EXAMEN – Troisième Année des Etudes Médicales 2ème SESSION

1
Université Joseph Fourier
Année Universitaire
2013/2014
FACULTE DE MEDECINE
38700 LA TRONCHE
INDIQUEZ UNIQUEMENT SUR CETTE PAGE DE GARDE :
NOM :………………………………… PRENOM :………………………
N° PLACE :
VOUS NE DEVEZ PAS REPORTER VOTRE NOM
SUR LES AUTRES FEUILLES DU QUESTIONNAIRE
VERIFIEZ QUE LE PRESENT QUESTIONNAIRE COMPORTE
12 PAGES, PAGE DE GARDE COMPRISE
EN AUCUN CAS, VOUS NE DEVEZ DETACHER
LES FEUILLES DE CE QUESTIONNAIRE
ATTENTION !
Toute infraction au Règlement des Examens et toute tentative de fraude
seront passibles de sanction pouvant aller jusqu’au conseil de discipline
et à l’exclusion de l’Université.
EXAMEN
–
Troisième Année des
Etudes Médicales
2
ème
SESSION
UE 6 : Système lymphatique - Immunologie
Mardi 22 avril 2014 – 9h à 11h30
Durée 150 minutes

2
La partie "Noeud lymphatique" compte pour 50% de la note totale, chaque cas clinique ayant le même
poids (25%). L'autre moitié de la note se répartit de la façon suivante : questions d’immunologie du Pr
Cesbron (1/6
ème
des 50%), de Mme Clavarino (2/6
ème
), de Mme Dumestre (2/6
ème
) ; question d’histologie
(1/6
ème
).
I - IMMUNOLOGIE
QUESTION 1 (
Pr CESBRON)
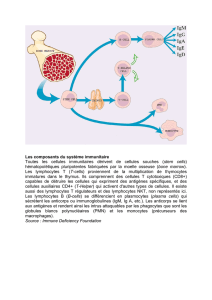
Décrire brièvement les différents acteurs de la réponse immunitaire innée mise en jeu lors de l’infection
virale à influenza.
Dans l’infection virale à influenza, les mécanismes de l’immunité sont :
- L’épithélium respiratoire (mucus, cils, macrophage alvéolaire)
- Synthèse d’interféron alpha/beta, en réponse à une activation des TLR par des produits
viraux; effet antiviral et activation de différents acteurs de la réponse immunitaire
- Activation des cellules NK (cytotoxicité)
- Initiation d’une réponse inflmmatoire:IL6, IL8, IL12, chemokines, IL1, etc. , afflux de
monocytes et macrophages
- Et maturation des cellules dendritiques locales

3
QUESTION 2 (
Dr CLAVARINO)
1) T cells
Indicate whether each of the properties below is exhibited by T
H
(T helper) cells, CTLs (T cytotoxic cells),
both T
H
and CTLs, or neither cell type (N).
a) ……T
H
and CTLs……..can make IL-2
b) ……CTLs…………….. are class I MHC restricted
c) ……CTLs…………….. express CD8
d) ……T
H
…………….. ... are required for B-cell activation
e) ……CTLs…………….. are cytotoxic for target cells
f) ……T
H
…………………are class II MHC restricted
g) ……T
H
……………… ..express CD4
i) …… Neither………… express costimulatory molecules of B7 family
l) …… CTLs……………. .produce perforin
m) ……T
H
and CTLs…… ..express the T-cell receptor

4
2) Tolerance and autoimmunity
Briefly explain the following mechanisms for the development of autoimmunity, and for each of them give an
example.
a) Viral infection……………
The immune response against a virus may cross-react with normal cellular antigens
(molecular mimicry).
Example: myelin basic protein and peptides from viruses such as measles virus, influenza,
adenovirus, hepatitis B, Epstein-Barr
b) Tissue damage…………….
If normally sequestered antigens are exposed, self-reactive T cells may be stimulated.
Example:
Tissue lesion following an accident or a viral or bacterial infection (release of lens
protein after eye damage or of heart muscle antigens after myocardial infarction)
c) Polyclonal B cell activation……….
Some viruses and bacteria can induce nonspecific polyclonal B cell activation; B cells reactive
to self antigens can be activated, with production of autoantibodies
Example: Gram-negative bacteria, cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
d) Increased expression of class II MHC molecules…….
Inappropriate antigen presentation may stimulate self-reactive T cells
Example: increased expression of class II MHC molecules has been found on pancreatic beta
cells of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and on thyroid cells from patients with
Grave’s disease

5
QUESTION 3
(Dr DUMESTRE-PERARD)
Dire si chacune des propositions suivantes est vraie ou fausse. Si vous pensez qu’une proposition est fausse,
expliquez pourquoi.
1) A propos des hypersensibilités immédiates de type I :
a. L’Il-4 diminue la production d’IgE par les lymphocytes B.
b. Les enfants peuvent acquérir des allergies médiées par l’IgE par transfert passif de
l’anticorps maternel.
c. Les polynucléaires éosinophiles jouent un rôle dans la phase tardive de la réponse à
l’asthme.
d. On pense que la désensibilisation fonctionne en augmentant la réponse TH2 des sujets
allergiques.
e. Le calcium joue un rôle important dans la dégranulation des mastocytes.
f. Elles sont provoquées par des anticorps IgE, dont la région Fc se lie aux récepteurs de mastocytes.
Faux car : a : L’Il-4 augmente la production d’IgE par les lymphocytes B.
b : Contrairement à l’IgG, l’IgE ne peut pas passer à travers le placenta.
d : la désensibilisation fonctionne en augmentant la réponse TH1 des sujets allergiques.
 6
6
 7
7
 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
1
/
12
100%