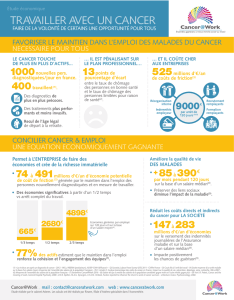
How to do your Resume in english

111
1
C.V/RESUMES
L’ETAT CIVIL(personal details)
I) LE NOM
Nom de famille: last name (US), family name (GB)
Prénom: Christian name (à éviter au Japon).
NB: pour les étrangers dont le nom est long et compliqué, soulignez le nom de famille si
celui-ci n’est pas en caractères d’imprimerie different des prénoms.
EX: Ian Wang Fat Cheung.
2) L’ADRESSE
Adresse permanente ou pour les périodes non scolaires:
Home address; permanent address.
Adresse sur le campus ou actuelle:
Present/current address
Temporary address/campus address.
3) LE NUMERO DE TELEPHONE
Home number/private number.
Les indicatifs se traduisent par: national code
Area code.
4) L’AGE OU LA DATE DE NAISSANCE
Ils se traduisent respectivement par:
Age et date of birth/born.
EX: 3 February 1974
ou: 3rd February 1974( plus classique)
ou February 3, 1974 (américain).
5) LE LIEU DE NAISSANCE
Place of birth ou birth place (GB)
6) LA NATIONALITE
Nationality; citizenship (citoyenneté)
Dual nationality.
Work permit.
Permanent resident visa.
Residence permit: permis de séjour.

222
2
EX: U.K. resident and work permit; Dutch (U.K resident permit).
7) SITUATION DE FAMILLE
Vous pouvez indiquer selon le cas: single; married; married with one child; married with
two children; engaged (fiancé(e)).
L’OBJECTIF DE CARRIERE
En général les objectifs de carrière viennent immédiatement après la rubrique ‘état civil’.
S’intitule comme suit: career objective ou position sought
EX: Position sought: financial controller.
A position in the information systems field.
A position in international banking.
AUTRES FACONS DE REDIGER LES OBJECTIFS DE CARRIERE.
a) Un verbe au gérondif
ex: beginning auditing work....
b) Un verbe à l’infinitif:
ex: to work in a high technology firm....
To be/become associated with a firm where...
To be in charge of...
To be affiliated with...
To develop my career...
c) Un verbe conjugué:
ex: I would like to ....; I would enjoy working with...
I plan to continue...
I am looking for a post in...
d) Un adjectif:
ex: I am keen to work as../I am interested in+ ing./I have a keen interest in...
NB: Pour un stage, précisez summer position in...ou bien ne donnez pas d’objectif.
Autres possibilités:
My interest lies in the field of...
A career in ...would appeal
An opportunity to..would be of interest.
e) Une apposition:
ex: having enjoyed...I am now looking to......I am aiming for...
Having taken...I now seek a position...
...I would like to...
f) Du général au spécifique
Afin d’éviter les remarques floues, il est habile de préciser les aspects de vos centres
d’intérêt qui vous attirent le plus spécifiquement.
ex: With a specialty in...
With special interest in...
Specific areas of interest are..
With an emphasis in...

333
3
EXEMPLES D’OBJECTIFS:
A position in international banking or with a multinational firm, in corporate finance,
international lending or project financing.
I would enjoy working in industrial marketing, combining engineering skills, financial
capabilities and stategic management, preferably for an international company.
Looking for a post in the marketing or market strategy areas of management where I
feel my ability and interest can make a positive contribution.
To develop my career in a financial institution that offers a complete range of financial
services and international employment prospects.
LA FORMATION
***Attention à la traduction en anglais: ‘education’
1) Le diplômedu baccalauréat:
a) A la française, sans traduire: ‘baccalauréat’
b) Par analogie au système américain: ‘High School Diploma’ou ‘School/Higher Leaving
Certificate’
Graduated from X high School.
c) Par analogie au système britannique: 3’A’ levels(suivi de 3 matières principales), ou 4
‘A’ levels (suivi de 4 matières principales)
2) La section et les matières
Pour indiquer la section(A, B, C, )indiquez la en français puis expliquez entr parenthèses
en inscrivant les matières principales)
EX: Baccalaureat B (Economics, History, Geography)
3) Les mentions
With honors/with highest honors = mention T.B.
With distinction = avec mention.
NB: Public school correspond aux US à l’école publique, mais correspond, en GB, à une
école privée réservée à l’élite.
Le mot anglais ‘college’ correspond aux 2 premières années d’université et n’a rien à voir
avec le ‘collège’ français.
4) Les concours d’entrée
Voici le vocabulaire qu’il est possible d’utiliser concernant les préparations aux concours:
Preparation for the competitive entrance examinations to French Engineering
schools/Business schools/ ‘Grandes Ecoles’
Post secondary program leading to th nationwide competitive exam for admission to a
graduate-level Engineering School(Grande Ecole) at lycée...
French Business Schools competitive examination: two years of preparation
Pour les admissions sur titres, on peut dire:

