Dynamic Crust Review
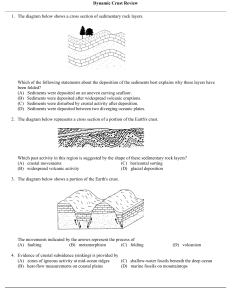
1. The diagram below shows a cross section of sedimentary rock layers.
Which of the following statements about the deposition of the sediments best explains why these layers have
been folded?
(A) Sediments were deposited on an uneven curving seafloor.
(B) Sediments were deposited after widespread volcanic eruptions.
(C) Sediments were disturbed by crustal activity after deposition.
(D) Sediments were deposited between two diverging oceanic plates.
2. The diagram below represents a cross section of a portion of the Earth's crust.
Which past activity in this region is suggested by the shape of these sedimentary rock layers?
(A) crustal movements (C) horizontal sorting
(B) widespread volcanic activity (D) glacial deposition
3. The diagram below shows a portion of the Earth's crust.
The movements indicated by the arrows represent the process of
(A) faulting (B) metamorphism (C) folding (D) volcanism
4. Evidence of crustal subsidence (sinking) is provided by
(A) zones of igneous activity at mid-ocean ridges (C) shallow-water fossils beneath the deep ocean
(B) heat-flow measurements on coastal plains (D) marine fossiIs on mountaintops

Dynamic Crust Review
5. The diagram below represents a section of the Earth's bedrock. The arrows show the direction of forces that are
gradually compressing this section.
Which diagram represents the most probable result of these forces?
(A)
(B) (C)
(D)
6. The block diagram below represents a geologic cross section of a mountain range.
What action most likely formed this mountain range?
(A) contact metamorphism (C) volcanic eruptions
(B) earthquake faulting (D) glacial erosion
7. Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great
ocean depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth scientists as evidence that
(A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water organisms
(B) sunlight once penetrated to the deepest parts of the ocean
(C) sections of the Earth's crust have changed their elevations relative to sea level
(D) organisms that live in deep water evolved from species that once lived in shallow water
8. Fossils of marine plants and animals are found in the bedrock of mountains many thousands of feet above sea
level. The most likely reason for this observation is that
(A) forces within the Earth caused uplift
(B) the ocean level has dropped several thousand feet
(C) the mountains were part of a mid-ocean ridge
(D) transported materials were deposited at high elevations
9. Which observed feature would provide the best evidence of crustal stability?
(A) folded, faulted, and tilted rock strata (C) marine fossils at elevations high above sea level
(B) changed benchmark elevations (D) horizontal sedimentary layers

Dynamic Crust Review
10. An observer discovers shallow-water marine fossils in rock strata at an elevation of 5,000 meters. What is the
best explanation for this observation?
(A) The level of the ocean was once 5,000 meters higher.
(B) Crustal uplift has occurred in this area.
(C) Violent earthquakes caused crustal subsidence.
(D) Marine organisms have evolved into land organisms.
11. The diagram below shows land features that have been disrupted by an earthquake.
Which type of crustal movement most likely caused the displacement of features in this area?
(A) down-warping of the crust (C) folding of surface rock
(B) vertical lifting of surface rock (D) movement along a transform fault
12. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows crustal plate boundaries located
along the Pacific coastline of the United States. The arrows show the general directions in which some of the
plates appear to be moving slowly.
The best way to find the direction of crustal movement along the San Andreas fault is to
(A) observe erosion along the continental coastline
(B) measure gravitational strength on opposite sides of the fault
(C) study the Earth's present magnetic field
(D) match displaced rock types from opposite sides of the fault
13. A huge undersea earthquake off the Alaskan coastline could produce a
(A) cyclone (B) thunderstorm (C) hurricane (D) tsunami

Dynamic Crust Review
14. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below of geologic cross sections of the upper
mantle and crust at four different Earth locations, A, B, C, and D. Movement of the crustal sections (plates) is
indicated by arrows, and the locations of frequent earthquakes are indicated by !. Diagrams are not drawn to
scale.
Which diagram represents plate movement associated with transform faults such as those causing California
earthquakes?
(A) A(B) B(C) C(D) D
15. Which event provides direct evidence of crustal movement?
(A) the erosion of the outside of a river curve
(B) the displacement of rock strata during an earthquake
(C) the deposition of sediments in the ocean
(D) the weathering of rock to form a residual soil
16. The movement of tectonic plates is inferred by many scientists to be driven by
(A) tidal motions in the hydrosphere (C) density differences in the troposphere
(B) solidification in the lithosphere (D) convection currents in the asthenosphere

Dynamic Crust Review
Base your answers to questions 17 and 18 on the map below, which shows the risk of damage from seismic activity in
the United States.
17. Which New York State location has the greatest risk of earthquake damage?
(A) Buffalo (B) Binghamton (C) Elmira (D) Plattsburgh
18. In the United States, most of the major damage expected from a future earthquake is predicted to occur near a
(A) mid-ocean ridge and a divergent plate boundary (C) divergent plate boundary, only
(B) convergent plate boundary, only (D) transform plate boundary and a hot spot
19. According to tectonic plate maps, New York State is presently located
(A) above a mantle hot spot (C) near the center of a large plate
(B) above a mid-ocean ridge (D) at a convergent plate boundary
20. Which two tectonic plates are separated by a mid-ocean ridge?
(A) Indian-Australian and Eurasian (C) North American and Eurasian
(B) Indian-Australian and Pacific (D) North American and South American
21. In which Earth layer are most convection currents that cause seafloor spreading thought to be located?
(A) outer core (B) inner core (C) crust (D) asthenosphere
22. The two most abundant elements by mass in Earth’s crust are oxygen and
(A) silicon (B) nitrogen (C) hydrogen (D) potassium
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
1
/
22
100%