Les intervalles de temps systoliques en réanimation Systolic

NOTE PHYSIOLOGIQUE
Les intervalles de temps systoliques en réanimation
Systolic-time intervals in intensive care
K. Bendjelid
Division des soins intensifs adultes, hôpitaux universitaires de Genève CH-1211, rue Micheli du Crest, 14 Genève, Suisse
Disponible sur internet le 13 mars 2007
MOTS CLÉS
Phases ;
Périodes ;
Cycle ;
Systole ;
Hémodynamique
Résumé Le monitorage hémodynamique et cardiovasculaire est indispensable pour la prise en
charge d’un patient de soins intensifs. Diverses techniques de mesures de pressions, de surfa-
ces, de volumes et de débits sont utilisées en réanimation. Les intervalles de temps systoli-
ques, largement utilisés en cardiologie il y a une trentaine d’années, pourraient avoir une
place dans la prise en charge d’un patient présentant une instabilité hémodynamique. La pré-
sente revue tente de proposer certains indices, pour l’évaluation de la fonction cardiocircula-
toire en réanimation.
© 2007 Société de réanimation de langue française. Publié par Elsevier Masson SAS. Tous
droits réservés.
KEYWORDS
Phases;
Periods;
Cycle;
Systole;
Hemodynamics
Abstract Hemodynamic and cardiovascular monitoring is essential for the management of cri-
tically ill patients. Various techniques of pressure surface, area, volume and flow measure-
ments are used in intensive care. Systolic time intervals were widely used in cardiology
30 years ago and could be usefull in managing patients with hemodynamic instability. The pre-
sent review tries to propose indices to estimate cardio-circulatory function in intensive care.
© 2007 Société de réanimation de langue française. Publié par Elsevier Masson SAS. Tous
droits réservés.
Introduction
La dysfonction contractile ventriculaire résulte en une dimi-
nution de la force générée par le myocarde, une baisse du
volume d’éjection systolique du ventricule gauche et une
variation de la durée des différentes phases de la contraction
[1]. Il y a une trentaine d’années, la détermination des inter-
valles de temps systoliques était souvent utilisée par les car-
diologues pour le suivi des cardiopathies ischémiques, des
maladies valvulaires, des cardiomyopathies hypertrophiques,
de la maladie hypertensive et de certains effets pharmaco-
logiques sur le myocarde [1–6]. Cette méthode permettait
d’évaluer la fonction ventriculaire gauche moyennant des
méthodes non sanglantes utilisant l’enregistrement phono-
cardiograhique (+ carotidogramme) [7],l’échocardiographie
doppler ou bien le doppler œsophagien [8],combinésà
l’ECG. Les intervalles de temps systoliques les plus utilisés
étaient : la période de prééjection (PEP), le temps d’éjec-
tion ventriculaire gauche (LVET) et le rapport PEP/LVET [1].
Depuis une vingtaine d’années, ces différentes durées et
phases de la systole ventriculaire ont été utilisées dans le
cadre d’un monitorage hémodynamique non invasif en réani-
mation en utilisant un doppler œsophagien ou bien l’impé-
dancemétrie [8–12].
Réanimation 16 (2007) 120–123
Adresse e-mail : [email protected] (K. Bendjelid).
1624-0693/$ - see front matter © 2007 Société de réanimation de langue française. Publié par Elsevier Masson SAS. Tous droits réservés.
doi:10.1016/j.reaurg.2007.02.007
available at www.sciencedirect.com
journal homepage: http://france.elsevier.com/direct/REAURG/

Les intervalles de temps systoliques
La période de prééjection (PEP)
La PEP est définie par l’intervalle de temps séparant la
dépolarisation ventriculaire (début du QRS sur l’ECG) du
début de l’éjection ventriculaire gauche (ouverture de la
valve aortique) [1]. Cette durée de temps dépend de la pré-
charge, de la postcharge et de la contractilité [13].La
valeur normale chez l’adulte est de 106 ± 7 ms [14].Il
n’existe pas de consensus entre les diverses études publiées
concernant la dépendance de cette durée vis-à-vis de la
fréquence cardiaque [13–15].
