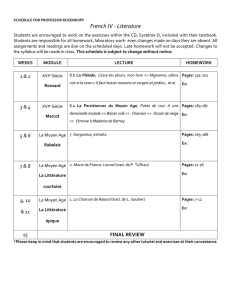
2006-2007 PCEM2 Purpan Anglais Semestre1 Contrôle Continu

2006-2007 PCEM2 Purpan Anglais Semestre1 Contrôle Continu Niveau 1
Votre nom :
1- Compléter le tableau (sur5)
Saigner /se/
sentir
Coller Filer,
tourner
/se/Réveiller
Nourrir
Penser
Distribuer
Rétrécir
Lier, relier
2- Mettre « listen to the teacher » aux formes verbales et personnes suivantes (sur 5)
Présent, 3
ème
fém sg
Conditionnel passé, 1
ère
.sg
Present perfect, 3
ème
masc sg
Futur antérieur, 1
ère
sg
Passif, présent progressif
Present perfect progressif, 3
ème
pl
Conditionnel, 2
ème
sg
Passif, present prefect
Prétérit progressif, 1
ère
.sg forme
négative
Past perfect, 2
ème
sg
3- Compléter avec le vocabulaire revu ou appris ce trimestre avec « Facts & Figures » (sur 5)
We have here the results of a recent survey which was 1-*** to investigate the relationship between GPs & their
patients in this country….This 2-*** shows the percentage of consultations….Some visits to the GP 3***several
different types of 4-***.If you take the same 5-***, the same therapeutic areas, and if you add in the specialists, you
have a different picture.
1***
6- Rhume→
2***
7- ORL→
3***
8- Mal de gorge→
4***
9- Rhumatologie→
5***
10- Raideur→

4- Mettre les verbes en gras à la forme voulue (sur 5)
New York Times Guide to Essential Knowledge: AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency disease (AIDS) 1- cause by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
The disease 2-discover in 1981 and the causative agent 3- identify in 1983. By 2003 an estimated
42 million people 4- infect worldwide and more than 20 million people 5- die of the disease. A
United Nations report presented in 2002
6- predict that unless prevention programs 7- greatly expand, AIDS 8- claim an additional 68
million lives by 2020. Sub-Saharan Africa 9- be the region hardest hit by the HIV/AIDS pandemic;
more than two-thirds of all people with HIV/AIDS are in this region. In the United States, an
estimated 900,000 people 10- live with HIV/AIDS in 2002.
HIV 11- spread through contact with infected body fluids such as blood and semen. Infected
people may harbor the virus within their bodies for several years or even longer before developing
symptoms of AIDS. Though symptomless, they can still infect others. Worldwide, most HIV
transmission 12- occur during sexual relations between heterosexual partners. In the United States,
the majority of transmission 13- be between homosexual partners. Transmission among drug
addicts who 14- share infected needles 15- be another significant route of transmission in many
countries.
In the body, HIV 16- invade immune system cells called T-helper lymphocytes. The viruses 17-
reproduce in the cells and send out new viruses to attack additional T-helper lymphocytes.
Eventually, the lymphocytes
18- destroy, leaving the patient vulnerable to Pneumocystis carinii and other “opportunistic”
pathogens.
partners. Transmission among drug addicts who share infected needles is another significant route
of transmission in many countries.
No cure for AIDS is known. Researchers 19- work on preventative AIDS vaccines, but none are
expected to be ready for market in the near future. Meanwhile, drug therapies introduced in the
mid-1990's 20- be extremely effective in controlling AIDS progression for some patients.
However, the medications are expensive, putting them beyond the reach of the vast majority of the
world's HIV-positive people.
1
6 11 16
2
7 12 17
3
8 13 18
4
9 14 19
5
10 15 20
Félicie Pastore Décembre 2006
1
/
2
100%