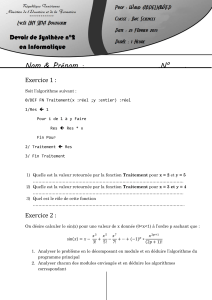
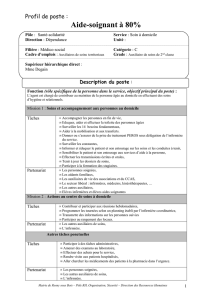
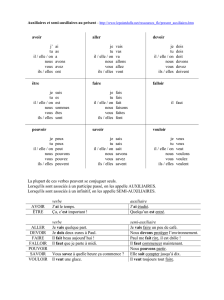
Permutations Fonctions auxiliaires Programme

Permutations
Fonctions
auxiliaires
La fonction add1
La fonction teste
La fonction
convertbase10
La fonction
convert10base
Programme
principal
L’algorithme
La fonction
L’exécution
Et la
récursivité ?
Fonctions auxiliaires
Programme principal
Fonction auxiliaire no1
La fonction add1
La fonction suivante prend pour argument une liste et renvoie
la liste dont tous les éléments sont augmentés de 1.
def add1 (l ):
res=[]
for xin l:
res . appe nd (x +1)
return res
Exécution
>>> l =[3 ,5 ,6]
>>> add1 (l )
[4 , 6 , 7]

Permutations
Fonctions
auxiliaires
La fonction add1
La fonction teste
La fonction
convertbase10
La fonction
convert10base
Programme
principal
L’algorithme
La fonction
L’exécution
Et la
récursivité ?
Fonctions auxiliaires
Programme principal
Fonction auxiliaire no1
La fonction add1
La fonction suivante prend pour argument une liste et renvoie
la liste dont tous les éléments sont augmentés de 1.
def add1 (l ):
res=[]
for xin l:
res . appe nd (x +1)
return res
Exécution
>>> l =[3 ,5 ,6]
>>> add1 (l )
[4 , 6 , 7]

Permutations
Fonctions
auxiliaires
La fonction add1
La fonction teste
La fonction
convertbase10
La fonction
convert10base
Programme
principal
L’algorithme
La fonction
L’exécution
Et la
récursivité ?
Fonctions auxiliaires
Programme principal
Fonction auxiliaire no1
La fonction add1
La fonction suivante prend pour argument une liste et renvoie
la liste dont tous les éléments sont augmentés de 1.
def add1 (l ):
res=[]
for xin l:
res . appe nd (x +1)
return res
Exécution
>>> l =[3 ,5 ,6]
>>> add1 (l )
[4 , 6 , 7]

Permutations
Fonctions
auxiliaires
La fonction add1
La fonction teste
La fonction
convertbase10
La fonction
convert10base
Programme
principal
L’algorithme
La fonction
L’exécution
Et la
récursivité ?
Fonctions auxiliaires
Programme principal
Fonction auxiliaire no2
La fonction teste
La fonction suivante prend pour argument une liste de longueur
net teste si elle contient tous les éléments de J0,n−1K.
def teste ( l):
n= len(l)
for iin range (n):
if not ( i in l):
return False
return True
Exécution
>>> teste ([1 ,2 ,4 ,0 ,3])
>>> True
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
1
/
24
100%