Le temps d’éjection ventriculaire gauche (LVET)
Le LVET est défini par l’intervalle de temps systolique
durant lequel le ventricule gauche éjecte du sang dans
l’aorte (ouverture–fermeture de la valve aortique) [13].La
phonocardiographie sert à situer le moment de la fermeture
de la valve aortique qui correspond à la composante aor-
tique du second bruit. Cette durée de temps dépend princi-
palement du volume d’éjection systolique [16]. La valeur
normale chez l’adulte est de 292 ± 18 ms [14]. Cette valeur
est inversement corrélée à la fréquence cardiaque, en
accord avec le fait que le volume d’éjection systolique
diminue lorsque la fréquence cardiaque augmente [16].
Le rapport PEP/LVET
Le rapport PEP/LVET est un indice fiable de la fonction
contractile cardiaque [13]. En effet, l’apparition d’une dys-
fonction cardiaque augmente la valeur de la PEP et diminue
la durée de LVET [13]. De ce fait le rapport PEP/LVET aug-
mente en cas d’une baisse de la contractilité. La valeur
normale chez l’adulte est de 0,37 ± 0,03 [14]. Diverses étu-
des ont retrouvé une corrélation entre ce rapport et les dif-
férents indices évaluant la performance ventriculaire gau-
che [3–6,17–22]. Néanmoins, la diminution du LVET faisant
suite à une dysfonction ventriculaire gauche peut paraître
illogique [13]. En effet, durant l’éjection, la vitesse de
contraction est diminuée lors de la présence d’une insuffi-
sance cardiaque. Cette situation devrait prolonger le LVET.
Cependant, lors d’une dysfonction contractile, l’amplitude
du raccourcissement de la fibre cardiaque est diminuée
aussi, ce qui participe à une diminution de la valeur LVET
[13]. De plus, LVET étant un temps lié au volume d’éjection
systolique, une diminution de ce dernier suite à la dysfonc-
tion cardiaque doit impérativement avoir le même effet sur
LVET [13].
Les intervalles de temps systoliques
en réanimation
Le temps d’éjection ventriculaire gauche (LVET)
La mesure semi-invasive (doppler œsophagien) de la vitesse
d’écoulement du sang dans l’aorte thoracique ascendante
ou descendante permet une mesure précise du débit car-
diaque [23]. Les principes techniques de la mesure du
débit cardiaque par effet Doppler consistent en l’obtention
d’un signal Doppler continu ou tous les écoulements ren-
contrés par le faisceau ultrasonore se trouvent alignés sur
le trajet étudié. Cette technique permet aussi d’obtenir la
PEP et le LVET moyennant l’enregistrement simultané de
l’électrocardiogramme [9]. De nombreuses équipes ont
objectivé que la mesure du LVET indexé à la fréquence car-
diaque (LVETI) était un indice statique de la précharge ven-
triculaire gauche chez des patients anesthésiés au bloc opé-
ratoire ou en réanimation [8,10,11]. Néanmoins, cette
mesure n’est pas utilisée en pratique clinique, sujet à de
nombreux débats et rares sont les études récentes sur ce
sujet [24–26].
La période de prééjection (PEP)
Du fait que la majorité des patients des soins intensifs sont
porteurs de cathéter artériel, Bendjelid et al. ont proposé
de mesurer la PEP moyennant l’enregistrement simultané
de courbe de pression artérielle sanglante et l’électrocar-
diogramme (Fig. 1)[27]. La PEP a été définie comme le
temps séparant l’onde Q ou R sur l’ECG et le début de mon-
tée en pression artérielle mesuré classiquement au niveau
radial [27]. Du fait que ces auteurs se soient intéressés à la
variation (dynamique) de ce temps au cours d’un cycle ven-
tilatoire par pression positive, la valeur absolue de PEP
mesurée avait peu d’importance (onde Q ou R sur l’ECG)
du moment que les deux mesures au cours du cycle de ven-
tilation étaient acquises de façon identique [27].
