,56]). L’analyse de la littérature ne permet pas de connaître
16 Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil, vol. 10, suppl ´
ement 1, mars 2012
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

Journal Identification = PNV Article Identification = 0335 Date: March 2, 2012 Time: 2:41 pm
Tolérance cardiovasculaire des anticholinestérasiques
l’origine des syncopes, dont les étiologies sont souvent
multifactorielles chez la personne âgée.
Le risque de mortalité
Dans une étude incluant des patients ayant un déficit
cognitif léger, la galantamine était comparée à un pla-
cebo pendant une période de 2 ans ; il avait été constaté
une surmortalité dans le groupe traité (1,4 % vs 0,3 %)
ce qui avait donné lieu à une alerte par la Food and
drug administration [12]. L’analyse de la mortalité réali-
sée sur l’ensemble des études comparant la galantamine
(n=4116) et un placebo (n = 2 386) [13] ne montre pas
de différence significative de risque de mortalité entre les
2 groupes (OR = 0,67 [0,41-1,10]), et indique même plutôt
une tendance vers une réduction de mortalité du groupe
traité par galantamine. Pour le donepezil et la rivastigmine,
deux méta-analyses indiquent également l’absence de dif-
férence de mortalité avec le groupe placebo [14, 15]. Si
l’on ne prend en compte que les patients à risque vas-
culaire élevé, on n’observe pas non plus d’augmentation
des risques cardiaque et vasculaire. Ainsi dans une méta-
analyse regroupant les patients présentant une démence
vasculaire [16], il n’est pas observé d’augmentation des
événements cardiovasculaires sous donepezil 5 et 10 mg,
galantamine 24 mg ni rivastigmine 12 mg. Dans une étude
incluant 699 patients de plus de 75 ans présentant à la fois
une maladie d’Alzheimer et des facteurs de risque vascu-
laires, un traitement par rivastigmine n’entraînait pas plus
d’événement cardiovasculaire, ni de modifications de l’ECG
comparé au groupe placebo [[17]. Une autre étude [18]
comparant la rivastigmine (n = 362) à un placebo (n = 179)
chez des patients souffrant de démence parkinsonienne ou
de démence à corps de Lewy montrait même une réduction
des anomalies cardiovasculaires (p = 0,002), en particulier
les hypotensions orthostatiques et les syncopes (p = 0,018)
dans le groupe traité. Les anomalies de l’ECG de surface
(espace PR, QRS, QT) étaient similaires, ceci de manière
simultanée à un ralentissement de la fréquence cardiaque
de 1,5 à 2 bpm en moyenne, comme dans toutes les
études.
Si l’on examine les taux d’arrêt d’étude et leur cause sur
l’ensemble des essais comparatifs publiés jusqu’en 2008
[19], il n’y a pas de différence pour les arrêts dus à des
événements cardiovasculaires dans les groupes traités de
ces différentes études.
Au total, tous les essais thérapeutiques randomisés
vont dans le même sens et n’indiquent pas de sur-risque car-
diovasculaire. Seule une augmentation des syncopes sans
complication cardiovasculaire ni traumatique est rarement
observée.
Propositions de bon usage
des anticholinestérasiques vis-à-vis
du risque cardiovasculaire
L’ensemble des données de la littérature et les pré-
cautions d’emploi indiquent qu’il est préférable de réaliser
un ECG avant la prescription d’un anticholinestérasique
dans les situations suivantes : antécédent cardiaque, bra-
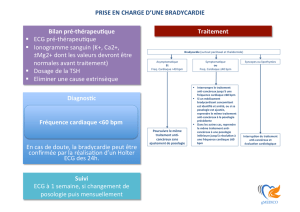
dycardie (FC <60 bpm) ou lorsque le patient rec¸ oit un
traitement ayant un effet bradycardisant (exemple un
bêtabloquant, digoxine, cordarone, diltiazem, verapamil...).
Dans ce cadre, les recommandations de la HAS 2011 sou-
lignent que «un ECG est recommandé avant la prescription
d’un inhibiteur de la cholinestérase chez les patients ayant
des antécédents cardiaques, bradycardes, ou sous traite-
ment bradycardisant ».
Au cours du suivi, une surveillance de la fréquence
cardiaque et de l’ECG (en cas de bradycardie ou de syn-
cope/malaise) suffit.
Il faut envisager un arrêt des anticholinestérasiques si
on observe :
– une bradycardie (FC <50 bpm) ;
– ou des anomalies ECG (BAV 2 ou 3 degré, un bloc sino-
auriculaire) ;
– ou une syncope.
Lorsque les symptômes ne présentent pas de carac-
tère de sévérité (bradycardie >50 bpm ou BAV de premier
degré), absence de syncope, le traitement peut être main-
tenu éventuellement en diminuant la posologie. Si les
signes s’aggravent, le traitement sera arrêté.
Dans tous les cas, après arrêt du traitement il convient
de poursuivre la surveillance de la fréquence cardiaque
et de l’ECG car le plus souvent ces troubles témoignent
d’anomalies sous-jacentes du tissu nodal, qui risquent de
nécessiter à terme la mise en place d’un pace-maker.
Ainsi, si on observe une persistance des symptômes après
l’arrêt des anticholinestérasiques, une exploration électro-
physiologique peut être indiquée.
On peut rappeler dans les précautions d’emploi, le méta-
bolisme hépatique passant par le cytochrome P 450 pour
le donepezil et la galantamine. Ces anticholinestérasiques
auront une élimination ralentie par les inhibiteurs de ces
mêmes cytochromes (amiodarone, vérapamil, diltiazem, flé-
caïnide, fluoxetine, paroxétine, érythromycine, quinidine,
fluconazole, ketoconazole). En cas de prescription simul-
tanée de ces traitements, il conviendra d’effectuer une
surveillance accrue, de réaliser une titration lente avec sur-
veillance de la fréquence cardiaque.
Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil, vol. 10, suppl ´
ement 1, mars 2012 17
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.

Journal Identification = PNV Article Identification = 0335 Date: March 2, 2012 Time: 2:41 pm
O. Hanon
Conclusion
Les anticholinestérasiques, en élevant les taux d’acé-
tylcholine, ont un effet vagotonique potentiel. Le ralentisse-
ment de la fréquence cardiaque peut en cas d’anomalies
sous-jacentes ou lors d’antécédents cardiaques avoir une
traduction clinique. En cas de bradycardie inférieure à
50 bpm, de signe de dysfonction sinusale ou de bloc
auriculo-ventriculaire 2 ou 3, les anticholinestérasiques ne
sont pas recommandés. Les accidents restent rares voire
exceptionnels si l’on prend la précaution de réaliser un ECG
lors de la prescription. C’est pourquoi toutes les recom-
mandations actuelles dont les plus récentes (NICE 2011,
HAS 2011), recommandent la prescription des anticholines-
térasiques dans la stratégie thérapeutique de la maladie
d’Alzheimer aux stades léger et modéré.
Conflits d’intérêts : l’auteur a déjà rec¸u des honoraires de
l’industrie pharmaceutique dans le cadre de conférences ou
conseils (Novartis, Janssen, Eisai, Lunbeck, Boehringer-Ingelheim,
Ménarini, Pfizer, Bayer, Astra-Zeneca, Sanofi-Aventis, BMS, Servier,
Solvay, Abott, Exonhit).
Références
1. Frishman WH, Heiman M, Karpenos A, Ooi WL, Mitzner A, Goldkorn
R, et al. Twenty-four-hour ambulatory electrocardiography in elderly
subjects : prevalenceof various arrhythmias and prognostic implica-
tions (report from the Bronx Longitudinal Aging Study). Am Heart J
1996 ; 132 : 297-302.
2. Gill SS, Anderson GM, Fischer HD, Bell CM, Li P, Normand SL, et al.
Syncope and its consequences in patients with dementia receiving cho-
linesterase inhibitors : a population-based cohort study. Arch Intern Med
2009 ; 169 : 867-73.
3. Hernandez RK, Farwell W, Cantor MD, Lawler EV. Cholinesterase
inhibitors and incidence of bradycardia in patients with dementia in
the veterans affairs new England healthcare system. J Am Geriatr Soc
2009 ; 57 : 1997-2003.
4. Small GW, Kaufer D, Mendiondo MS, Quarg P, Spiegel R. Cognitive
performance in Alzheimer’s disease patients receiving rivastigmine for
up to 5 years. Int J Clin Pract 2005 ; 59 : 473-7.
5. Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Gordon B, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD ; Done-
pezil Study Group. Open-label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of
the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease.
Arch Neurol 2001 ; 58 : 427-33.
6. Benetos A, Rudnichi A, Thomas F, Safar M, Guize L. Influence of
heart rate on mortality in a French population : role of age, gender, and
blood pressure. Hypertension 1999 ; 33 : 44-52.
7. Fox K, Ford I, Steg PG, Tendera M, Robertson M, FerrariR;BeautifuL
investigators. Heart rate as a prognostic risk factor in patients with coro-
nary artery disease and left-ventricular systolic dysfunction (Beautiful) :
a subgroup analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008 ; 372 :
817-21.
8. Pratt RD, Perdomo CA, Surick IW, Ieni JR. Donepezil : tolerability and
safety in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Clin Pract 2002 ; 56 : 710-7.
9. Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam
EM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study of the
efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in
the nursing home setting. J Am Geriatr Soc 2001 ; 49 : 1590-9.
10. Morganroth J, Graham S, Hartman R, Anand R. Electrocardiographic
effects of rivastigmine. J Clin Pharmacol 2002 ; 42 : 558-68.
11. Kim DH, Brown RT, Ding EL, Kiel DP, Berry SD. Dementia medi-
cations and risk of falls, syncope, and related adverse events :
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Geriatr Soc
2011 ; 59 : 1019-31.
12. (Food and Drug Administration. Alert for Healthcare Professionals
on Galantamine hydrochloride [FDA ALERT 02/23/2005]).
13. Feldman HH, Pirttila T, Dartigues JF, Everitt B, Van Baelen
B, Brashear HR, et al. Analyses of mortality risk in patients with
dementia treated with galantamine. Acta Neurol Scand 2009 ; 119 :
22-31.
14. Birks J, Harvey RJ. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer’s
disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;1:CD001190.
15. Birks J, Grimley Evans J, Iakovidou V, Tsolaki M, Holt FE.
Rivastigmine for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev
2009;2:CD001191.
16. Kavirajan H, Schneider LS. Efficacy and adverse effects of
cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in vascular dementia : a meta-
analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol 2007;6:
782-92.
17. Kumar V, Anand R, Messina J, Hartman R, Veach J. An efficacy and
safety analysis of Exelon in Alzheimer’s disease patients with concur-
rent vascular risk factors. Eur J Neurol 2000;7:159-69.
18. Ballard C, Lane R, Barone P, Ferrara R, Tekin S. Cardiac safety of
rivastigmine in Lewy body and Parkinson’s disease dementias. Int J Clin
Pract 2006;60:1146.
19. Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Webb AP, Morgan LC, Moore CG, Jonas
DE. Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine for
the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease:asystematic review and meta-
analysis. Clin Interv Aging 2008;3:211-25.
18 Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil, vol. 10, suppl ´
ement 1, mars 2012
Copyright © 2017 John Libbey Eurotext. Téléchargé par un robot venant de 88.99.165.207 le 25/05/2017.
1
/
4
100%