Climate and Weather
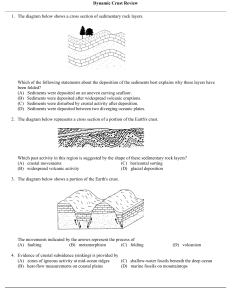
The day-to-day characteristics of
temperature, rain, cloud cover and wind
Long-term patterns of weather
Weather:
Climate:

…
Canada’s Weather

Canada’s Climate
•Canada has 8 climate regions Arctic
Taiga
Cordilleran
Pacific Maritime
Boreal
Prairie
Southeastern
Atlantic Maritime

Canada’s Climate
•There are 6 factors that cause
Canada’s climate to be diverse
(i.e. not the same everywhere).

LOWERN
L= Latitude
O= Ocean Currents
W= Wind
E = Elevation
R= Relief (topography)
N= Nearness to Water
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
1
/
26
100%