En effet, les variations cycliques des volumes d’éjection
systolique secondaires à la ventilation mécanique sont les
déterminants de ce qu’on appelle communément les pré-
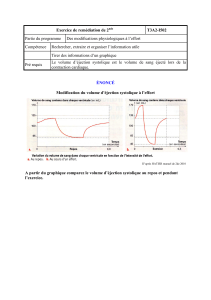
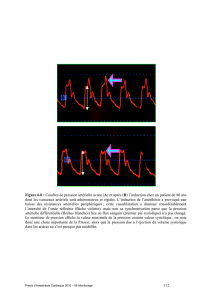
Figure 1 Technique de mesure de la période de prééjection (PEP) moyennant le défilement simultané de l’électrocardio-
gramme et de l’onde de pression artérielle sanglante. L’intervalle est mesuré depuis le début de la dépolarisation électrique du
ventricule (onde Q) jusqu’au début de la montée en pression de l’onde artérielle.
Les intervalles de temps systoliques en réanimation 121

dicteurs (indices) dynamiques (en opposition avec indices
statiques mesurés en fin d’expiration) de la réponse au
remplissage vasculaire (augmentation ou non du débit car-
diaque au-dessus de 15 %) [28]. Ces indices dynamiques se
traduisent par une variation ventilatoire de la pression
artérielle systolique, de la pression pulsée systémique, du
volume d’éjection systolique, et des vélocités doppler
trans-aortiques [29]. Toutes ces mesures nous renseignent
sur la « précharge-dépendance » des ventricules avec une
utilité clinique pour quantifier les effets hémodynamiques
d’une expansion volémique [29].
Bien que le temps PEP soit aussi dépendant de la
contractilité et de la postcharge, la valeur de cet intervalle
de temps diminue toujours avec l’augmentation de la pré-
charge [1,30]. Wallace et al. ont démontré que l’augmenta-
tion du volume d’éjection systolique diminue la valeur de
PEP [31]. De plus, plusieurs études réalisées chez l’homme
ont démontré que la diminution du temps PEP après un
remplissage vasculaire était associée à une augmentation
du volume d’éjection systolique [32–34]. De façon intéres-
sante, Brundin et al. ont démontré que la ventilation à
pression positive augmente la valeur de l’intervalle PEP en
diminuant le retour veineux et donc le volume d’éjection
systolique [35]. Bendjelid et al. ont utilisé la variation res-
piratoire du temps PEP (mesuré moyennant l’ECG et un
cathéter artériel radial) pour estimer la réponse au remplis-
sage vasculaire chez les patients profondément sédatés et
sous ventilation mécanique par pression positive après une
chirurgie cardiaque [27]. Ils ont objectivé que le temps PEP
au cours de l’insufflation était plus court que ce même
temps au cours de l’expiration chez les patients hypovolé-
miques. Le raisonnement physiologique était de dire que la
variation de la valeur PEP entre l’insufflation et l’expiration
du respirateur ne pouvait être expliquée que par la varia-
tion du retour veineux [36] et du volume d’éjection systo-
lique. Moyennant ces deux mesures, ils ont calculé la diffé-
rence qu’ils ont indexée à la moyenne pour l’estimer en
pourcentage (ΔPEP en %) [27]. Chez huit patients qui ont
bénéficié d’un remplissage vasculaire le ΔPEP avant rem-
plissage était significativement corrélé à la variation du
volume d’éjection systolique après infusion de volume
(r
2
= 0,57, p= 0,03) [27]. Dans cette étude l’indice ΔPEP
était moins bien corrélé à la variation du volume d’éjection
systolique après administration de volume que ne l’était la
variation ventilatoire de la pression pulsée. Cependant, il
faut intégrer que dans cette étude l’acquisition et l’enre-
gistrement des différentes données étaient faits avec une
fréquence de 100 hertz soit une résolution de mesure de
10 ms.