444
4
To qualify for admission to...
To meet the entry requirements
Admission on record (sur dossier).
NB: un jury d’admission: admissions committee.
Passer les concours: to take/to sit for nationwide entry exams.
Etre admissible: to qualify for the oral entry examinations.
Etre admis: to be admitted to...
5) Les grandes écoles.
Une fois entré dans l’école vous pouvez être plus précis en décrivant votre
établissement.
Ex: Essec: a major French Graduate school of management/ OU one of the leading
Postgraduate Business Schools in France.
Dans ce dernier exemple vous vous placez au niveau ‘Graduate School’ (US) et
‘Postgraduate Studies ‘(GB), c’est à dire post-licence,ce que le terme ‘business school’
tout seul ne permettrait pas.
NB: Obtenir un diplôme: to earn a degree/ to gain a degree.
Obtenir un diplôme de: to graduate from.
Un diplômé: a graduate.
L’année d’obtention du diplôme: graduation year.
Un étudiant de 1ère /2nde/3ème année: a first/second/third year student.
Un diplôme: a degree (éviter ‘diploma’ ou ‘certificate’)
Les anciens: the alumni/former students.
Intégrer: to get into/to enter a Grande Ecole.
Faire l’Essec etc...: to study at/ to be a...graduate/to be a graduate from.
6) Les études universitaires.
a) LE DEUG.
Ne le mentionnez pas si vous êtes titulaire d’une licence; si vous devez en parler, vous
devrez expliquer et paraphraser comme suit:
Diploma gained after the first two years in French Higher Education.
Two-year study in...at...University.
b) LA LICENCE
Dans les pays anglo-saxons, les quatre premières années de ‘college’sont dites de niveau
‘undergraduate’.Elles aboutissent à ce qui équivaut approximativement à une licence. Vous
pouvez dire que vous en possédez l’équivalent si vos études correspondent à un Bac+3ou
4. Les principaux diplômes de ce types sont les suivants:
B.A. Bachelor of Arts
B.S (US)/ B.Sc(GB) Bachelor of Science
Remarque: vous pouvez vous inspirer de ces exemples en les adaptant à votre cas
particulieret en inscrivant à la suite de votre diplôme français:
...University Degree in Mathematics.Granted three years after the Baccalauréat.
...Bachelor of Commerce. Specialised in Economics, Finance and Business Law.
...Equivalent to a British Bachelor of Science specialising in Computer Science.
c) LA MAITRISE

555
5
Elle s’inscrit sans la formation des ‘graduate schools’ aux US et des ‘postgraduate sudies’
en GB.
Se traduit de la façon suivante:
M.A. Master of Arts.
M.S (US)/ M.Sc. (GB) Master of Science
Tous s’abrègent en ‘Master’s degree’ ou Master’s.
EX: M.A. in Politics.
Gained M.A. degree (Economics) specialising in Macroeconomics.
Master of Management.
M.S.degree in Public Relations.
d) LE D.E.A.
Se traduit comme suit:
Postgraduate Degree. Granted 5 years/6 years after the Baccalauréat.Specialisation
in...
e) LE DOCTORAT.
Se traduit comme suit:
Ph.D. (doctor of philosophy);Ph.D. Degree, Doctorate; Doctoral Degree.
Ph.D. in Economics.
To register for a Ph.D: s’inscrire en doctorat.
To study for a Ph.D.: doctorat en cours.
Dissertation topic: sujet de thèse
In progress: en cours.
f) L’AGREGATION
Se traduit comme suit:
Highly competitive nationwide examination with specialisation in...
g) LES DIPOMES EN COURS D’OBTENTION
Candidate for the Degree of Master in Business Administration in June...
Reading for Master’s Degree in Business Studies in...
Expected graduation: June 199../2000
h) COURS SUIVIS NE DEBOUCHANT PAS SUR UN DIPLOME.
Advanced courses in Production Method and Management.
Special courses/ Additional education
18 month correspondence course on...
Attended program in ...
Attended Extra-mural Studies Programme in Economics and Politics (summer 19..)
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
1
/
9
100%