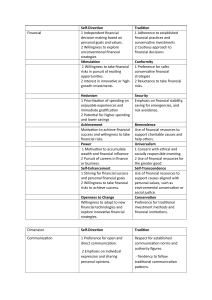
Self-Direcon
Tradion
Financial
1 Independent nancial
decision-making based on
personal goals and values.
2 Willingness to explore
unconvenonal nancial
strategies
1 Adherence to established
nancial pracces and
conservave investments
2 Cauous approach to
nancial decisions
Smulaon
Conformity
1 Willingness to take nancial
risks in pursuit of excing
opportunies.
2 Interest in innovave or high-
growth investments
1 Preference for safer,
conservave nancial
strategies
2 Reluctance to take nancial
risks.
Hedonism
Security
1 Priorizaon of spending on
enjoyable experiences and
immediate gracaon
2 Potenal for higher spending
and lower savings
Emphasis on nancial stability,
saving for emergencies, and
risk avoidance.
Achievement
Benevolence
Movaon to achieve nancial
success and willingness to take
nancial risks.
Use of nancial resources to
support charitable causes and
help others.
Power
Universalism
1 Movaon to accumulate
wealth and nancial inuence
2 Pursuit of careers in nance
or business.
1 Concern with ethical and
socially responsible invesng
2 Use of nancial resources for
the greater good
Self-Enhancement
Self-Transcendence
1 Striving for nancial success
and personal nancial goals
2 Willingness to take nancial
risks to achieve success.
Use of nancial resources to
support causes aligned with
personal values, such as
environmental conservaon or
social jusce.
Openness to Change
Conservaon
Willingness to adapt to new
nancial technologies and
explore innovave nancial
strategies.
Preference for tradional
investment methods and
nancial instuons.
Dimension
Self-Direcon
Tradion
Communicaon
1 Preference for open and
direct communicaon.
2 Emphasis on individual
expression and sharing
personal opinions.
Respect for established
communicaon norms and
authority gures.
- Tendency to follow
tradional communicaon
paerns.

Smulaon
Conformity
Interest in dynamic,
smulang, and innovave
forms of communicaon.
- Willingness to explore new
communicaon plaorms.
- Preference for respecul and
convenonal communicaon
styles.
- Avoidance of confrontaonal
or unconvenonal
communicaon.
Hedonism
Security
Use of communicaon for
entertainment, pleasure, and
humor.
- Enjoyment of light-hearted
and engaging conversaons.
- Emphasis on clear and secure
communicaon.
- Avoidance of risks in
communicaon.
Achievement
Benevolence
- Use of communicaon to
showcase personal
achievements and goals.
- Interest in networking for
career advancement.
- Focus on empathec and
compassionate
communicaon.
- Engagement in
communicaon that supports
community and social causes.
Power
Universalism
- Preference for inuenal and
persuasive communicaon
styles.
- Use of communicaon to
assert power and inuence.
- Emphasis on ethical and
socially responsible
communicaon.
- Advocacy for values-based
communicaon.
Self-Enhancement
Self-Transcendence
Communicaon focused on
self-promoon and self-
enhancement.
- Use of communicaon for
self-presentaon and status.
Communicaon that promotes
ethical and values-aligned
causes.
- Expression of concern for
global and societal issues.
Openness to Change
Conservaon
- Willingness to embrace new
communicaon technologies
and plaorms.
- Preference for tradional and
me-tested communicaon
channels.

- Interest in unconvenonal
and creave communicaon
methods.
- Resistance to rapid changes in
communicaon pracces.
Dimension
Self-Direcon
Tradion
Negociaon
- Preference for negoaon
based on individual goals and
values.
- Willingness to explore
unconvenonal negoaon
strategies.
- Adherence to established
negoaon norms and
tradional approaches.
- Respect for authority gures
in negoaons.
Smulaon
Conformity
Interest in dynamic,
innovave, and creave
negoaon taccs.
- Willingness to explore new
negoaon techniques.
- Preference for respecul and
convenonal negoaon
styles.
- Avoidance of confrontaonal
or unconvenonal negoaon
methods.
Hedonism
Security
- Use of negoaon for
personal enjoyment and
sasfacon.
- Priorizaon of harmonious
and enjoyable negoaons.
- Emphasis on secure and
predictable negoaon
outcomes.
- Avoidance of risks in
negoaons.
Achievement
Benevolence
- Focus on achieving personal
success and goals through
negoaon.
- Willingness to take calculated
negoaon risks.
Priorizaon of win-win
negoaon outcomes.
- Emphasis on negoaon that
benets others and the
community..
Power
Universalism
Preference for negoaon that
results in power and inuence.
- Use of negoaon to assert
control and dominance.
- Emphasis on ethical and
socially responsible
negoaon.
- Advocacy for negoaon that
aligns with personal values.
Self-Enhancement
Self-Transcendence

Negoaon strategies focused
on self-promoon and self-
enhancement.
- Use of negoaon for
personal gain and status.
- Negoaon that promotes
ethical and values-aligned
causes.
- Expression of concern for
societal and global issues in
negoaons.
Openness to Change
Conservaon
- Willingness to adapt to new
negoaon techniques and
approaches.
- Interest in unconvenonal
and creave negoaon
methods.
- Preference for tradional and
me-tested negoaon
pracces.
- Resistance to rapid changes
in negoaon strategies.
1. Self-Direcon vs. Tradion: This dimension is about whether people prefer to think for
themselves and make their own choices (self-direcon) or if they like to follow established
customs and obey authority gures (tradion). People who value self-direcon tend to be
independent and creave, while those who value tradion are more likely to respect rules
and tradions passed down through generaons.
2. Smulaon vs. Conformity: This dimension is about whether people like excitement, new
experiences, and challenging ideas (smulaon) or if they prefer to t in, follow rules, and
avoid rocking the boat (conformity). People who value smulaon are oen more
adventurous and open to change, while those who value conformity like things to stay the
same and follow established norms.
3. Hedonism vs. Security: This dimension is about whether people seek pleasure, fun, and
enjoyment in life (hedonism) or if they priorize safety, stability, and avoiding risks (security).
People who value hedonism enjoy life's pleasures and take risks, while those who value
security are more cauous and focused on maintaining stability.
4. Achievement vs. Benevolence: This dimension is about whether people emphasize personal
success, ambion, and competence (achievement) or if they value caring for others, showing
compassion, and working for the well-being of society (benevolence). People who value
achievement strive for personal excellence, while those who value benevolence are
concerned with the welfare of others.
5. Power vs. Universalism: This dimension is about whether people seek power, control, and
inuence over others (power) or if they priorize fairness, social jusce, and protecng the
environment (universalism). People who value power want to lead and have control, while
those who value universalism are concerned with equality and ethical principles.
6. Self-Enhancement vs. Self-Transcendence: This dimension is about whether people focus on
personal success, status, and their own interests (self-enhancement) or if they care about the
welfare of others, spiritual and ethical values, and a sense of connecon with nature and the
universe (self-transcendence). People who value self-enhancement are oen ambious,
while those who value self-transcendence have a broader concern for the world and others.

7. Openness to Change vs. Conservaon: This dimension is about whether people are open to
new ideas, innovaon, and change (openness to change) or if they prefer to preserve
tradions, stability, and established social norms (conservaon). People who value openness
to change are more adaptable and open-minded, while those who value conservaon want
to maintain tradional ways of life.
These dimensions help us understand how dierent cultures and individuals priorize these values,
and it can inuence their behaviors, beliefs, and decision-making. Remember that individuals may
have a mix of values from these dimensions, and cultural values can vary signicantly from one
society to another.
1
/
5
100%