À ce jour, rares sont les indices non invasifs permettant
de quantifier les précharges ventriculaires droite ou gauche
et/ou de prédire la réponse hémodynamique lors d’un rem-
plissage vasculaire. En effet, en dehors de l’échocardiogra-
phie, peu de techniques ont été développées aujourd’hui.
Intégrant l’outil des intervalles de temps systoliques, Feis-
sel et al. ont proposé de mesurer le ΔPEP par un autre
moyen [37]. En effet, au moyen de la courbe de pléthysmo-
graphie et de l’enregistrement électrocardiographique, cet
intervalle de temps systolique a été mesuré et sa variation
ventilatoire en pourcentage estimée chez des patients sep-
tiques et en ventilation mécanique [37]. Dans cette étude
récente, les auteurs ont montré qu’un ΔPEP, mesuré à
l’aide d’une courbe de pléthysmographie, supérieure à
4 %, était capable de prédire la réponse positive au remplis-
sage vasculaire avec une sensibilité de 100 % et une spécifi-
cité de 67 % [37]. Dans cette étude l’acquisition et l’enre-
gistrement des différentes données étaient faits avec une
fréquence de 500 hertz soit une résolution de mesure de
2ms[37].
Les intervalles de temps systoliques du ventricule
droit
L’évaluation de la fonction ventriculaire droite reste un
challenge en réanimation du fait qu’en dehors de l’échocar-
diographie trans-thoracique et trans-œsophagienne, il
n’existe pas d’autres moyens diagnostiques au lit du
patient. En conséquence, certains auteurs ont proposé
l’utilisation des intervalles de temps systoliques du ventri-
cule droit pour évaluer la fonction systolique du cœur droit
[38]. Her et al. ont utilisé l’enregistrement simultané de
l’électrocardiogramme, du phonocardiogramme et de la
courbe de pression artérielle pulmonaire (cathéter artériel
pulmonaire) pour mesurer la PEP du ventricule droit (PEP
VD
)
et le temps d’éjection ventriculaire droit (RVET) [39].La
phonocardiographie a permis de situer la fermeture de la
valve pulmonaire qui correspond à la composante pulmo-
naire du second bruit [39]. Cette équipe a démontré que
chez les patients insuffisants respiratoires ventilés mécani-
quement, le rapport PEP
VD
/RVET était un très bon reflet de
la fonction ventriculaire droite comme objectivé par la très
bonne corrélation (r
2
= 0,67, p< 0,001) entre ce rapport et
la pente d’élastance télésystolique du ventricule droit
(courbe pression–volume) [39]. De façon identique et utili-
sant seulement l’enregistrement simultané de l’électrocar-
diogramme et de la courbe de pression artérielle pulmo-
naire (cathéter artériel pulmonaire) pour mesurer la PEP
du ventricule droit (PEP
VD
) et le temps d’éjection ventricu-
laire droit (RVET), Guerrero et al. ont démontré que le rap-
port PEP
VD
/RVET était un très bon reflet de la fonction ven-
triculaire droite comme objectivé par la très bonne
corrélation (r
2
= 0,90, p< 0,001) entre ce rapport et la frac-
tion d’éjection du ventricule droit mesuré par thermodilu-
tion [38].
Conclusion
La mesure des intervalles de temps systoliques est une
méthode non invasive permettant de quantifier la fonction
contractile cardiaque ainsi que l’état de remplissage du
cœur chez des patients profondément sédatés et sous ven-
tilation par pression positive. En réanimation, cette tech-
nique possède des avantages certains, car elle ne nécessite
qu’un enregistrement ECG et une courbe de pression arté-
rielle sanglante de bonne qualité ou un doppler œsopha-
gien.
