questionloop.doc ( DOC - 67 ko )

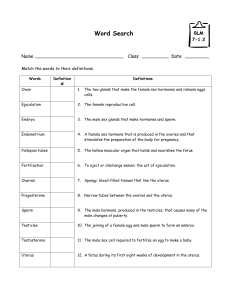
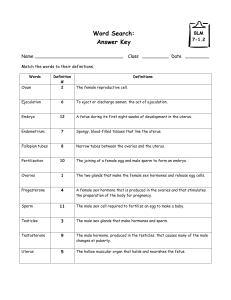
An embryo is an animal in the early stages of growth from an egg
cell which is the result of the union of a female gamete with a male
gamete
What is a gamete ?
A gamete is a mature male or female germ cell usually possessing a
haploid chromosome set
What is the name of the male gamete ?
A sperm cell is a male gamete
What is the name of the female gamete ?
The ovum is the female gamete
What is fertilisation ?
The fertilisation is the process of union of two gametes whereby the
somatic chromosome number is restored and the development of a
new individual is initiated
How could fertilisation be prevented ?
Birth control prevents conception or pregnancy
Which devices prevent conception ?
Condoms, diaphragms and pills can prevent conception
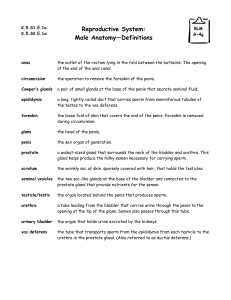
What is a condom ?
A condom is a sheath commonly of rubber worn over the penis
What is a diaphragm ?
A diaphragm is a molded cap usually of thin rubber fitted over the
uterine cervix to act as a mechanical contraceptive barrier
What is the cervix ?
The cervix is the narrow outer end of the uterus producing mucus
What is a pill ?
A pill is any of various preparations that usually contain a
combination of a progesterone and an estrogen which are taken
orally especially on a daily basis, and act as contraceptives typically
preventing ovulation by suppressing secretion of gonadotropins (as
luteinizing hormone) or preventing endometrium development or
cervix mucus fluidity
What is a morning after pill ?
A morning after pill is an oral drug usually containing high doses of
estrogen taken up to usually three days after unprotected sexual
intercourse that interferes with pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation or
by blocking implantation of a fertilized egg in the human uterus
What is an IUD
IUD stands for intrauterine device which is a device inserted into
and left in the uterus to prevent effective pregnancy
What is pregnancy ?
Pregnancy is gestation : the carrying embryos in the uterus
How can pregnancy be detected ?
Pregnancy can be known thanks to a test based on the detection of
HCG produced by the trophoblast which is a part of the blastocyst
What does HCG stands for ?
HCG stands for human chorionic gonadotropin
How could infertile couples be helped ?

Infertile couples may be helped thanks to Assisted procreation
which includes techniques such as IVF; ICSI, ZIFT, surrogacy
What does IVF stand for ?
IVF stands for in vitro fertilization
What does ICSI stand for ?
ICSI stands for intracytoplasmic sperm injection
What does ZIFT stand for ?
ZIFT stands for zygote intra fallopian transfer
What is a surrogate mother ?
A surrogate mother lets her womb
What is a womb ?
A womb is a uterus
What is a uterus ?
A uterus is the muscular organ of the female mammal for containing
and usually for nourishing the young during development prior to
birth
What is a Fallopian tube ?
A Fallopian tube is either of the pair of tubes that carry the egg from
the ovary to the uterus
What is an ovary ?
An ovary is the female gonad producing gametes and sexual
hormones : estrogens and progesterone
What are estrogens ?
Estrogens are any of various natural steroids (as estradiol) that are
secreted chiefly by the ovaries, placenta, and that stimulate the
development of female secondary sex characteristics and promote
the growth of the endometrium
What is progesterone ?
Progesterone is the female steroid sex hormone that is secreted by
the corpus luteum to prepare the endometrium for implantation and
later by the placenta during pregnancy to prevent rejection of the
developing embryo or fetus;
What is corpus luteum ?
A corpus luteum is a yellowish mass of progesterone-secreting
endocrine tissue that forms immediately after ovulation from the
ruptured graafian follicle in the mammalian ovary
What is a follicle ?
A follicle is a vesicle in the mammalian ovary that contains a
developing oocyte surrounded by a covering of cells
What is an oocyte ?
An oocyte is a female non mature gamete
Which hormone stimulates follicle
maturation ?
FSH stimulates the follicles growth
What does FSH stand for ?
FSH stands for follicle-stimulating hormone
What is ovulation ?

Ovulation is the discharge of a mature ovum from the ovary
Which hormone stimulates ovulation ?
LH stimulates ovulation
What does LH stand for ?
LH stands for luteinizing hormone
What are the different functions of LH ?
LH stimulates ovulation, corpus luteum development and
progesterone secretion, and Leydig cells production of testosterone
What are Leydig cells ?
Leydig cells belong to the interstitial tissue inside the testis which
produces testosterone
What is testosterone ?
Testosterone is a hormone produced especially by the testes and that
is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex
characters
What are the testes ?
The testes are the male gonads
What is a gonad ?
A gonad is a reproductive gland (as an ovary or testis) that produces
gametes
When are gonads active ?
Gonads become active after puberty ?
What is puberty ?
Puberty is the period of becoming first capable of reproducing
sexually marked by maturing of the genital organs, development of
secondary sex characteristics, and in the human and in higher
primates by the first occurrence of menstruation in the female
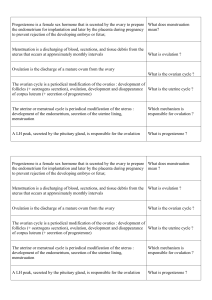
What is menstruation ?
Menstruation is a discharging of blood, secretions, and tissue debris
from the uterus that occurs at approximately monthly intervals
What is a menstrual cycle ?
The menstrual cycle is the cycle of physiological changes in the
endometrium from the beginning of one menstrual period to the
beginning of the next
Which organs control the menstrual
cycle ?
Ovaries control the menstrual cycle thanks to their hormones
secreted during the ovarian cycle
What is the ovarian cycle ?
The ovarian cycle is the periodical modifications of the ovaries :
development of follicles, ovulation, development and disappearance
of corpus luteum
Which organ controls the ovarian cycle
?
The pituitary gland controls the ovarian cycle thanks to FSH and
LH
What is the pituitary gland ?
The pituitary gland is a gland connected to the hypothalamus and
producing LH and FSH
What is the hypothalamus ?
The hypothalamus is a nervous tissue connected to the pituitary
gland and producing GnRH
What does GnRH stand for ?

GnRH stands for gonadotropin-releasing hormone
What is the function of GnRH ?
GnRH stimulates the production of LH by the pituitary gland ?
Is there any control on the hypothalamus
and the pituitary gland ?
There are positive feed-back and negative feed-back from sexual
hormones on hypothalamus and pituitary gland
What is a negative feed back ?
A negative feed back is a in return control that tends to dampen a
process by applying the output against the initial conditions for
example testosterone or low quantity of estrogens or progesterone
on the production of GnRH and LH
What is a positive feed back ?
A positive feed back is a in return control that tends to magnify a
process for example a high quantity of estrogens induces a large
discharge of LH
What is the consequence of a large
discharge of LH ?
A large discharge of LH induces ovulation
After ovulation, fertilisation may occur
followed by nidation, what is the
process of termination of a beginning
pregnancy ?
Abortion is the process of termination of a pregnancy closely
followed by the death of the embryo
What is an embryo ?
1
/
4
100%