En français

Introduction 1-1
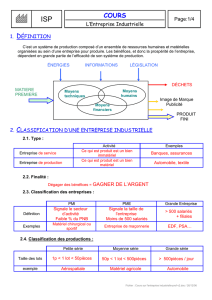
Chapter 1
Introduction
Computer Networking:
A Top Down Approach
Featuring the Internet,
3rd edition.
Jim Kurose, Keith Ross
Addison-Wesley, July
2004.
A note on the use of these ppt slides:
We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers).
They’re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete slides
(including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously
represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the
following:
If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form,
that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!)
If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that
you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our slides, and
note our copyright of this material.
Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR
All material copyright 1996-2004
J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved

Introduction 1-2
Chapter 1: Introduction
Sommaire:
Qu’est ce qu’Internet
Qu’est ce qu’un protocole?
Les “bords” du réseau
Le coeur du réseau
Accès au réseau, média physique
Structure de l’Internet
Performance: pertes, delais, débit
Couches de protocole, modèle de service
Modélisation

Introduction 1-3
Qu’est ce qu’ Internet: approche
descriptive
Des millions d’ordinateurs
connectés: hôtes(PC,
serveurs, PDA, iPod, cells,
véhicules, applications variées)
Exécutent des
applications
Liens de communication
Fibre optique, cuivre,
radio, satellite
transmission rate = bande
passante [bandwidth, bps]
routeurs: routent des
paquets
FAI local
Réseau
local
FAI regional
routeur station
serveur mobile

Introduction 1-4
Qu’est ce qu’ Internet: approche
descriptive
Les protocoles controlent
l’envoi, la réception de
messages
Ex:TCP, IP, HTTP, FTP, PPP
Internet = “réseau de
réseaux”
Peu hiérarchisé
Standards d’Internet
RFC: Request for comments
IETF: Internet Engineering
Task Force www.ietf.org
IEEE: Institute of Electrical &
Electronics Engineers
local ISP
company
network
regional ISP
router workstation
server mobile

Introduction 1-5
Qu’est ce qu’ Internet : les services
L’infrastructure de
communication favorise les
applications distribuées:
Web, email, jeux, e-commerce,
partage de fichiers
Services de communication
services fournis aux applications
Deux formes:
•Sans connection, non fiable (non
garanti)
•Orienté connection, fiable
(garanti)
Évolution constante
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
 51
51
 52
52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
1
/
58
100%