Le rapport ΔPEP
VD
/RVET semble être très intéressant car
àl’opposé de l’échocardiographie, il reflète la contractilité
du ventricule droit indépendamment des conditions de
charge [39]. Cette technique basée sur la mesure des
durées des différentes phases composant la systole ventri-
K. Bendjelid122

culaire droite ou gauche pourrait devenir dans le futur un
outil utile pour le monitorage hémodynamique en réanima-
tion.
Références
[1] Weissler AM. Current concepts in cardiology. Systolic-time
intervals. N Engl J Med 1977;296:321–4.
[2] Weissler AM. Interpreting systolic time intervals in man. J Am
Coll Cardiol 1983;2:1019–20.
[3] Weissler AM. The systolic time intervals and risk stratification
after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987;9:
161–2.
[4] Weissler AM, Garrard Jr. CL. Systolic time intervals in cardiac
disease (II). Mod Concepts Cardiovasc Dis 1971;40:5–8.
[5] Weissler AM, Garrard Jr. CL. Systolic time intervals in cardiac
disease. I. Mod Concepts Cardiovasc Dis 1971;40:1–4.
[6] Weissler AM, Harris WS, Schoenfeld CD. Systolic time intervals
in heart failure in man. Circulation 1968;37:149–59.
[7] Weissler AM, Harris WS, Schoenfeld CD. Bedside technics for
the evaluation of ventricular function in man. Am J Cardiol
1969;23:577–83.
[8] Singer M, Clarke J, Bennett ED. Continuous hemodynamic
monitoring by esophageal Doppler. Crit Care Med 1989;17:
447–52.
[9] Tournadre JP, Muchada R, Lansiaux S, Chassard D. Measure-
ments of systolic time intervals using a transoesophageal pul-
sed echo-Doppler. Br J Anaesth 1999;83:630–6.
[10] Singer M, Allen MJ, Webb AR, Bennett ED. Effects of altera-
tions in left ventricular filling, contractility, and systemic vas-
cular resistance on the ascending aortic blood velocity wave-
form of normal subjects. Crit Care Med 1991;19:1138–45.
[11] Singer M, Bennett ED. Noninvasive optimization of left ventri-
cular filling using esophageal Doppler. Crit Care Med 1991;19:
1132–7.
[12] Mattar JA, Shoemaker WC, Diament D, Lomar A, Lopes AC, De
Freitas E, et al. Systolic and diastolic time intervals in the cri-
tically ill patient. Crit Care Med 1991;19:1382–6.
[13] Boudoulas H. Systolic time intervals. Eur Heart J 1990;11:93–
104.
[14] Mertens HM, Mannebach H, Trieb G, Gleichmann U. Influence
of heart rate on systolic time intervals: effects of atrial
pacing versus dynamic exercise. Clin Cardiol 1981;4:22–7.
[15] Spodick DH, Doi YL, Bishop RL, Hashimoto T. Systolic time
intervals reconsidered. Reevaluation of the preejection
period: absence of relation to heart rate. Am J Cardiol 1984;
53:1667–70.
[16] Ferro G, Ricciardelli B, Sacca L, Chiariello M, Volpe M, Tari MG,
et al. Relationship between systolic time intervals and heart
rate during atrial or ventricular pacing in normal subjects.
Jpn Heart J 1980;21:765–71.
[17] Hamada M, Hiwada K, Kokubu T. Clinical significance of systo-
lic time intervals in hypertensive patients. Eur Heart J 1990;
11:105–13.
[18] Hamada M, Ito T, Hiwada K, Kokubu T, Genda A, Takeda R.
Characteristics of systolic time intervals in patients with
pheochromocytoma. Jpn Circ J 1991;55:417–26.
[19] Kulkarni AU, Krishnaswami S, Prasad NK, Jose J, Kothari SS.
Systolic time intervals in dilated cardiomyopathy. Indian
Heart J 1989;41:95–8.
