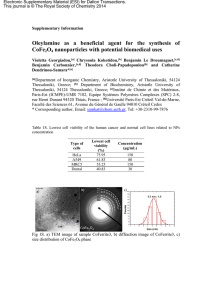
HORMONES et RESISTANCE des PLANTES

HORMONES
et RESISTANCE
des PLANTES
UMR « Résistance des Plantes aux Bioagresseurs »
Pathogène
Noyau
Eliciteurs endogènes
Eliciteurs exogènes
Récepteurs membranaires
Messagers
secondaires
HR
H
2
0
2
H
2
0
2
SA
SA
H
2
0
2
SA
SAR
SAR
SAR
ou

Agent pathogène
HR: réaction d’hypersensibilité
SIGNALISATION à distance
ISR : résistance
systémique
induite
SAR: résistance
systémique
acquise

Molécules « signal »
INFORMATION
MECANISME
Etape 1
Etape 2
.
.
.
.
.
Etape x
MS
DEFENSE
Voies de signalisation
Transduction du signal
HORMONES

• ……………..a small group of genes responsible
for "telling" plants when, where and how to
produce a hormone that is key to their
development. ……… shed light on the ways in
which hormone production in plants affects both
a plant's growth and its ability to adapt to
changing environments
Stepanova et al. 2008 - CELL - Genes Key To Hormone Production In Plants Identified

Cell membrane
Recognition
parasite/elicitor
R guard system
Jasmonate
oxidative burst
Kinases
Phosphatases
lipid peroxidation
lipoxygenase
Transcription
Transcription factors
factors activation
activation
Ethylene Salicylic
Acid
Defense genes
Anti-microbial products
PR - Proteins
Phytoalexins
Apoptosis genes
CELL DEATH
Cell protection
Peroxydases
GST, HSP
Signal
amplification
NADPH-oxidase
O
2.-
SOD
peroxidase
OH
-
NO
H
2
O
2
H
2
O
2
Resistance
Ca++
ions fluxes
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
1
/
22
100%