[20] Schoemaker RG, Smits JF. Systolic time intervals as indicators
for cardiac function in rat models for heart failure. Eur Heart
J 1990;11:114–23.
[21] Vanfraechem JH. Stroke volume and systolic time interval
adjustments during bicycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 1979;46:
588–92.
[22] Wanderman KL, Hayek Z, Ovsyshcher I, Loutaty G, Cantor A,
Gussarsky Y, et al. Systolic time intervals in adolescents. Nor-
mal standards for clinical use and comparison with children
and adults. Circulation 1981;63:204–9.
[23] Berton C, Cholley B. Equipment review: new techniques for
cardiac output measurement–oesophageal Doppler, Fick prin-
ciple using carbon dioxide, and pulse contour analysis. Crit
Care 2002;6:216–21.
[24] Chemla D, Nitenberg A. Systolic duration, preload, and after-
load: is a new paradigm needed? Intensive Care Med 2006;32:
1454–5.
[25] Monnet X, Pinsky M, Teboul JL. FTc is not an accurate predic-
tor of fluid responsiveness. Intensive Care Med 2006;32:1090–
1.
[26] Singer M. The FTc is not an accurate marker of left ventricular
preload. Reply to the comment by Chemla and Nitenberg.
Intensive Care Med 2006;32:1456–7.
[27] Bendjelid K, Suter PM, Romand JA. The respiratory change in
preejection period: a new method to predict fluid responsive-
ness. J Appl Physiol 2004;96:337–42.
[28] Bendjelid K, Romand JA. Fluid responsiveness in mechanically
ventilated patients: a review of indices used in intensive care.
Intensive Care Med 2003;29:352–60.
[29] Michard F, Teboul JL. Predicting fluid responsiveness in ICU
patients(*) : a critical analysis of the evidence. Chest 2002;
121:2000–8.
[30] Groza P, Zamfir V, Vrincianu R. Systolic time intervals in pas-
sive head down position (-85 degrees) and exercise. Physiolo-
gie 1983;20:143–8.
[31] Wallace AG, Mitchell JH, Sheldon Skinner N, Sarnoff SJ. Dura-
tion of the phases of left ventricular systole. Circ Res 1963;12:
611–9.
[32] Buch J, Egeblad H, Hansen PB, Kjaergard H, Waldorff S, Stei-
ness E. Correlation between changes in systolic time intervals
and left. Br Heart J 1980;44:668–71.
[33] Engel UR, Burckhardt D, Kloppenburg P. Response of systolic
time intervals to fluid challenge in uncomplicated acute myo-
cardial infarction. Bibl Cardiol 1976;00:22–6.
[34] Matsuno Y, Morioka S, Murakami Y, Kobayashi S, Moriyama K.
Mechanism of prolongation of pre-ejection period in the
hypertrophied left ventricle with normal systolic function in
unanesthetized hypertensive dogs. Clin Cardiol 1988;11:702–
6.
[35] Brundin T, Hedenstierna G, McCarthy G. Effect of intermittent
positive pressure ventilation on cardiac systolic time inter-
vals. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1976;20:278–84.
[36] Bendjelid K. Right atrial pressure: determinant or result of
change in venous return? Chest 2005;128:3639–40.
[37] Feissel M, Badie J, Merlani PG, Faller JP, Bendjelid K. Pre-
ejection period variations predict the fluid responsiveness of
septic ventilated patients. Crit Care Med 2005;33:2534–9.
[38] Guerrero JE, Munoz J, De La Calle B, Valero R, Alberca MT.
Right ventricular systolic time intervals determined by
means of a pulmonary artery catheter. Crit Care Med 1992;
20:1529–37.
[39] Her C, Frost EA. Assessment of right ventricular function by
right ventricular systolic time intervals in acute respiratory
failure. Crit Care Med 1999;27:2703–6.
Les intervalles de temps systoliques en réanimation 123
1
/
4
100%